RDS Module
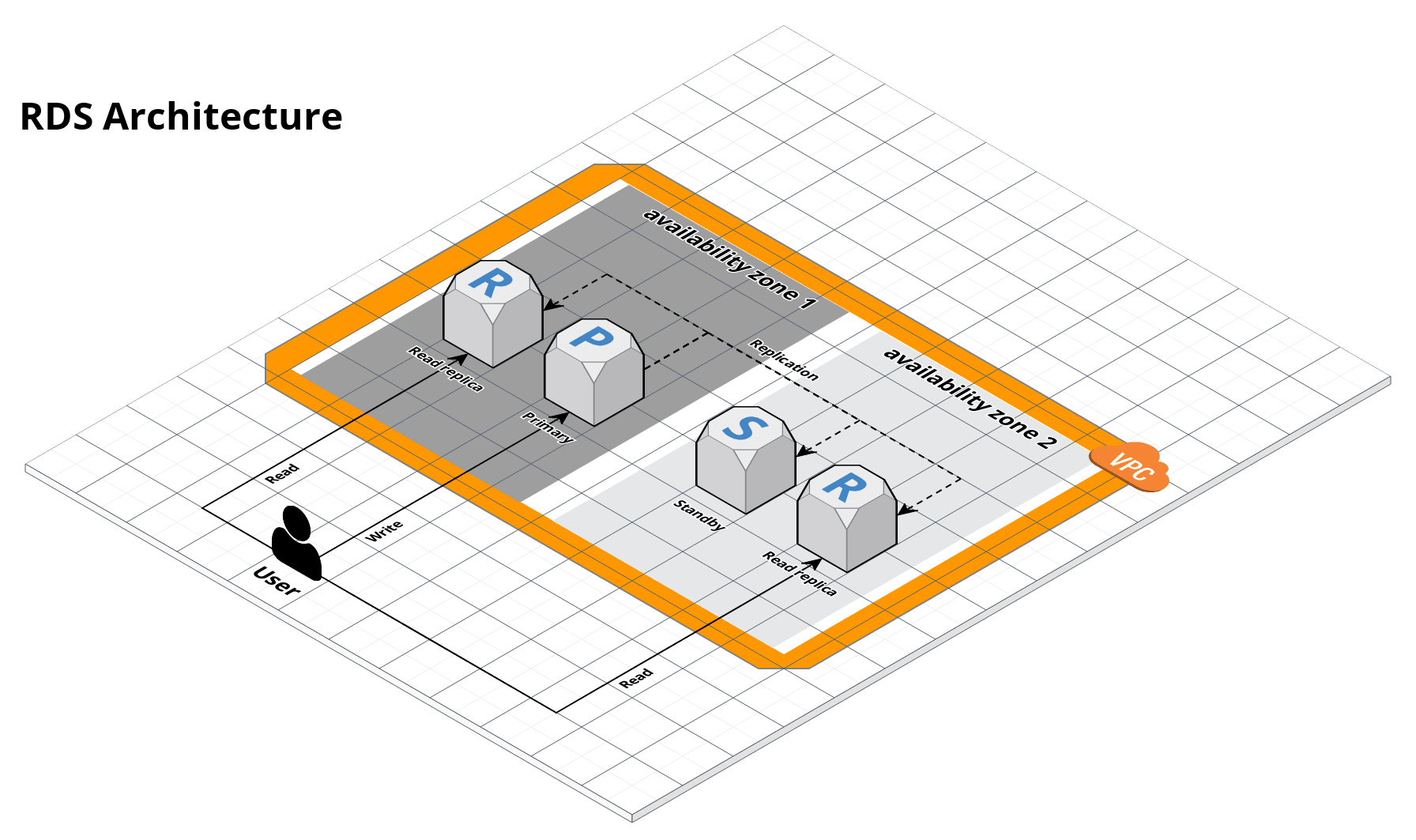
This module creates an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) cluster that can run MySQL, Postgres, MariaDB, Oracle, or SQL Server. The cluster is managed by AWS and automatically handles standby failover, read replicas, backups, patching, and encryption.
 img
img
About RDS
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a web service that makes it easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the AWS Cloud. It provides cost-efficient, resizable capacity for an industry-standard relational database and manages common database administration tasks. Refer to the What is Amazon RDS page for more information.
Common Gotcha's
- All RDS upgrades (version upgrades, instance type upgrades, etc.) require a few minutes of scheduled downtime.
- If an RDS instance that uses Multi-AZ fails, Amazon will automatically kick off a fail-over, but you will still experience about 3 - 5 minutes of downtime.
- Based on the above, make sure you've written your app to gracefully handle database downtime.
- An RDS instance that runs out of disk space will stop working, so be sure to monitor and set an alert on the FreeStorageSpace CloudWatch Metric. Consider monitoring other RDS CloudWatch Metrics as well.
How do you scale this database?
- Storage: Use the
allocated_storagevariable. - Vertical scaling: To scale vertically (i.e. bigger DB instances with more CPU and RAM), use the
instance_type,storage_type, andiopsinput variables. For a list of AWS RDS server types, see DB Instance Class - Horizontal scaling: To scale horizontally, you can add more replicas using the
num_read_replicasinput variable, and RDS will automatically deploy the new instances, begin asynchronous replication, and make them available as read replicas. For more info, see Working with PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MariaDB Read Replicas. - Storage performance: N.B: only available when
var.storage_typeis set togp3. When you are using gp3, you can optionally fine-tune storage performance characteristics via thestorage_throughputvariable. See the RDS User Guide for more information.
How do you connect to the database?
