Machine users
This documentation pertains to an old version of Gruntwork Pipelines which used the infrastructure-pipelines repository. Click here to view documentation for the most recent version.
Gruntwork recommends using CI users in Gruntwork Pipelines, separate from human users in your organization. Using a CI user ensures that a workflow won't break due to an employee leaving your company. Further, using CI users allow you to apply granular permissions that may normally be too restrictive for a normal employee to do their daily work.
This guide will take approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Creating machine users
Gruntwork Pipelines requires using two machine users; one with the ability to open pull requests and run workflows on your behalf and another that can only read code from GitHub. Restrictive permissions are then applied to each user to limit them to only perform the required actions to accomplish their tasks. This means that in order to actually run a pipeline job, both users must be involved at separate stages.
We’ll refer to this user as ci-user and ci-read-only-user, but you may name them anything you like. These users must:
- Both be members of your GitHub Organization
- Both be members of your team in Gruntwork’s GitHub Organization (See instructions on inviting a user to your team and linking the user’s GitHub ID to Gruntwork)
Storing secrets
During this setup, you will need to generate and securely store three GitHub tokens for two GitHub users. You will need a temporary location for these sensitive values between generating them and storing them in GitHub Actions. Do so according to your company's recommended security best practices (e.g., do not store them in Slack, a sticky note, etc., during this exercise.)
Your organization is required to rotate the GitHub tokens and update all GitHub secrets that use them.
ci-user
The ci-user orchestrates workflows, can open pull requests from automated code generation, and leave comments on pull requests. This user should have two GitHub Fine Grained Personal Access Tokens (PAT)s with the following permissions.
First, invite the ci-user to both your infrastructure-live and infrastructure-pipelines repositories with collaborator access. Then, create the following access tokens in the ci-user's GitHub account:
