Amazon EKS Core Services
Overview
This service contains Terraform and Helm code to deploy core administrative services, such as FluentD and the ALB Ingress Controller, onto Elastic Kubernetes Service(EKS).
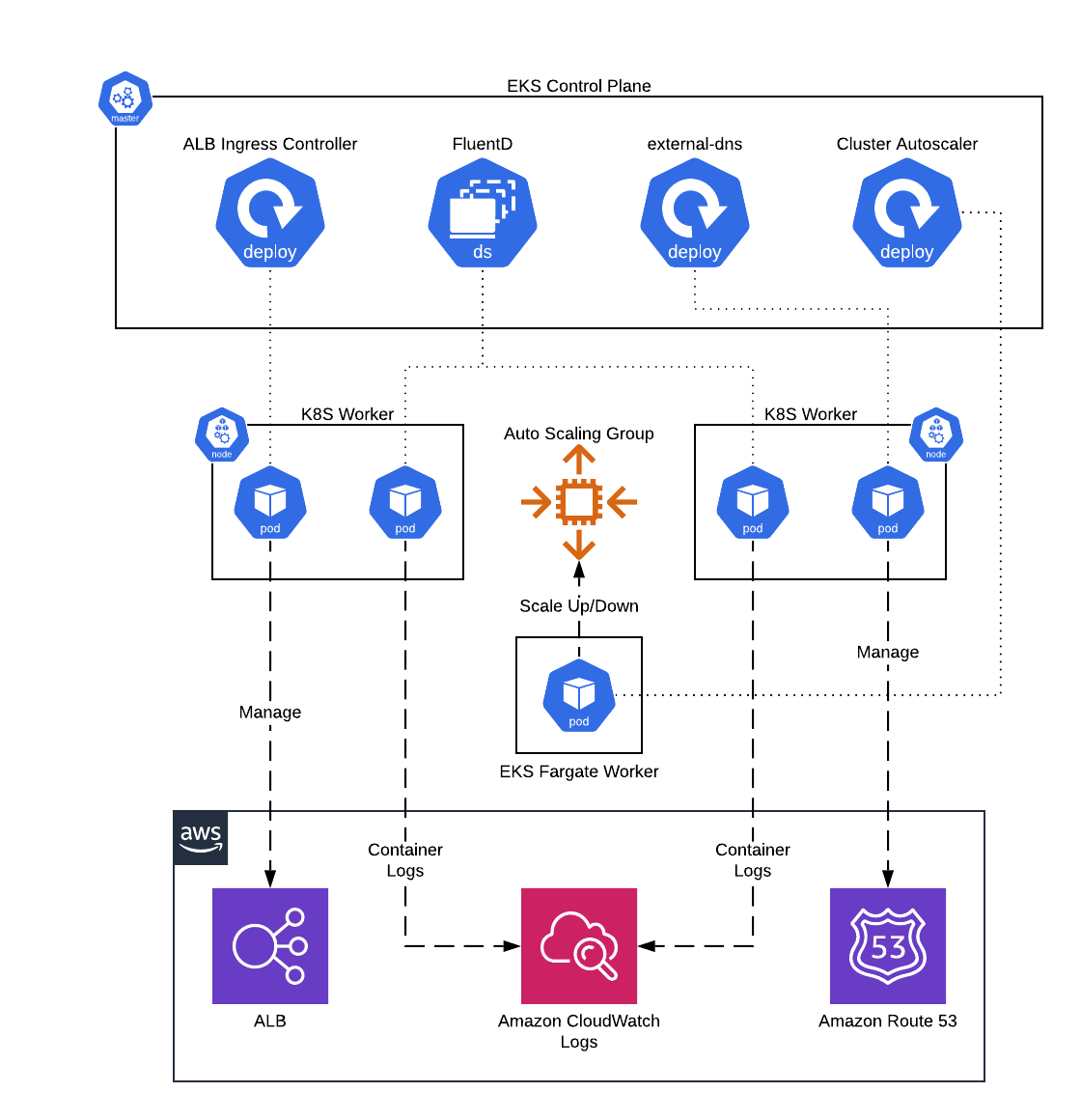 EKS Core Services architecture
EKS Core Services architecture
Features
- Deploy FluentD DaemonSet to ship container logs to CloudWatch Logs
- Deploy ALB Ingress Controller to configure ALBs from within Kubernetes
- Deploy external-dns to manage Route 53 DNS records from within Kubernetes
- Deploy Kubernetes cluster-autoscaler to configure auto scaling of ASGs based on Pod demand
- Deploy AWS CloudWatch Agent to configure container and node level metrics from worker nodes
Learn
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
Under the hood, this is all implemented using Terraform modules from the Gruntwork terraform-aws-eks repo. If you are a subscriber and don’t have access to this repo, email support@gruntwork.io.