This module provides the connection details as Terraform output variables:
- Primary endpoint: The endpoint for the primary DB. You should always use this URL for writes, as it points to the primary.
- Read replica endpoints: A comma-separated list of read replica URLs.
- Port: The port to use to connect to the endpoints above.
You can programmatically extract these variables in your Terraform templates and pass them to other resources (e.g.
pass them to User Data in your EC2 instances). You'll also see the variables at the end of each terraform apply call
or if you run terraform output.
Note that the database is likely behind a Bastion Host, so you may need to first connect to the Bastion Host (or use SSH Tunneling) before you can connect to the database.
Deployment
Before making any deployment for the RDS database, start by backing up the database and taking a snapshot of the infrastructure state. Review the release notes for any breaking changes and new features. Update the infrastructure code by modifying the Terraform configurations and testing them in a non-production environment. Conduct post-upgrade testing to ensure application functionality and performance, while monitoring the database health. Communicate the potential downtime to relevant stakeholders and involve them in the process.
Minor version upgrades
RDS supports automatically installing minor version upgrades. For example, it can automatically update a MySQL database from version 5.7.10 to 5.7.11. To enable this functionality, follow these steps:
- Set the
auto_minor_version_upgradeparameter totrue. - Set the
engine_versionparameter toMAJOR.MINORand omit thePATCHnumber.
Major Version Upgrade
RDS supports automatically installing major version upgrades. To enable this functionality, follow these steps:
- Set the
allow_major_version_upgradeparameter totrue. - Set the
engine_versionparameter toMAJOR.MINORand omit thePATCHnumber.
Note: A minimal downtime is expected during a major version upgrade. Make sure to communicate the potential downtime to relevant stakeholders in advance.
PostgreSQL Major Version Upgrades: Two-Phase Process Required
PostgreSQL major version upgrades (e.g., 15→16) require a two-phase process due to parameter group family incompatibility. Each PostgreSQL major version requires a specific parameter group family (postgres15 for v15, postgres16 for v16), and Terraform cannot handle the transition in a single operation.
Root Cause: The Terraform AWS provider cannot simultaneously detach the old parameter group and attach the new one, creating an unresolvable dependency cycle. See terraform-provider-aws #38984 and #6448.
Step-by-Step Upgrade Process
Phase 1: Detach Custom Parameter Group
# Temporarily use AWS default parameter group
parameter_group_name = "default.postgres15" # Use default for current version
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
engine_version = "15.7" # Keep current version
Apply: terraform apply
Phase 2: Upgrade Version with New Parameter Group
# Update version and parameter group together
engine_version = "16.3"
parameter_group_name = aws_db_parameter_group.postgres16.name
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
# Create new parameter group
resource "aws_db_parameter_group" "postgres16" {
name = "${var.name}-postgres16"
family = "postgres16"
# Add custom parameters here
}
Apply: terraform apply
Critical Notes:
- Always backup before upgrading
- Expect 5-30 minutes downtime
- Test in non-production first
- After upgrade, set
allow_major_version_upgrade = falseto prevent accidental upgrades
Blue/Green Deployment for Low-Downtime Updates
By default, RDS updates DB Instances in-place, which can cause service interruptions. Low-downtime updates minimize interruptions by using an RDS Blue/Green deployment. To enable this, set the enable_blue_green_update variable to true.
Note that low-downtime updates are only supported for MySQL, MariaDB, and Postgresql, and backups must be enabled. When using terraform, the Blue/Green Deployment won't finish until the Green instances become the new instance and the Blue instance is deleted. Therefore, Blue/Green Deployment cannot be used for scenarios outside of terraform's resource update, such as manual testing of the Green deployment or reverting back to the Blue deployment.
Standby Deployment
Set multi_az=true. When setting up a multi-AZ (Availability Zone) RDS deployment in AWS, both the primary and standby RDS instances are created in different Availability Zones for high availability. However, this doesn't mean they will have different endpoints. Both instances will have the same DNS endpoint, and AWS's internal infrastructure will handle the failover process transparently for you. AWS RDS provides automatic failover support for DB instances using Multi-AZ deployments for the supported database engines. Failover is automatically handled by RDS without any manual intervention.
Sample Usage
- Terraform
- Terragrunt
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S RDS MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
module "rds" {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-data-storage.git//modules/rds?ref=v0.47.0"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The DB engine to use (e.g. mysql).
engine = <string>
# The version of var.engine to use (e.g. 5.7.11 for mysql). If
# var.auto_minor_version_upgrade is set to true, set the version number to
# MAJOR.MINOR and omit the PATCH (e.g., set it to 5.7 and not 5.7.11) to avoid
# state drift. See
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details. NOTE: Running database engine versions past their
# end-of-standard-support date will automatically enroll in RDS Extended
# Support, which incurs additional charges. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html
# for details.
engine_version = <string>
# The instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro). For best
# price-performance, consider Graviton-based instances (db.m7g.*, db.r7g.*,
# db.m8g.*, db.r8g.*). Graviton4 (M8g/R8g) instances offer up to 40% better
# performance vs. Graviton3.
instance_type = <string>
# The name used to namespace all resources created by these templates,
# including the DB instance (e.g. drupaldb). Must be unique for this region.
# May contain only lowercase alphanumeric characters, hyphens, underscores,
# periods, and spaces.
name = <string>
# The port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306)
port = <number>
# A list of subnet ids where the database should be deployed. In the standard
# Gruntwork VPC setup, these should be the private persistence subnet ids.
# This is ignored if create_subnet_group=false.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The id of the VPC in which this DB should be deployed.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the primary RDS instance.
additional_primary_instance_security_group_ids = []
# List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the read replica RDS
# instance.
additional_read_replica_instance_security_group_ids = []
# The amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB. If
# max_allocated_storage is configured, this argument represents the initial
# storage allocation and differences from the configuration will be ignored
# automatically when Storage Autoscaling occurs.
allocated_storage = null
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB.
# Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC
# plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read replica
# instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same security
# group as master instance.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB.
# Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this
# VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read
# replica instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same
# security group as master instance.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# A list of Security Groups that can connect to this DB.
allow_connections_from_security_groups = []
# A list of Security Groups that can connect to read replica instances. If not
# set read replica instances will use the same security group as master
# instance.
allow_connections_from_security_groups_to_read_replicas = []
# Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be
# permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and
# will never automatically applied.
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed to
# send traffic to. Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app
# subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_outbound_connections_to_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed
# to send traffic to. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private
# app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_outbound_connections_to_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# The availability zones within which it should be possible to spin up
# replicas
allowed_replica_zones = []
# Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or
# during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may
# cause degraded performance or downtime.
apply_immediately = false
# Indicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB
# instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set
# var.engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use
# 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details.
auto_minor_version_upgrade = true
# The description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Security group for the var.name DB' if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to var.name
# if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_name = null
# The description of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Subnet group for the var.name DB' if not specified.
aws_db_subnet_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created, or an existing one to
# use if create_subnet_group is false. Defaults to var.name if not specified.
aws_db_subnet_group_name = null
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must
# be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means disable automated backups.
backup_retention_period = 21
# The daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g.
# 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup
# runs.
backup_window = "06:00-07:00"
# The Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS
# instance.
ca_cert_identifier = null
# The character set name to use for DB encoding in Oracle and Microsoft SQL
# instances (collation). This must be null for all other engine types. Note
# that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after
# creation.
character_set_name = null
# Copy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
copy_tags_to_snapshot = false
# If false, the DB will bind to aws_db_subnet_group_name and the CIDR will be
# ignored (allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks)
create_subnet_group = true
# Timeout for DB creating
creating_timeout = "40m"
# The instance profile associated with the underlying Amazon EC2 instance of
# an RDS Custom DB instance.
custom_iam_instance_profile = null
# Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new
# parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be
# launched with the default parameter group.
custom_parameter_group = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group
# created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
custom_tags = {}
# The mode of Database Insights to enable for the DB instance. Valid options
# are 'standard' or 'advanced'. This is the recommended replacement for
# Performance Insights (deprecated June 30, 2026). 'standard' provides 7 days
# of counter metrics at no extra cost. 'advanced' provides 15 months of all
# metrics, execution plans, and on-demand analysis. When setting this to
# 'advanced', performance_insights_enabled must be set to true and
# 'performance_insights_retention_period' set to at least 465 days.
database_insights_mode = null
# The name for your database. Must contain 1-64 alphanumeric characters for
# MySQL/MariaDB, 1-63 for PostgreSQL, 1-8 for Oracle. Must begin with a
# letter. Cannot be a reserved word. Not supported for SQL Server (must be
# null). If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create a database
# in the DB instance you are creating.
db_name = null
# Use a dedicated log volume (DLV) for the DB instance. A DLV moves database
# transaction logs onto a separate storage volume, which can improve database
# write performance. Only supported for Provisioned IOPS storage types
# (io1/io2) — gp3 is NOT supported. Engine version requirements: MariaDB
# 10.6.7+, MySQL 8.0.28+, PostgreSQL 13.10+/14.7+/15.2+. A reboot is required
# after enabling/disabling on an existing instance.
dedicated_log_volume = null
# A map of the default license to use for each supported RDS engine.
default_license_models = {"mariadb":"general-public-license","mysql":"general-public-license","oracle-ee":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-ee-cdb":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se1":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se2":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se2-cdb":"bring-your-own-license","postgres":"postgresql-license","sqlserver-ee":"license-included","sqlserver-ex":"license-included","sqlserver-se":"license-included","sqlserver-web":"license-included"}
# Specifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB
# instance is deleted
delete_automated_backups = true
# Timeout for DB deleting
deleting_timeout = "60m"
# The database can't be deleted when this value is set to true. The default is
# false.
deletion_protection = false
# Enable blue/green deployment to minimize down time due to changes made to
# the RDS Instance. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/blue-green-deployments-overview.html
# for more detailed information.
enable_blue_green_update = false
# List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no
# logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit,
# error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and
# upgrade (PostgreSQL).
enabled_cloudwatch_logs_exports = []