-
INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS. This is a fine-grained GitHub access token and will be used to grant GitHub Actions access to clone yourinfrastructure-liverepository, open PRs, and create comments & issues.This token must have the following permissions to your
infrastructure-liverepo in your GitHub Organization:- Content read & write access
- Issues read & write access
- Metadata read access
- Pull requests read & write access
- Workflows read & write access
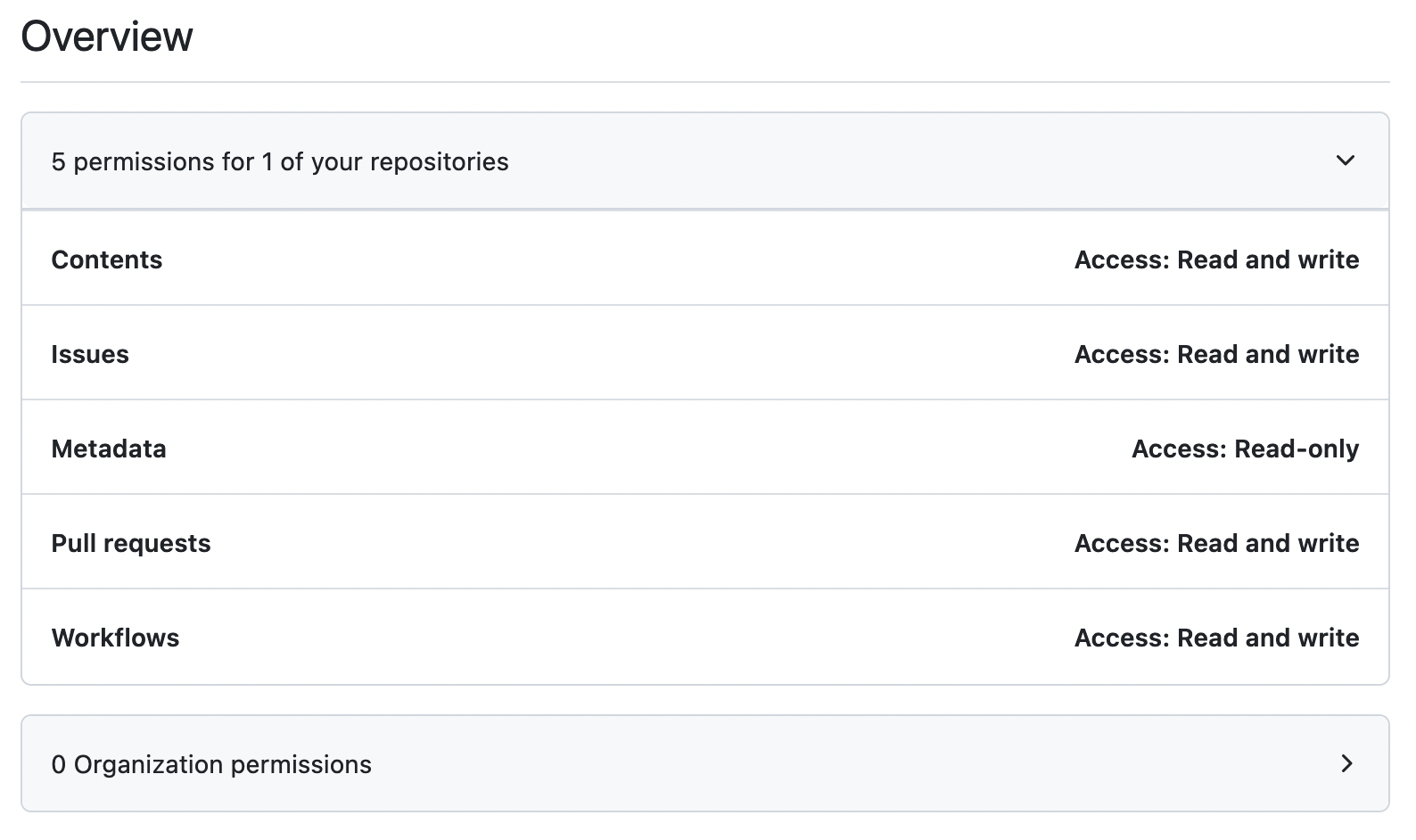 INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS PAT Configuration
INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS PAT Configuration -
PIPELINES_DISPATCH. This token will be used to grant GitHub Actions, in yourinfrastructure-liverepository, permission to trigger workflows in yourinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository.This token must have:
- Actions read & write access
- Contents read only access
- Metadata read access
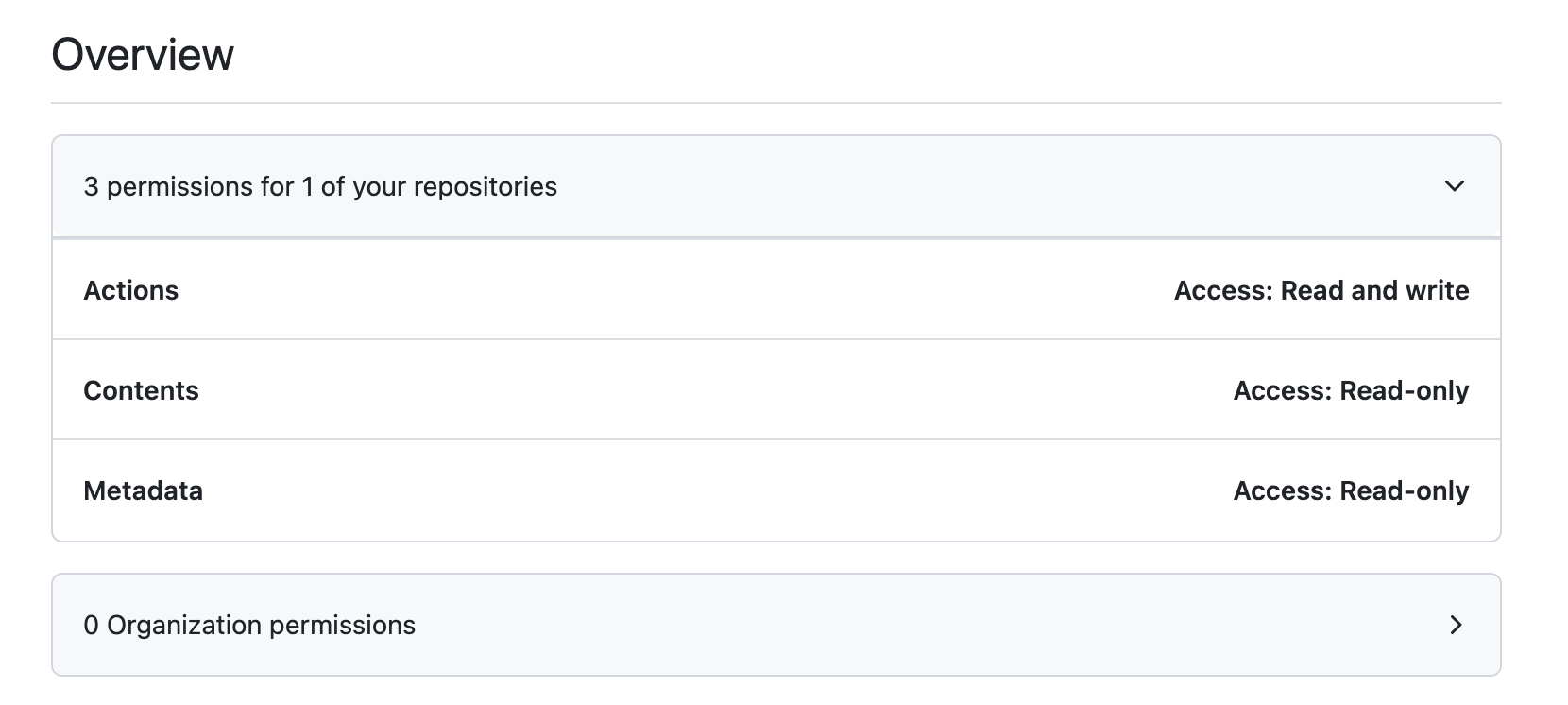 PIPELINES_DISPATCH PAT Configuration
PIPELINES_DISPATCH PAT Configuration -
