Leveraging Advanced Terragrunt Features
Introduction
When Pipelines detects changes to Infrastructure as Code (IaC) in your repositories, it invokes terragrunt with a predefined set of command-line arguments for the detected changes. For instance, if a single unit is modified in a pull request, Pipelines will chdir into the unit's directory and execute terragrunt plan --terragrunt-non-interactive.
You can view the specific commands used in different scenarios by examining the logs of a Pipelines workflow run.
In some situations, you may need to provide additional options to terragrunt to accommodate specific requirements. Many Terragrunt CLI options can be controlled through environment variables, allowing for flexible customization of its behavior.
Refer to the complete list of available options in the Terragrunt CLI documentation.
Adding environment variables
GitHub/GitLab workflows do not automatically pass environment variables from your repository's workflows into those included from Gruntwork repositories. To propagate environment variables to Terragrunt executions, you must add them to the Pipelines configuration file.
You can configure Pipelines to pass additional environment variables to Terragrunt using the env configuration option in .gruntwork/config.yml.
Each entry in the env sequence represents an environment variable name and its value.
For example, to enable the --terragrunt-strict-include flag in your Terragrunt runs, set the environment variable TERRAGRUNT_STRICT_INCLUDE to true in the Pipelines configuration file.
pipelines:
env:
- name: TERRAGRUNT_STRICT_INCLUDE
value: true
On the next workflow run, review the workflow logs and locate the env: block for the action that executes Terragrunt. If the configuration is correct, your additional environment variable will appear in the env: block, confirming it has been successfully passed to the action.
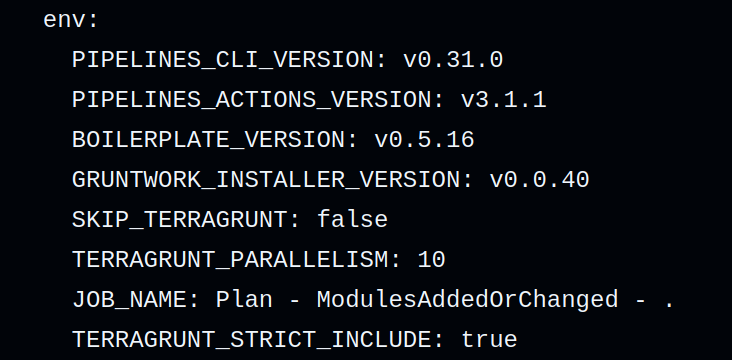 Screenshot of additional Environment Variable
Screenshot of additional Environment Variable