# The life cycle type for this DB instance. Valid values are
# 'open-source-rds-extended-support' (default) and
# 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled'. When set to the default, the
# instance will automatically enroll in RDS Extended Support after the engine
# version reaches end of standard support, which incurs additional charges.
# Set to 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled' to opt out and avoid
# unexpected billing — the instance will then be upgraded to the next major
# version at the end of standard support. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html
engine_lifecycle_support = null
# The name of the final_snapshot_identifier. Defaults to
# var.name-final-snapshot if not specified.
final_snapshot_name = null
# Specifies whether IAM database authentication is enabled. This option is
# only available for MySQL and PostgreSQL engines.
iam_database_authentication_enabled = null
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this
# implies a storage_type of 'io1','io2, or 'gp3'. Set to 0 to disable.
iops = 0
# The ARN of a KMS key that should be used to encrypt data on disk. Only used
# if var.storage_encrypted is true. If you leave this blank, the default RDS
# KMS key for the account will be used. This variable needs to be set to an
# AWS KMS CMK if provisioning a custom RDS instance.
kms_key_arn = null
# The license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for
# available license models. Valid values: general-public-license,
# postgresql-license, license-included, bring-your-own-license.
license_model = null
# The weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur
# (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or
# there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
maintenance_window = "sun:07:00-sun:08:00"
# Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets
# Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
manage_master_user_password = null
# The password for the master user. If var.snapshot_identifier is non-empty,
# this value is ignored.
master_password = null
# The Amazon Web Services KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias
# ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different Amazon
# Web Services account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. If not specified,
# the default KMS key for your Amazon Web Services account is used.
master_user_secret_kms_key_id = null
# The username for the master user.
master_username = null
# When configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale
# the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore
# differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to
# allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
max_allocated_storage = 0
# The interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics
# are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring
# metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced
# Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes
# or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
monitoring_interval = 0
# The ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring
# metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but
# monitoring_role_arn is let as an empty string, a default IAM role that
# allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
monitoring_role_arn = null
# Optionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will
# default to just /.
monitoring_role_arn_path = "/"
# The name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to
# var.name-monitoring-role if not specified.
monitoring_role_name = null
# Specifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability
# zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
multi_az = true
# The national character set is used in the NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, and NCLOB data
# types for Oracle instances. This must be null for all other engine types.
# Note that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after
# creation.
nchar_character_set_name = null
# (Optional) The network type of the DB instance. Valid values: IPV4, DUAL. By
# default, it's set to IPV4
network_type = null
# The number of read replicas to create. RDS will asynchronously replicate all
# data from the master to these replicas, which you can use to horizontally
# scale reads traffic.
num_read_replicas = 0
# Name of a DB option group to associate.
option_group_name = null
# Name of a DB parameter group to associate.
parameter_group_name = null
# Name of a DB parameter group to associate with read replica instances.
# Defaults to var.parameter_group_name if not set.
parameter_group_name_for_read_replicas = null
# Specifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can
# be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See
# https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details. NOTE: The
# Performance Insights console and flexible retention periods are deprecated
# as of June 30, 2026. Consider using var.database_insights_mode ('standard'
# or 'advanced') instead, which replaces Performance Insights with CloudWatch
# Database Insights.
performance_insights_enabled = false
# The ARN for the KMS key to encrypt Performance Insights data. When
# specifying performance_insights_kms_key_id, performance_insights_enabled
# needs to be set to true. Once KMS key is set, it can never be changed. When
# set to `null` default aws/rds KMS for given region is used.
performance_insights_kms_key_id = null
# The amount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Either 7 (7
# days) or 731 (2 years). When specifying
# performance_insights_retention_period, performance_insights_enabled needs to
# be set to true. Defaults to `7`. NOTE: Flexible PI retention periods (paid
# tier) are deprecated as of June 30, 2026. For long-term retention, use
# var.database_insights_mode = 'advanced' which provides 15 months of
# retention via CloudWatch Database Insights.
performance_insights_retention_period = null
# The ARN of the policy that is used to set the permissions boundary for the
# role of enhanced monitoring role. This policy should be created outside of
# this module.
permissions_boundary_arn = null
# WARNING: - In nearly all cases a database should NOT be publicly accessible.
# Only set this to true if you want the database open to the internet.
publicly_accessible = false
# Redefine replica instance type, if you want to define a different RDS
# instance type for replica.
read_replica_instance_type = null
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for read replicas. If null, the replica will
# use the same value as the primary, which is set in var.iops.
read_replica_iops = null
# The type of storage to use for read replicas. If null, the replica will use
# the same value as the primary, which is set in var.storage_type.
read_replica_storage_type = null
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the
# read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means
# disable automated backups.
replica_backup_retention_period = 0
# A configuration block for restoring a DB instance to an arbitrary point in
# time. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance#restore-to-point-in-time
# for more details
restore_to_point_in_time = null
# Determines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is
# deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete
# this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data!
skip_final_snapshot = false
# If non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID.
# This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g:
# rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
snapshot_identifier = null
# Specifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
storage_encrypted = true
# The storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when
# var.storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage
# value is below a per-engine threshold. See the RDS User Guide:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_Storage.html#gp3-storage
storage_throughput = null
# The type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of
# 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose
# SSD), 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD), or 'io2' (2nd gen provisioned IOPS SSD).
# AWS recommends 'gp3' for most workloads as it provides a baseline of 3,000
# IOPS and 125 MiB/s at a lower cost than gp2, with the ability to provision
# up to 64,000 IOPS independently of storage size.
storage_type = "gp2"
# Time zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by
# Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL
# User Guide
# (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone)
# for more information.
timezone = null
# Timeout for DB updating
updating_timeout = "80m"
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S RDS MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
terraform {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-data-storage.git//modules/rds?ref=v0.47.0"
}
inputs = {
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The DB engine to use (e.g. mysql).
engine = <string>
# The version of var.engine to use (e.g. 5.7.11 for mysql). If
# var.auto_minor_version_upgrade is set to true, set the version number to
# MAJOR.MINOR and omit the PATCH (e.g., set it to 5.7 and not 5.7.11) to avoid
# state drift. See
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details. NOTE: Running database engine versions past their
# end-of-standard-support date will automatically enroll in RDS Extended
# Support, which incurs additional charges. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html
# for details.
engine_version = <string>
# The instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro). For best
# price-performance, consider Graviton-based instances (db.m7g.*, db.r7g.*,
# db.m8g.*, db.r8g.*). Graviton4 (M8g/R8g) instances offer up to 40% better
# performance vs. Graviton3.
instance_type = <string>
# The name used to namespace all resources created by these templates,
# including the DB instance (e.g. drupaldb). Must be unique for this region.
# May contain only lowercase alphanumeric characters, hyphens, underscores,
# periods, and spaces.
name = <string>
# The port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306)
port = <number>
# A list of subnet ids where the database should be deployed. In the standard
# Gruntwork VPC setup, these should be the private persistence subnet ids.
# This is ignored if create_subnet_group=false.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The id of the VPC in which this DB should be deployed.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the primary RDS instance.