MANAGE_REPOS. This token will be used to create newinfra-live-<TEAM-NAME>repositories in your GitHub Organization when vending delegated team accounts.This token must have the following permissions to all repositories the
ci-userhas access to:- Administration read & write access
- Contents read & write access
- Metadata read access
- Pull requests read & write access
- Workflows read & write access
and Organization permissions to:
- Secrets read & write access
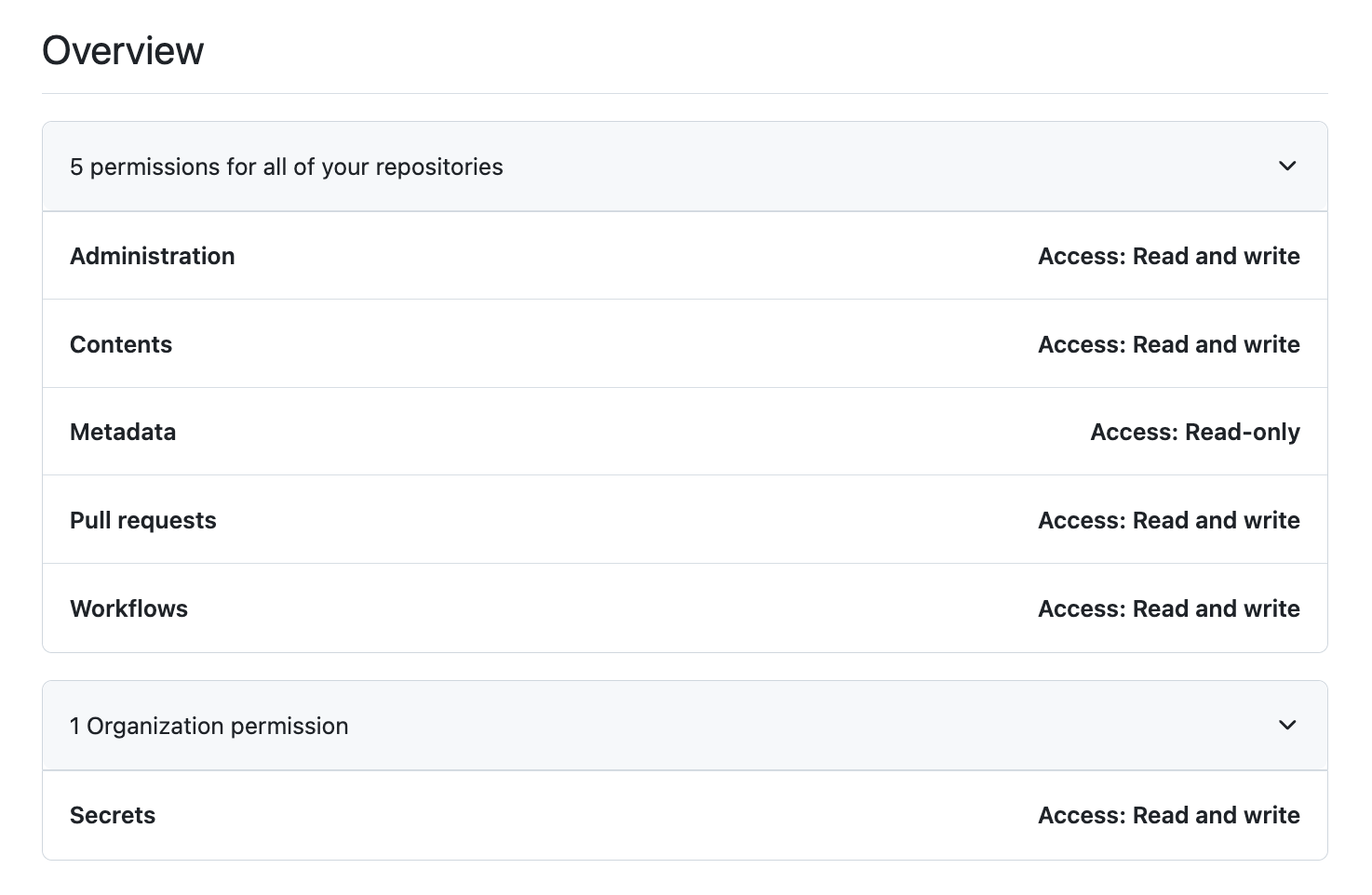 MANAGE_REPOS PAT Configuration
MANAGE_REPOS PAT Configuration -
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP. This token will be used to grant GitHub Actions permission to create open PRs and create comments in yourinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository in your GitHub Organization. This is only required during the bootstrap process of the pipelines repository and should be removed immediately after.This token must have:
- Contents read & write access
- Metadata read access
- Pull requests read & write access
- Workflows read & write access
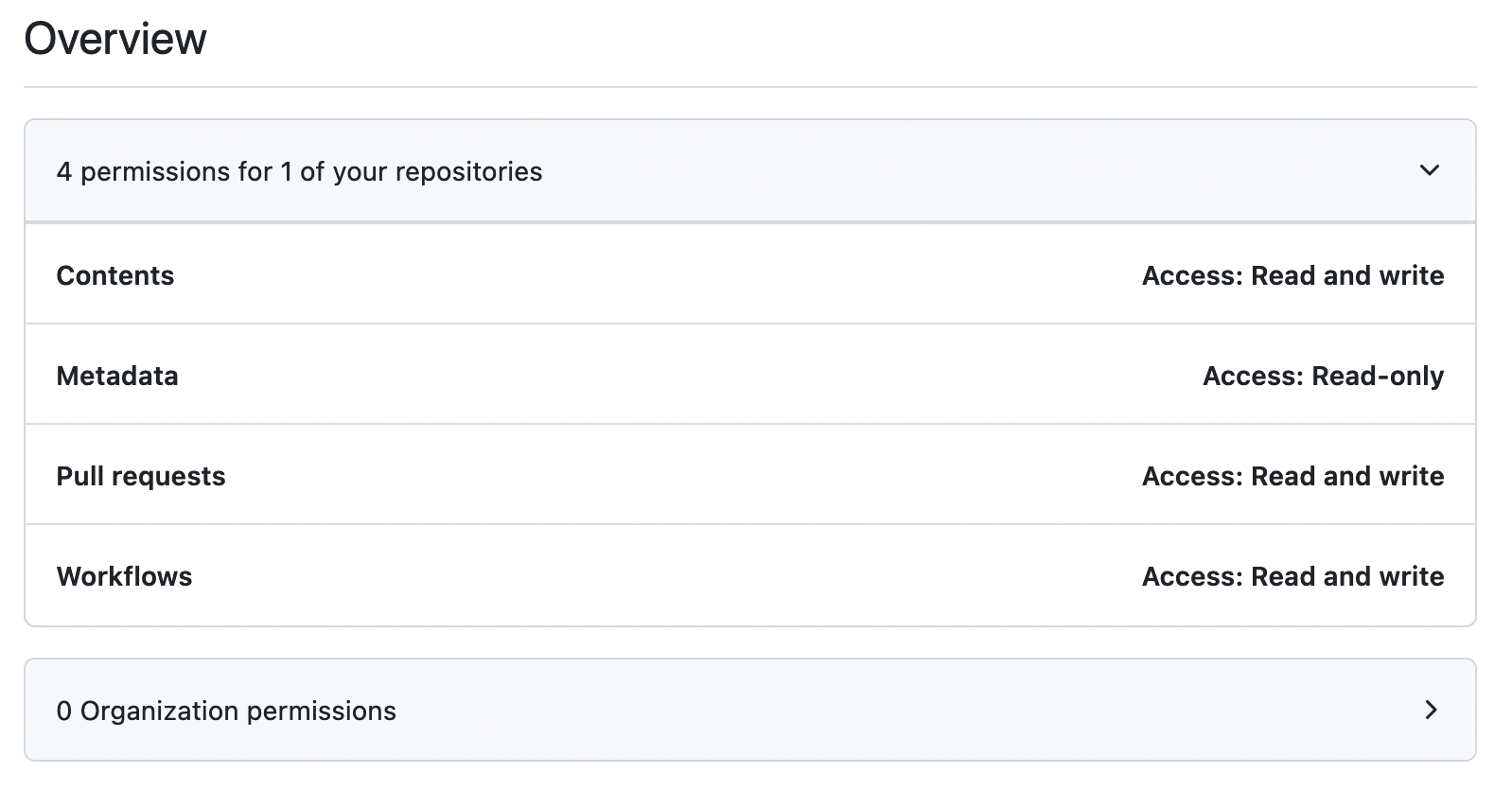 PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP PAT Configuration
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP PAT Configuration
ci-read-only-user
This user is created to pull down Terraform/OpenTofu code, but not to apply it. The ci-read-only-user is used clone infrastructure-live and in Terragrunt actions to access Gruntwork Library modules and your own infrastructure-modules repository or any custom module repositories that are private.
The ci-read-only-user should have a single classic token Personal Access Tokens (PAT) with read permissions. Classic PATs have coarse granularity, we recommend putting this user in a GitHub team that only has READ access to infrastructure-live and any relevant module repositories in your own GitHub Organization. By adding this user to the Gruntwork Developer portal, they will automatically gain access to the Gruntwork Library.
Invite ci-user-read-only to your infrastructure-live repository with collaborator access. Create the following token for the ci-read-only-user:
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS. This token will be used to manage access to Gruntwork resources during GitHub Action runs.
This token must have repo scopes.