Core concepts
For information on each of the core services deployed by this service, see the documentation in the terraform-aws-eks repo.
Repo organization
- modules: the main implementation code for this repo, broken down into multiple standalone, orthogonal submodules.
- examples: This folder contains working examples of how to use the submodules.
- test: Automated tests for the modules and examples.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
-
examples/for-production folder: The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog. -
How to deploy a production-grade Kubernetes cluster on AWS: A step-by-step guide for deploying a production-grade EKS cluster on AWS using the code in this repo.
Sample Usage
- Terraform
- Terragrunt
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S EKS-CORE-SERVICES MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
module "eks_core_services" {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/services/eks-core-services?ref=v1.3.0"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The AWS region in which all resources will be created
aws_region = <string>
# The name of the EKS cluster where the core services will be deployed into.
eks_cluster_name = <string>
# Configuration for using the IAM role with Service Accounts feature to
# provide permissions to the applications. This expects a map with two
# properties: `openid_connect_provider_arn` and `openid_connect_provider_url`.
# The `openid_connect_provider_arn` is the ARN of the OpenID Connect Provider
# for EKS to retrieve IAM credentials, while `openid_connect_provider_url` is
# the URL. Set to null if you do not wish to use IAM role with Service
# Accounts.
eks_iam_role_for_service_accounts_config = <object(
openid_connect_provider_arn = string
openid_connect_provider_url = string
)>
# ARN of IAM Role to use as the Pod execution role for Fargate. Required if
# any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate. Set to null if none of
# the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
pod_execution_iam_role_arn = <string>
# The ID of the VPC where the EKS cluster is deployed.
vpc_id = <string>
# The subnet IDs to use for EKS worker nodes. Used when provisioning Pods on
# to Fargate. Required if any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate.
# Set to empty list if none of the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
worker_vpc_subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ARN of IAM Role to assume to create and control ALB's. This is useful if
# your VPC is shared from another account and needs to be created somewhere
# else.
alb_ingress_controller_alb_iam_role_arn = null
# The version of the aws-load-balancer-controller helmchart to use.
alb_ingress_controller_chart_version = "1.4.1"
# Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this controller
alb_ingress_controller_default_tags = {}
# The repository of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should
# be deployed.
alb_ingress_controller_docker_image_repo = "602401143452.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/amazon/aws-load-balancer-controller"
# The tag of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should be
# deployed.
alb_ingress_controller_docker_image_tag = "v2.4.1"
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile IAM
# Execution Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag
# value.
alb_ingress_controller_eks_fargate_profile_execution_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_eks_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Policies if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_iam_role_tags = {}
# Configure affinity rules for the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
alb_ingress_controller_pod_node_affinity = []
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to
# schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
alb_ingress_controller_pod_tolerations = []
# Minimum time to wait after a scale up event before any node is considered
# for scale down.
autoscaler_down_delay_after_add = "10m"
# ARN of permissions boundary to apply to the autoscaler IAM role - the IAM
# role created for the Autoscaler
autoscaler_iam_role_permissions_boundary = null
# Number for the log level verbosity. Lower numbers are less verbose, higher
# numbers are more verbose. (Default: 4)
autoscaler_log_level_verbosity = 4
# Minimum time to wait since the node became unused before the node is
# considered for scale down by the autoscaler.
autoscaler_scale_down_unneeded_time = "10m"
# If true cluster autoscaler will never delete nodes with pods with local
# storage, e.g. EmptyDir or HostPath
autoscaler_skip_nodes_with_local_storage = true
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Agent IAM Role if enabled. The key is