additional_primary_instance_security_group_ids = []
# List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the read replica RDS
# instance.
additional_read_replica_instance_security_group_ids = []
# The amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB. If
# max_allocated_storage is configured, this argument represents the initial
# storage allocation and differences from the configuration will be ignored
# automatically when Storage Autoscaling occurs.
allocated_storage = null
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB.
# Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC
# plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read replica
# instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same security
# group as master instance.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB.
# Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this
# VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read
# replica instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same
# security group as master instance.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# A list of Security Groups that can connect to this DB.
allow_connections_from_security_groups = []
# A list of Security Groups that can connect to read replica instances. If not
# set read replica instances will use the same security group as master
# instance.
allow_connections_from_security_groups_to_read_replicas = []
# Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be
# permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and
# will never automatically applied.
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
# A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed to
# send traffic to. Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app
# subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_outbound_connections_to_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed
# to send traffic to. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private
# app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_outbound_connections_to_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# The availability zones within which it should be possible to spin up
# replicas
allowed_replica_zones = []
# Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or
# during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may
# cause degraded performance or downtime.
apply_immediately = false
# Indicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB
# instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set
# var.engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use
# 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details.
auto_minor_version_upgrade = true
# The description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Security group for the var.name DB' if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to var.name
# if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_name = null
# The description of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Subnet group for the var.name DB' if not specified.
aws_db_subnet_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created, or an existing one to
# use if create_subnet_group is false. Defaults to var.name if not specified.
aws_db_subnet_group_name = null
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must
# be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means disable automated backups.
backup_retention_period = 21
# The daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g.
# 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup
# runs.
backup_window = "06:00-07:00"
# The Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS
# instance.
ca_cert_identifier = null
# The character set name to use for DB encoding in Oracle and Microsoft SQL
# instances (collation). This must be null for all other engine types. Note
# that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after
# creation.
character_set_name = null
# Copy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
copy_tags_to_snapshot = false
# If false, the DB will bind to aws_db_subnet_group_name and the CIDR will be
# ignored (allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks)
create_subnet_group = true
# Timeout for DB creating
creating_timeout = "40m"
# The instance profile associated with the underlying Amazon EC2 instance of
# an RDS Custom DB instance.
custom_iam_instance_profile = null
# Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new
# parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be
# launched with the default parameter group.
custom_parameter_group = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group
# created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
custom_tags = {}
# The mode of Database Insights to enable for the DB instance. Valid options
# are 'standard' or 'advanced'. This is the recommended replacement for
# Performance Insights (deprecated June 30, 2026). 'standard' provides 7 days
# of counter metrics at no extra cost. 'advanced' provides 15 months of all
# metrics, execution plans, and on-demand analysis. When setting this to
# 'advanced', performance_insights_enabled must be set to true and
# 'performance_insights_retention_period' set to at least 465 days.
database_insights_mode = null
# The name for your database. Must contain 1-64 alphanumeric characters for
# MySQL/MariaDB, 1-63 for PostgreSQL, 1-8 for Oracle. Must begin with a
# letter. Cannot be a reserved word. Not supported for SQL Server (must be
# null). If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create a database
# in the DB instance you are creating.
db_name = null
# Use a dedicated log volume (DLV) for the DB instance. A DLV moves database
# transaction logs onto a separate storage volume, which can improve database
# write performance. Only supported for Provisioned IOPS storage types
# (io1/io2) — gp3 is NOT supported. Engine version requirements: MariaDB
# 10.6.7+, MySQL 8.0.28+, PostgreSQL 13.10+/14.7+/15.2+. A reboot is required
# after enabling/disabling on an existing instance.
dedicated_log_volume = null
# A map of the default license to use for each supported RDS engine.
default_license_models = {"mariadb":"general-public-license","mysql":"general-public-license","oracle-ee":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-ee-cdb":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se1":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se2":"bring-your-own-license","oracle-se2-cdb":"bring-your-own-license","postgres":"postgresql-license","sqlserver-ee":"license-included","sqlserver-ex":"license-included","sqlserver-se":"license-included","sqlserver-web":"license-included"}
# Specifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB
# instance is deleted
delete_automated_backups = true
# Timeout for DB deleting
deleting_timeout = "60m"
# The database can't be deleted when this value is set to true. The default is
# false.
deletion_protection = false
# Enable blue/green deployment to minimize down time due to changes made to
# the RDS Instance. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/blue-green-deployments-overview.html
# for more detailed information.
enable_blue_green_update = false
# List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no
# logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit,
# error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and
# upgrade (PostgreSQL).
enabled_cloudwatch_logs_exports = []