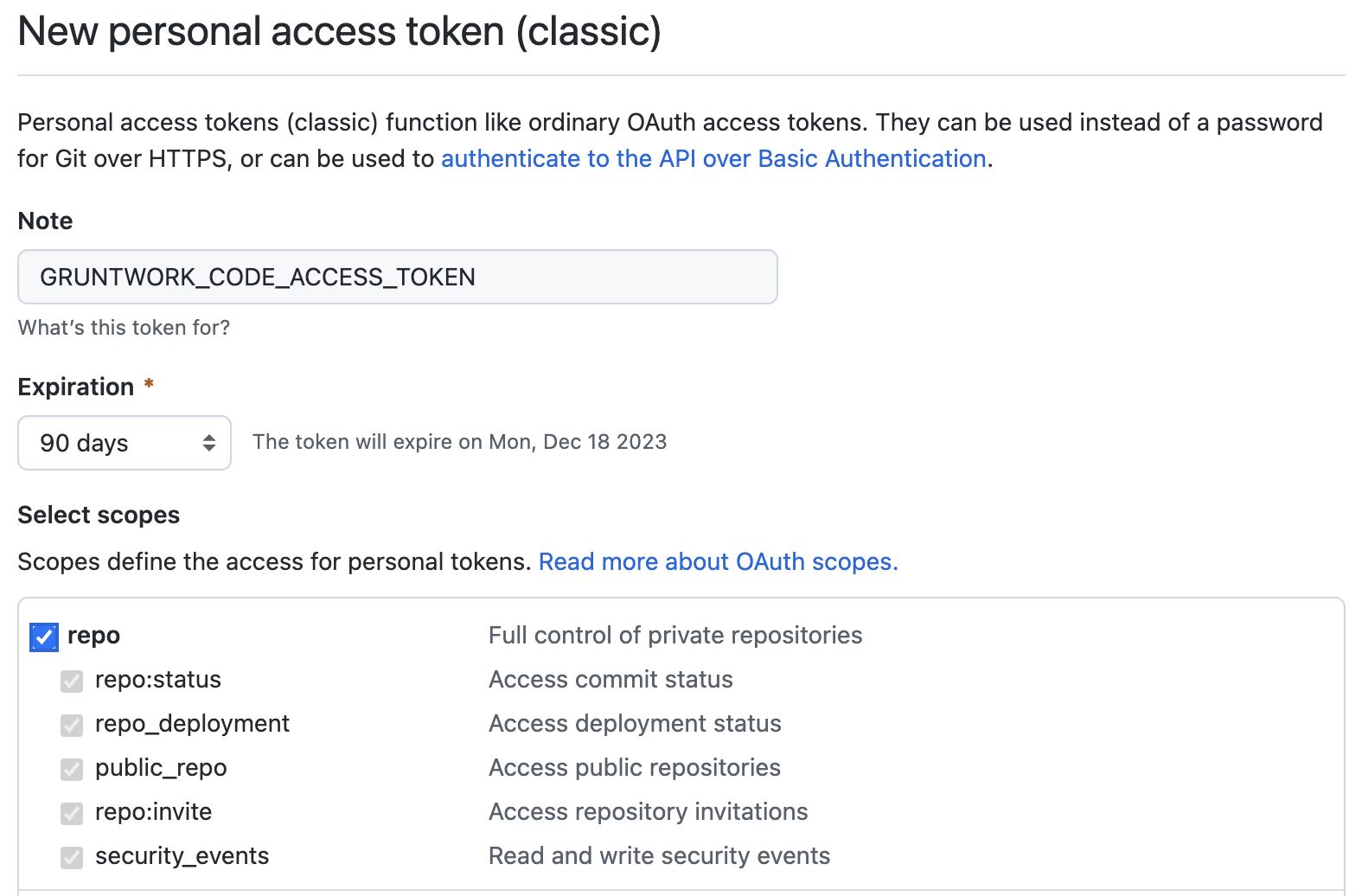 GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS PAT Configuration
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS PAT Configuration
The expiration of this token is up to you and the security posture of your organization, Gruntwork recommend 90 days to avoid having to regularly rotate a token and secrets.