# the tag name and the value is the tag value.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_iam_role_tags = {}
# The Container repository to use for looking up the cloudwatch-agent
# Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default
# repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_image_repository = null
# Configure affinity rules for the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_node_affinity = []
# Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
# for more information.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_resources = null
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pods to
# schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_tolerations = []
# Which version of amazon/cloudwatch-agent to install. When null, uses the
# default version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_version = null
# The name of the aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart to fetch from the repository.
# This should always be aws-for-fluent-bit unless fetching from a different
# repository.
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# The Kubernetes namespace to install the Helm chart to.
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_namespace = "kube-system"
# The version of the aws-for-fluent-bit helm chart to deploy. Note that this
# is different from the app/container version (use
# var.aws_for_fluent_bit_version to control the app/container version).
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_version = "0.1.34"
# The Helm Release Name to create when installing the chart to the cluster.
aws_for_fluent_bit_release_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# Restrict the cluster autoscaler to a list of absolute ASG ARNs upon initial
# apply to ensure no new ASGs can be managed by the autoscaler without
# explicitly running another apply. Setting this to false will ensure that the
# cluster autoscaler is automatically given access to manage any new ASGs with
# the k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/CLUSTER_NAME tag applied.
cluster_autoscaler_absolute_arns = true
# The version of the cluster-autoscaler helm chart to deploy. Note that this
# is different from the app/container version, which is sepecified with
# var.cluster_autoscaler_version.
cluster_autoscaler_chart_version = "9.46.6"
# Map of extra arguments to pass to the container.
cluster_autoscaler_container_extra_args = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile IAM Role if
# enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_fargate_profile_iam_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Policies if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_iam_role_tags = {}
# Annotations to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_annotations = {}
# Labels to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_labels = {}
# Configure affinity rules for the cluster-autoscaler Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_node_affinity = []
# Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
# for more information. This is most useful for configuring CPU+Memory
# availability for Fargate, which defaults to 0.25 vCPU and 256MB RAM.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_resources = {"limits":{"cpu":"250m","memory":"1024Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"250m","memory":"1024Mi"}}
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the cluster-autoscaler Pod to schedule
# on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_tolerations = []
# The name to use for the helm release for cluster-autoscaler. This is useful
# to force a redeployment of the cluster-autoscaler component.
cluster_autoscaler_release_name = "cluster-autoscaler"
# Which docker repository to use to install the cluster autoscaler. Check the
# following link for valid repositories to use
# https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/releases
cluster_autoscaler_repository = "registry.k8s.io/autoscaling/cluster-autoscaler"
# ARN of IAM Role to use for the Cluster Autoscaler. Only used when
# var.create_cluster_autoscaler_role is false.
cluster_autoscaler_role_arn = null
# Specifies an 'expander' for the cluster autoscaler. This helps determine
# which ASG to scale when additional resource capacity is needed.
cluster_autoscaler_scaling_strategy = "least-waste"
# The name of the service account to create for the cluster autoscaler.
cluster_autoscaler_service_account_name = "cluster-autoscaler-aws-cluster-autoscaler"
# Which version of the cluster autoscaler to install. This should match the
# major/minor version (e.g., v1.20) of your Kubernetes Installation. See
# https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler#releases
# for a list of versions.
cluster_autoscaler_version = "v1.33.0"
# When set to true, create a new dedicated IAM Role for the cluster
# autoscaler. When set to true, var.iam_role_for_service_accounts_config is
# required.
create_cluster_autoscaler_role = true
# Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this module.