# The life cycle type for this DB instance. Valid values are
# 'open-source-rds-extended-support' (default) and
# 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled'. When set to the default, the
# instance will automatically enroll in RDS Extended Support after the engine
# version reaches end of standard support, which incurs additional charges.
# Set to 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled' to opt out and avoid
# unexpected billing — the instance will then be upgraded to the next major
# version at the end of standard support. See
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html
engine_lifecycle_support = null
# The name of the final_snapshot_identifier. Defaults to
# var.name-final-snapshot if not specified.
final_snapshot_name = null
# Specifies whether IAM database authentication is enabled. This option is
# only available for MySQL and PostgreSQL engines.
iam_database_authentication_enabled = null
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this
# implies a storage_type of 'io1','io2, or 'gp3'. Set to 0 to disable.
iops = 0
# The ARN of a KMS key that should be used to encrypt data on disk. Only used
# if var.storage_encrypted is true. If you leave this blank, the default RDS
# KMS key for the account will be used. This variable needs to be set to an
# AWS KMS CMK if provisioning a custom RDS instance.
kms_key_arn = null
# The license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for
# available license models. Valid values: general-public-license,
# postgresql-license, license-included, bring-your-own-license.
license_model = null
# The weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur
# (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or
# there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
maintenance_window = "sun:07:00-sun:08:00"
# Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets
# Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
manage_master_user_password = null
# The password for the master user. If var.snapshot_identifier is non-empty,
# this value is ignored.
master_password = null
# The Amazon Web Services KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias
# ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different Amazon
# Web Services account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. If not specified,
# the default KMS key for your Amazon Web Services account is used.
master_user_secret_kms_key_id = null
# The username for the master user.
master_username = null
# When configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale
# the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore
# differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to
# allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
max_allocated_storage = 0
# The interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics
# are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring
# metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced
# Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes
# or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
monitoring_interval = 0
# The ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring
# metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but
# monitoring_role_arn is let as an empty string, a default IAM role that
# allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
monitoring_role_arn = null
# Optionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will
# default to just /.
monitoring_role_arn_path = "/"
# The name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to
# var.name-monitoring-role if not specified.
monitoring_role_name = null
# Specifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability
# zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
multi_az = true
# The national character set is used in the NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, and NCLOB data
# types for Oracle instances. This must be null for all other engine types.
# Note that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after
# creation.
nchar_character_set_name = null
# (Optional) The network type of the DB instance. Valid values: IPV4, DUAL. By
# default, it's set to IPV4
network_type = null
# The number of read replicas to create. RDS will asynchronously replicate all
# data from the master to these replicas, which you can use to horizontally
# scale reads traffic.
num_read_replicas = 0
# Name of a DB option group to associate.
option_group_name = null
# Name of a DB parameter group to associate.
parameter_group_name = null
# Name of a DB parameter group to associate with read replica instances.
# Defaults to var.parameter_group_name if not set.
parameter_group_name_for_read_replicas = null
# Specifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can
# be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See
# https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details. NOTE: The
# Performance Insights console and flexible retention periods are deprecated
# as of June 30, 2026. Consider using var.database_insights_mode ('standard'
# or 'advanced') instead, which replaces Performance Insights with CloudWatch
# Database Insights.
performance_insights_enabled = false
# The ARN for the KMS key to encrypt Performance Insights data. When
# specifying performance_insights_kms_key_id, performance_insights_enabled
# needs to be set to true. Once KMS key is set, it can never be changed. When
# set to `null` default aws/rds KMS for given region is used.
performance_insights_kms_key_id = null
# The amount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Either 7 (7
# days) or 731 (2 years). When specifying
# performance_insights_retention_period, performance_insights_enabled needs to
# be set to true. Defaults to `7`. NOTE: Flexible PI retention periods (paid
# tier) are deprecated as of June 30, 2026. For long-term retention, use
# var.database_insights_mode = 'advanced' which provides 15 months of
# retention via CloudWatch Database Insights.
performance_insights_retention_period = null
# The ARN of the policy that is used to set the permissions boundary for the
# role of enhanced monitoring role. This policy should be created outside of
# this module.
permissions_boundary_arn = null
# WARNING: - In nearly all cases a database should NOT be publicly accessible.
# Only set this to true if you want the database open to the internet.
publicly_accessible = false
# Redefine replica instance type, if you want to define a different RDS
# instance type for replica.
read_replica_instance_type = null
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for read replicas. If null, the replica will
# use the same value as the primary, which is set in var.iops.
read_replica_iops = null
# The type of storage to use for read replicas. If null, the replica will use
# the same value as the primary, which is set in var.storage_type.
read_replica_storage_type = null
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the
# read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means
# disable automated backups.
replica_backup_retention_period = 0
# A configuration block for restoring a DB instance to an arbitrary point in
# time. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance#restore-to-point-in-time
# for more details
restore_to_point_in_time = null
# Determines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is
# deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete
# this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data!
skip_final_snapshot = false
# If non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID.
# This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g:
# rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
snapshot_identifier = null
# Specifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
storage_encrypted = true
# The storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when
# var.storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage
# value is below a per-engine threshold. See the RDS User Guide:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_Storage.html#gp3-storage
storage_throughput = null
# The type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of
# 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose
# SSD), 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD), or 'io2' (2nd gen provisioned IOPS SSD).
# AWS recommends 'gp3' for most workloads as it provides a baseline of 3,000
# IOPS and 125 MiB/s at a lower cost than gp2, with the ability to provision
# up to 64,000 IOPS independently of storage size.
storage_type = "gp2"
# Time zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by
# Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL
# User Guide
# (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone)
# for more information.
timezone = null
# Timeout for DB updating
updating_timeout = "80m"
}
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
enginestringThe DB engine to use (e.g. mysql).