Invite both machine users to Gruntwork
Ensure both of these machine users are members of your team in Gruntwork’s GitHub Organization (See instructions on inviting a user to your team and linking the user’s GitHub ID to Gruntwork)
Configure secrets for GitHub Actions
The recommended path for storing secrets in GitHub Actions is with Organization-level secrets, however not all GitHub plans support Organization secrets that can be used with specific repositories. If this is the case for your GitHub organization, you should use Repository-level secrets.
Since this guide implements secrets that are scoped to specific repositories, anytime a new infrastructure-live or infrastructure-pipelines repository is created, the permissions for these tokens will need to be updated.
- Organization Secrets
- Repository Secrets
-
Navigate to your top level GitHub Organization and select the Settings tab.
-
From the navigation bar on the left side, select Secrets and variables then select Actions.
-
Using the New organization secret option, add the following secrets:
-
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS_TOKEN-
This should be assigned the
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-read-only-userin the secrets section as its value. -
Repository access. Select the
Private Repositoriesoption.
-
-
PIPELINES_DISPATCH_TOKEN-
This should be assigned the
PIPELINES_DISPATCHtoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value. -
Repository access. Select the
Private Repositoriesoption.
infoGRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS&PIPELINES_DISPATCHtokens are made available to all private repositories so that every vendedinfra-live-team-*repository automatically has access to these secrets. Theinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository mitigates the misuse of these secrets by maintaining a list of allowed repositories than can trigger workflows in it using thePIPELINES_DISPATCHtoken.The alternative of granting access to these secrets during the vending process has various drawbacks (e.g., only works for GitHub owners, requires a new machine user, a new PAT, etc).
-
-
INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS_TOKEN-
This should be assigned the
INFRA_LIVE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value. -
Repository access. Using the
Selected repositoriesoption select both theinfrastructure-liveandinfrastructure-pipelinesrepositories.
-
-
MANAGE_REPOS_TOKEN-
This should be assigned the
MANAGE_REPOStoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value. -
Repository access. Using the
Selected repositoriesoption select only theinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository.
-
-
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN-
This should be assigned the
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAPtoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value. -
Repository access. Using the
Selected repositoriesoption select only theinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository.
-
After the bootstrap process is complete, you should delete the following tokens for security purposes:
- The
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAPPersonal Access Token from theci-userGitHub account - The
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP_TOKENGitHub Actions secret from theinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository
For additional information on creating and using Github Actions Organization secrets, please refer to the GitHub Documentation.
Gruntwork Pipelines reads these secrets from GitHub Actions secrets created in the repo. For steps on how to create repository Actions secrets, refer to creating secrets for a repository.
infrastructure-live
In the infrastructure-live repository create the following secrets:
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS_TOKEN. This should be assigned theGRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-read-only-userin the secrets section as its value.INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS_TOKEN. This should be assigned theINFRA_LIVE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value.PIPELINES_DISPATCH_TOKEN. This should be assigned thePIPELINES_DISPATCHtoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value.
Configuring the PIPELINES_DISPATCH and GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS tokens as repository secrets will result in needing a manual update for every new infrastructure-live-team-* repository created.
infrastructure-pipelines
In the infrastructure-pipelines repository create the following secrets:
GRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESS_TOKEN. This should be assigned theGRUNTWORK_CODE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-read-only-userin the secrets section as its value.INFRA_LIVE_ACCESS_TOKEN. This should be assigned theINFRA_LIVE_ACCESStoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value.MANAGE_REPOS_TOKEN. This should be assigned theMANAGE_REPOStoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value.PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN. This should be assigned thePIPELINES_BOOTSTRAPtoken generated by theci-userin the secrets section as its value.
After the bootstrap process is complete, you should delete the following tokens for security purposes:
- The
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAPPersonal Access Token from theci-userGitHub account - The
PIPELINES_BOOTSTRAP_TOKENGitHub Actions secret from theinfrastructure-pipelinesrepository
For additional information on creating and using Github Actions Repository secrets, please refer to the GitHub Documentation