default_tags = {}
# Whether or not to enable the AWS LB Ingress controller.
enable_alb_ingress_controller = true
# Whether to enable the AWS CloudWatch Agent DaemonSet for collecting
# container and node metrics from worker nodes (self-managed ASG or managed
# node groups).
enable_aws_cloudwatch_agent = true
# Whether or not to enable cluster-autoscaler for Autoscaling EKS worker
# nodes.
enable_cluster_autoscaler = true
# Whether or not to enable external-dns for DNS entry syncing with Route 53
# for Services and Ingresses.
enable_external_dns = true
# Whether or not to enable fluent-bit on EKS Fargate workers for log
# aggregation.
enable_fargate_fluent_bit = true
# Whether or not to enable fluent-bit for log aggregation.
enable_fluent_bit = true
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the interval between making changes to
# Route 53 by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart
# (1s).
external_dns_batch_change_interval = null
# The maximum number of changes that should be applied in a batch by
# external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (1000).
external_dns_batch_change_size = null
# Name of the Helm chart for external-dns. This should usually be
# 'external-dns' but may differ in the case of overriding the repository URL.
external_dns_chart_name = "external-dns"
# Helm chart repository URL to obtain the external-dns chart from. Useful when
# using Bitnami charts that are older than 6 months due to Bitnami's lifecycle
# policy which removes older chart from the main index.
external_dns_chart_repository_url = "https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami"
# The version of the helm chart to use. Note that this is different from the
# app/container version.
external_dns_chart_version = "6.12.2"
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile IAM Role
# if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_fargate_profile_iam_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile if
# enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Policies if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Role if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_iam_role_tags = {}
# The registry to use for the external-dns image.
external_dns_image_registry = null
# The container image repository to pull the images from. This allows
# overriding the default image repository for external-dns. For example,
# bitnamilegacy/external-dns.
external_dns_image_repository = "bitnamilegacy/external-dns"
# Configure affinity rules for the external-dns Pod to control which nodes to
# schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys `key`,
# `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
external_dns_pod_node_affinity = []
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the external-dns Pod to schedule on
# nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration
# rule.
external_dns_pod_tolerations = []
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the polling interval for syncing the
# domains by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart
# (1m).
external_dns_poll_interval = null
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided domain names.
# Empty list (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three
# constraints (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters = []
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided IDs. Empty list
# (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints
# (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters = []
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided tags. Each item
# in the list should specify tag key and tag value as a map. Empty list
# (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints
# (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters = []
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the amount of time the Hosted Zones are
# cached in external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (0 -
# no caching).
external_dns_route53_zones_cache_duration = null
# K8s resources type to be observed for new DNS entries by ExternalDNS.
external_dns_sources = ["ingress","service"]
# When enabled, triggers external-dns run loop on create/update/delete events
# (optional, in addition of regular interval)
external_dns_trigger_loop_on_event = false
# List of ARNs of Fargate execution IAM Roles that should get permissions to
# ship logs using fluent-bit. This must be provided if
# enable_fargate_fluent_bit is true.
fargate_fluent_bit_execution_iam_role_arns = []
# Additional filters that fluent-bit should apply to log output. This string
# should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_filter).
fargate_fluent_bit_extra_filters = ""
# Additional parsers that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string should
# be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
fargate_fluent_bit_extra_parsers = ""
# A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the Fargate
# Execution IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the
# tag value.
fargate_fluent_bit_iam_policy_tags = {}
# Whether or not Kubernetes metadata is added to the log files
fargate_fluent_bit_include_kubernetes_metadata = true
# Prefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for
# each Fargate pod.
fargate_fluent_bit_log_stream_prefix = "fargate"
# A list of availability zones in the region that we CANNOT use to deploy the
# EKS Fargate workers. You can use this to avoid availability zones that may
# not be able to provision the resources (e.g ran out of capacity). If empty,
# will allow all availability zones.
fargate_worker_disallowed_availability_zones = ["us-east-1d","us-east-1e","ca-central-1d"]
# Can be used to add additional filter configuration blocks. This string
# should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected
# directly into the fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_additional_filters = ""
# Can be used to add more inputs. This string should be formatted according to
# Fluent Bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/classic-mode/configuration-file#config_input).
fluent_bit_additional_inputs = ""
# Can be used to add additional outputs with this value.
fluent_bit_additional_outputs = ""