engine_versionstringThe version of engine to use (e.g. 5.7.11 for mysql). If auto_minor_version_upgrade is set to true, set the version number to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the PATCH (e.g., set it to 5.7 and not 5.7.11) to avoid state drift. See https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version for more details. NOTE: Running database engine versions past their end-of-standard-support date will automatically enroll in RDS Extended Support, which incurs additional charges. See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html for details.
instance_typestringThe instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro). For best price-performance, consider Graviton-based instances (db.m7g., db.r7g., db.m8g., db.r8g.). Graviton4 (M8g/R8g) instances offer up to 40% better performance vs. Graviton3.
namestringThe name used to namespace all resources created by these templates, including the DB instance (e.g. drupaldb). Must be unique for this region. May contain only lowercase alphanumeric characters, hyphens, underscores, periods, and spaces.
portnumberThe port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306)
subnet_idslist(string)A list of subnet ids where the database should be deployed. In the standard Gruntwork VPC setup, these should be the private persistence subnet ids. This is ignored if create_subnet_group=false.
vpc_idstringThe id of the VPC in which this DB should be deployed.
Optional
additional_primary_instance_security_group_idslist(string)List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the primary RDS instance.
[]List of IDs of AWS Security Groups to attach to the read replica RDS instance.
[]allocated_storagenumberThe amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB. If max_allocated_storage is configured, this argument represents the initial storage allocation and differences from the configuration will be ignored automatically when Storage Autoscaling occurs.
nullallow_connections_from_cidr_blockslist(string)A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB. Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
[]A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read replica instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same security group as master instance.
[]allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blockslist(string)A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to this DB. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
[]A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that can connect to read replica instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same security group as master instance.
[]allow_connections_from_security_groupslist(string)A list of Security Groups that can connect to this DB.
[]A list of Security Groups that can connect to read replica instances. If not set read replica instances will use the same security group as master instance.
[]Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and will never automatically applied.
trueallow_outbound_connections_to_cidr_blockslist(string)A list of CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed to send traffic to. Should typically be the CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
[]allow_outbound_connections_to_ipv6_cidr_blockslist(string)A list of IPv6 CIDR-formatted IP address ranges that the database is allowed to send traffic to. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
[]allowed_replica_zoneslist(string)The availability zones within which it should be possible to spin up replicas
[]Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may cause degraded performance or downtime.
falseIndicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/aws/r/db_instance.html#engine_version for more details.
trueThe description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to 'Security group for the name DB' if not specified.
nullThe name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to name if not specified.
nullThe description of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created. Defaults to 'Subnet group for the name DB' if not specified.
nullaws_db_subnet_group_namestringThe name of the aws_db_subnet_group that is created, or an existing one to use if create_subnet_group is false. Defaults to name if not specified.
nullbackup_retention_periodnumberHow many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means disable automated backups.
21backup_windowstringThe daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g. 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup runs.
"06:00-07:00"ca_cert_identifierstringThe Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS instance.
nullcharacter_set_namestringThe character set name to use for DB encoding in Oracle and Microsoft SQL instances (collation). This must be null for all other engine types. Note that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after creation.
nullCopy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
falseIf false, the DB will bind to aws_db_subnet_group_name and the CIDR will be ignored (allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks)
truecreating_timeoutstringTimeout for DB creating
"40m"The instance profile associated with the underlying Amazon EC2 instance of an RDS Custom DB instance.
nullcustom_parameter_groupobject(…)Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be launched with the default parameter group.
object({
# Name of the parameter group to create
name = string
# The family of the DB parameter group.
family = string
# The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
parameters = list(object({
# Parameter name to configure.
name = string
# Vaue to set the parameter.
value = string
# When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
apply_method = string
}))
})
nullDetails
The family of the DB parameter group.
Details
The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
Details
Vaue to set the parameter.
Details
When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
custom_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}database_insights_modestringThe mode of Database Insights to enable for the DB instance. Valid options are 'standard' or 'advanced'. This is the recommended replacement for Performance Insights (deprecated June 30, 2026). 'standard' provides 7 days of counter metrics at no extra cost. 'advanced' provides 15 months of all metrics, execution plans, and on-demand analysis. When setting this to 'advanced', performance_insights_enabled must be set to true and 'performance_insights_retention_period' set to at least 465 days.
nulldb_namestringThe name for your database. Must contain 1-64 alphanumeric characters for MySQL/MariaDB, 1-63 for PostgreSQL, 1-8 for Oracle. Must begin with a letter. Cannot be a reserved word. Not supported for SQL Server (must be null). If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create a database in the DB instance you are creating.
nullUse a dedicated log volume (DLV) for the DB instance. A DLV moves database transaction logs onto a separate storage volume, which can improve database write performance. Only supported for Provisioned IOPS storage types (io1/io2) — gp3 is NOT supported. Engine version requirements: MariaDB 10.6.7+, MySQL 8.0.28+, PostgreSQL 13.10+/14.7+/15.2+. A reboot is required after enabling/disabling on an existing instance.
nulldefault_license_modelsmap(string)A map of the default license to use for each supported RDS engine.
{
mariadb = "general-public-license",
mysql = "general-public-license",
oracle-ee = "bring-your-own-license",
oracle-ee-cdb = "bring-your-own-license",
oracle-se = "bring-your-own-license",
oracle-se1 = "bring-your-own-license",
oracle-se2 = "bring-your-own-license",
oracle-se2-cdb = "bring-your-own-license",
postgres = "postgresql-license",
sqlserver-ee = "license-included",
sqlserver-ex = "license-included",
sqlserver-se = "license-included",
sqlserver-web = "license-included"
}
Specifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB instance is deleted
truedeleting_timeoutstringTimeout for DB deleting
"60m"The database can't be deleted when this value is set to true. The default is false.
falseEnable blue/green deployment to minimize down time due to changes made to the RDS Instance. See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/blue-green-deployments-overview.html for more detailed information.
falseenabled_cloudwatch_logs_exportslist(string)List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit, error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and upgrade (PostgreSQL).