# Configurations for forwarding logs to AWS managed Elasticsearch. Set to null
# if you do not wish to forward the logs to ES.
fluent_bit_aws_elasticsearch_configuration = null
# Configurations for forwarding logs to CloudWatch Logs using a higher
# performance plugin. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to
# CloudWatch Logs using this plugin. This plugin is enabled by default in
# fluent-bit.
fluent_bit_cloudwatch_logs_configuration = {"autoCreateGroup":null,"autoRetryRequests":null,"enabled":true,"endpoint":null,"externalId":null,"extraOutputs":null,"logFormat":null,"logGroupName":"/aws/eks/fluentbit-cloudwatch/logs","logGroupTemplate":null,"logKey":null,"logRetentionDays":null,"logStreamName":null,"logStreamPrefix":"fluentbit-","logStreamTemplate":null,"match":"*","metricDimensions":null,"metricNamespace":null,"region":"us-east-1","roleArn":null,"stsEndpoint":null}
# Configurations for adjusting the default filter settings. Set to null if you
# do not wish to use the default filter.
fluent_bit_default_filter_configuration = {"bufferSize":"32k","enabled":true,"extraFilters":null,"k8sLoggingExclude":"On","k8sLoggingParser":"On","keepLog":"On","kubeURL":"https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local:443","match":"kube.*","mergeLog":"On","mergeLogKey":"data"}
# Configurations for adjusting the default input settings. Set to null if you
# do not wish to use the default filter.
fluent_bit_default_input_configuration = {"db":"/var/log/flb_kube.db","dockerMode":"On","enabled":true,"memBufLimit":"5MB","parser":"docker","path":"/var/log/containers/*.log","refreshInterval":"10","skipLongLines":"On","tag":"kube.*"}
# Can be used to provide additional kubernetes plugin configuration parameters
# for the default kubernetes filter that is pre-configured in the
# aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart. This string should be formatted according to
# Fluent Bit docs, as it will append to the default kubernetes filter
# configuration.
fluent_bit_extra_filters = ""
# Can be used to append to existing input. This string should be formatted
# according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the
# fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_extra_inputs = ""
# Additional output streams that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string
# should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
fluent_bit_extra_outputs = ""
# Can be used to add additional log parsers. This string should be formatted
# according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the
# fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_extra_parsers = ""
# Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis Firehose. Set to null if you
# do not wish to forward the logs to Firehose.
fluent_bit_firehose_configuration = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the fluentbit
# IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
fluent_bit_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the fluentbit IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
fluent_bit_iam_role_tags = {}
# Pull policy for the image. When null, uses the default setting
# `IfNotPresent` set in the chart.
fluent_bit_image_pull_policy = null
# The Container repository to use for looking up the aws-for-fluent-bit
# Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default
# repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
fluent_bit_image_repository = null
# Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis stream. Set to null if you do
# not wish to forward the logs to Kinesis.
fluent_bit_kinesis_configuration = null
fluent_bit_kinesis_streams_configuration = null
# If set to true, that means that the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should
# use for streaming logs already exists and does not need to be created.
fluent_bit_log_group_already_exists = false
# The ARN of the KMS key to use to encrypt the logs in the CloudWatch Log
# Group used for storing container logs streamed with FluentBit. Set to null
# to disable encryption.
fluent_bit_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# Name of the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should use to stream logs to.
# When null (default), uses the eks_cluster_name as the Log Group name.
fluent_bit_log_group_name = null
# number of days to retain log events. Possible values are: 1, 3, 5, 7, 14,
# 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 365, 400, 545, 731, 1827, 3653, and 0. Select 0
# to never expire.
fluent_bit_log_group_retention = 0
# ARN of the lambda function to trigger when events arrive at the fluent bit
# log group.
fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_arn = null
# Filter pattern for the CloudWatch subscription. Only used if
# var.fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_arn is set.
fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_filter = ""
# Prefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for
# each pod. When null (default), the prefix is set to 'fluentbit'.
fluent_bit_log_stream_prefix = null
# Node selector constraints for scheduling pods.
fluent_bit_node_selector = null
fluent_bit_opensearch_configuration = null
# Pod annotations to apply to the deployment.
fluent_bit_pod_annotations = null
# Configure affinity rules for the fluent-bit Pods to control which nodes to
# schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys `key`,
# `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
fluent_bit_pod_node_affinity = []
# Specify the resource limits and requests for the fluent-bit pods. Set to
# null (default) to use chart defaults.
fluent_bit_pod_resources = null
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the fluent-bit Pods to schedule on
# nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration
# rule.
fluent_bit_pod_tolerations = []
# Create a restricted pod security policy.
fluent_bit_rbac_psp_enabled = false
fluent_bit_s3_configuration = null
# Merge and mask sensitive values like apikeys or passwords that are part of
# the helm charts `values.yaml`. These sensitive values will show up in the
# final metadata as clear text unless passed in as K:V pairs that are injected
# into the `values.yaml`. Key should be the paramater path and value should be
# the value.
fluent_bit_sensitive_values = {}
# Annotations to apply to the Service Account. If
# `iam_role_for_service_accounts_config` is provided, then this module will
# automatically add the annotation `eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn = <IAM Role
# ARN> to the Service Account to leverage IRSA. Annotations provided by this
# variable will be merged with the module applied Annotations.
fluent_bit_service_account_annotations = {}
# Whether a new service account should be created.
fluent_bit_service_account_create = true
# Name of the service account.
fluent_bit_service_account_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# Optional update strategy for the Kubernetes Deployment.
fluent_bit_update_strategy_type = "RollingUpdate"
# Optionally use a cri parser instead of the default Docker parser. This
# should be used for EKS v1.24 and later.
fluent_bit_use_cri_parser_conf = true
# Which version of aws-for-fluent-bit to install. When null, uses the default
# version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
fluent_bit_version = null
# A map of PriorityClass configurations, with the key as the PriorityClass
# name.
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
kubernetes_priority_classes = {}
# Policy for how DNS records are sychronized between sources and providers
# (options: sync, upsert-only).
route53_record_update_policy = "sync"
# When true, the ALB ingress controller pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
schedule_alb_ingress_controller_on_fargate = false
# When true, the cluster autoscaler pods will be scheduled on Fargate. It is
# recommended to run the cluster autoscaler on Fargate to avoid the autoscaler
# scaling down a node where it is running (and thus shutting itself down
# during a scale down event). However, since Fargate is only supported on a
# handful of regions, we don't default to true here.
schedule_cluster_autoscaler_on_fargate = false
# When true, the external-dns pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
schedule_external_dns_on_fargate = false
# Configure Kubernetes Services to lookup external DNS records. This can be
# useful to bind friendly internal service names to domains (e.g. the RDS
# database endpoint).
service_dns_mappings = {}
# If this variable is set to true, then use an exec-based plugin to
# authenticate and fetch tokens for EKS. This is useful because EKS clusters
# use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the middle of an
# 'apply' or 'destroy', and since the native Kubernetes provider in Terraform
# doesn't have a way to fetch up-to-date tokens, we recommend using an
# exec-based provider as a workaround. Use the use_kubergrunt_to_fetch_token
# input variable to control whether kubergrunt or aws is used to fetch tokens.
use_exec_plugin_for_auth = true
# EKS clusters use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the
# middle of an 'apply' or 'destroy'. To avoid this issue, we use an exec-based
# plugin to fetch an up-to-date token. If this variable is set to true, we'll
# use kubergrunt to fetch the token (in which case, kubergrunt must be
# installed and on PATH); if this variable is set to false, we'll use the aws
# CLI to fetch the token (in which case, aws must be installed and on PATH).
# Note this functionality is only enabled if use_exec_plugin_for_auth is set
# to true.
use_kubergrunt_to_fetch_token = true
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S EKS-CORE-SERVICES MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
terraform {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/services/eks-core-services?ref=v1.3.0"
}
inputs = {
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The AWS region in which all resources will be created