[]engine_lifecycle_supportstringThe life cycle type for this DB instance. Valid values are 'open-source-rds-extended-support' (default) and 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled'. When set to the default, the instance will automatically enroll in RDS Extended Support after the engine version reaches end of standard support, which incurs additional charges. Set to 'open-source-rds-extended-support-disabled' to opt out and avoid unexpected billing — the instance will then be upgraded to the next major version at the end of standard support. See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/extended-support.html
nullfinal_snapshot_namestringThe name of the final_snapshot_identifier. Defaults to name-final-snapshot if not specified.
nullSpecifies whether IAM database authentication is enabled. This option is only available for MySQL and PostgreSQL engines.
nulliopsnumberThe amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this implies a storage_type of 'io1','io2, or 'gp3'. Set to 0 to disable.
0kms_key_arnstringThe ARN of a KMS key that should be used to encrypt data on disk. Only used if storage_encrypted is true. If you leave this blank, the default RDS KMS key for the account will be used. This variable needs to be set to an AWS KMS CMK if provisioning a custom RDS instance.
nulllicense_modelstringThe license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for available license models. Valid values: general-public-license, postgresql-license, license-included, bring-your-own-license.
nullmaintenance_windowstringThe weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
"sun:07:00-sun:08:00"Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
nullmaster_passwordstringThe password for the master user. If snapshot_identifier is non-empty, this value is ignored.
nullThe Amazon Web Services KMS key identifier is the key ARN, key ID, alias ARN, or alias name for the KMS key. To use a KMS key in a different Amazon Web Services account, specify the key ARN or alias ARN. If not specified, the default KMS key for your Amazon Web Services account is used.
nullmaster_usernamestringThe username for the master user.
nullmax_allocated_storagenumberWhen configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
0monitoring_intervalnumberThe interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
0monitoring_role_arnstringThe ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but monitoring_role_arn is let as an empty string, a default IAM role that allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
nullmonitoring_role_arn_pathstringOptionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will default to just /.
"/"monitoring_role_namestringThe name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to name-monitoring-role if not specified.
nullmulti_azboolSpecifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
truenchar_character_set_namestringThe national character set is used in the NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, and NCLOB data types for Oracle instances. This must be null for all other engine types. Note that this is only relevant at create time - it can not be changed after creation.
nullnetwork_typestring(Optional) The network type of the DB instance. Valid values: IPV4, DUAL. By default, it's set to IPV4
nullnum_read_replicasnumberThe number of read replicas to create. RDS will asynchronously replicate all data from the master to these replicas, which you can use to horizontally scale reads traffic.
0option_group_namestringName of a DB option group to associate.
nullparameter_group_namestringName of a DB parameter group to associate.
nullName of a DB parameter group to associate with read replica instances. Defaults to parameter_group_name if not set.
nullSpecifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details. NOTE: The Performance Insights console and flexible retention periods are deprecated as of June 30, 2026. Consider using database_insights_mode ('standard' or 'advanced') instead, which replaces Performance Insights with CloudWatch Database Insights.
falseThe ARN for the KMS key to encrypt Performance Insights data. When specifying performance_insights_kms_key_id, performance_insights_enabled needs to be set to true. Once KMS key is set, it can never be changed. When set to null default aws/rds KMS for given region is used.
nullThe amount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Either 7 (7 days) or 731 (2 years). When specifying performance_insights_retention_period, performance_insights_enabled needs to be set to true. Defaults to 7. NOTE: Flexible PI retention periods (paid tier) are deprecated as of June 30, 2026. For long-term retention, use database_insights_mode = 'advanced' which provides 15 months of retention via CloudWatch Database Insights.
nullpermissions_boundary_arnstringThe ARN of the policy that is used to set the permissions boundary for the role of enhanced monitoring role. This policy should be created outside of this module.
nullWARNING: - In nearly all cases a database should NOT be publicly accessible. Only set this to true if you want the database open to the internet.
falseRedefine replica instance type, if you want to define a different RDS instance type for replica.
nullread_replica_iopsnumberThe amount of provisioned IOPS for read replicas. If null, the replica will use the same value as the primary, which is set in iops.
nullThe type of storage to use for read replicas. If null, the replica will use the same value as the primary, which is set in storage_type.
nullHow many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means disable automated backups.
0restore_to_point_in_timemap(object(…))A configuration block for restoring a DB instance to an arbitrary point in time. Refer to https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance#restore-to-point-in-time for more details
map(object({
restore_time = string
source_db_instance_identifier = string
source_db_instance_automated_backups_arn = string
source_dbi_resource_id = string
use_latest_restorable_time = string
}))
nullDetermines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data!
falsesnapshot_identifierstringIf non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID. This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g: rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
nullSpecifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
truestorage_throughputstringThe storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage value is below a per-engine threshold. See the RDS User Guide: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_Storage.html#gp3-storage
nullstorage_typestringThe type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose SSD), 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD), or 'io2' (2nd gen provisioned IOPS SSD). AWS recommends 'gp3' for most workloads as it provides a baseline of 3,000 IOPS and 125 MiB/s at a lower cost than gp2, with the ability to provision up to 64,000 IOPS independently of storage size.
"gp2"timezonestringTime zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL User Guide (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone) for more information.
nullupdating_timeoutstringTimeout for DB updating
"80m"