aws_region = <string>
# The name of the EKS cluster where the core services will be deployed into.
eks_cluster_name = <string>
# Configuration for using the IAM role with Service Accounts feature to
# provide permissions to the applications. This expects a map with two
# properties: `openid_connect_provider_arn` and `openid_connect_provider_url`.
# The `openid_connect_provider_arn` is the ARN of the OpenID Connect Provider
# for EKS to retrieve IAM credentials, while `openid_connect_provider_url` is
# the URL. Set to null if you do not wish to use IAM role with Service
# Accounts.
eks_iam_role_for_service_accounts_config = <object(
openid_connect_provider_arn = string
openid_connect_provider_url = string
)>
# ARN of IAM Role to use as the Pod execution role for Fargate. Required if
# any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate. Set to null if none of
# the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
pod_execution_iam_role_arn = <string>
# The ID of the VPC where the EKS cluster is deployed.
vpc_id = <string>
# The subnet IDs to use for EKS worker nodes. Used when provisioning Pods on
# to Fargate. Required if any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate.
# Set to empty list if none of the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
worker_vpc_subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ARN of IAM Role to assume to create and control ALB's. This is useful if
# your VPC is shared from another account and needs to be created somewhere
# else.
alb_ingress_controller_alb_iam_role_arn = null
# The version of the aws-load-balancer-controller helmchart to use.
alb_ingress_controller_chart_version = "1.4.1"
# Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this controller
alb_ingress_controller_default_tags = {}
# The repository of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should
# be deployed.
alb_ingress_controller_docker_image_repo = "602401143452.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/amazon/aws-load-balancer-controller"
# The tag of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should be
# deployed.
alb_ingress_controller_docker_image_tag = "v2.4.1"
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile IAM
# Execution Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag
# value.
alb_ingress_controller_eks_fargate_profile_execution_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_eks_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Policies if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
alb_ingress_controller_iam_role_tags = {}
# Configure affinity rules for the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
alb_ingress_controller_pod_node_affinity = []
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to
# schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
alb_ingress_controller_pod_tolerations = []
# Minimum time to wait after a scale up event before any node is considered
# for scale down.
autoscaler_down_delay_after_add = "10m"
# ARN of permissions boundary to apply to the autoscaler IAM role - the IAM
# role created for the Autoscaler
autoscaler_iam_role_permissions_boundary = null
# Number for the log level verbosity. Lower numbers are less verbose, higher
# numbers are more verbose. (Default: 4)
autoscaler_log_level_verbosity = 4
# Minimum time to wait since the node became unused before the node is
# considered for scale down by the autoscaler.
autoscaler_scale_down_unneeded_time = "10m"
# If true cluster autoscaler will never delete nodes with pods with local
# storage, e.g. EmptyDir or HostPath
autoscaler_skip_nodes_with_local_storage = true
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Agent IAM Role if enabled. The key is
# the tag name and the value is the tag value.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_iam_role_tags = {}
# The Container repository to use for looking up the cloudwatch-agent
# Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default
# repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_image_repository = null
# Configure affinity rules for the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_node_affinity = []
# Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
# for more information.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_resources = null
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pods to
# schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_tolerations = []
# Which version of amazon/cloudwatch-agent to install. When null, uses the
# default version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
aws_cloudwatch_agent_version = null
# The name of the aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart to fetch from the repository.
# This should always be aws-for-fluent-bit unless fetching from a different
# repository.
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# The Kubernetes namespace to install the Helm chart to.
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_namespace = "kube-system"
# The version of the aws-for-fluent-bit helm chart to deploy. Note that this
# is different from the app/container version (use
# var.aws_for_fluent_bit_version to control the app/container version).
aws_for_fluent_bit_chart_version = "0.1.34"
# The Helm Release Name to create when installing the chart to the cluster.
aws_for_fluent_bit_release_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# Restrict the cluster autoscaler to a list of absolute ASG ARNs upon initial
# apply to ensure no new ASGs can be managed by the autoscaler without
# explicitly running another apply. Setting this to false will ensure that the
# cluster autoscaler is automatically given access to manage any new ASGs with
# the k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/CLUSTER_NAME tag applied.
cluster_autoscaler_absolute_arns = true
# The version of the cluster-autoscaler helm chart to deploy. Note that this
# is different from the app/container version, which is sepecified with
# var.cluster_autoscaler_version.
cluster_autoscaler_chart_version = "9.46.6"
# Map of extra arguments to pass to the container.
cluster_autoscaler_container_extra_args = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile IAM Role if
# enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_fargate_profile_iam_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Policies if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
cluster_autoscaler_iam_role_tags = {}
# Annotations to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_annotations = {}
# Labels to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_labels = {}
# Configure affinity rules for the cluster-autoscaler Pod to control which
# nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys
# `key`, `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_node_affinity = []
# Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
# for more information. This is most useful for configuring CPU+Memory
# availability for Fargate, which defaults to 0.25 vCPU and 256MB RAM.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_resources = {"limits":{"cpu":"250m","memory":"1024Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"250m","memory":"1024Mi"}}
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the cluster-autoscaler Pod to schedule
# on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a
# toleration rule.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_tolerations = []
# The name to use for the helm release for cluster-autoscaler. This is useful
# to force a redeployment of the cluster-autoscaler component.
cluster_autoscaler_release_name = "cluster-autoscaler"
# Which docker repository to use to install the cluster autoscaler. Check the
# following link for valid repositories to use
# https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/releases
cluster_autoscaler_repository = "registry.k8s.io/autoscaling/cluster-autoscaler"
# ARN of IAM Role to use for the Cluster Autoscaler. Only used when
# var.create_cluster_autoscaler_role is false.
cluster_autoscaler_role_arn = null
# Specifies an 'expander' for the cluster autoscaler. This helps determine
# which ASG to scale when additional resource capacity is needed.
cluster_autoscaler_scaling_strategy = "least-waste"
# The name of the service account to create for the cluster autoscaler.
cluster_autoscaler_service_account_name = "cluster-autoscaler-aws-cluster-autoscaler"
# Which version of the cluster autoscaler to install. This should match the
# major/minor version (e.g., v1.20) of your Kubernetes Installation. See
# https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler#releases
# for a list of versions.
cluster_autoscaler_version = "v1.33.0"
# When set to true, create a new dedicated IAM Role for the cluster
# autoscaler. When set to true, var.iam_role_for_service_accounts_config is
# required.
create_cluster_autoscaler_role = true
# Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this module.
default_tags = {}
# Whether or not to enable the AWS LB Ingress controller.
enable_alb_ingress_controller = true
# Whether to enable the AWS CloudWatch Agent DaemonSet for collecting
# container and node metrics from worker nodes (self-managed ASG or managed
# node groups).
enable_aws_cloudwatch_agent = true
# Whether or not to enable cluster-autoscaler for Autoscaling EKS worker
# nodes.
enable_cluster_autoscaler = true
# Whether or not to enable external-dns for DNS entry syncing with Route 53
# for Services and Ingresses.
enable_external_dns = true
# Whether or not to enable fluent-bit on EKS Fargate workers for log
# aggregation.
enable_fargate_fluent_bit = true
# Whether or not to enable fluent-bit for log aggregation.
enable_fluent_bit = true
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the interval between making changes to
# Route 53 by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart
# (1s).
external_dns_batch_change_interval = null
# The maximum number of changes that should be applied in a batch by
# external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (1000).
external_dns_batch_change_size = null
# Name of the Helm chart for external-dns. This should usually be
# 'external-dns' but may differ in the case of overriding the repository URL.
external_dns_chart_name = "external-dns"
# Helm chart repository URL to obtain the external-dns chart from. Useful when
# using Bitnami charts that are older than 6 months due to Bitnami's lifecycle
# policy which removes older chart from the main index.
external_dns_chart_repository_url = "https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami"
# The version of the helm chart to use. Note that this is different from the
# app/container version.
external_dns_chart_version = "6.12.2"
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile IAM Role
# if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_fargate_profile_iam_role_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile if
# enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_fargate_profile_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Policies if enabled.
# The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Role if enabled. The
# key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
external_dns_iam_role_tags = {}
# The registry to use for the external-dns image.
external_dns_image_registry = null
# The container image repository to pull the images from. This allows
# overriding the default image repository for external-dns. For example,
# bitnamilegacy/external-dns.
external_dns_image_repository = "bitnamilegacy/external-dns"
# Configure affinity rules for the external-dns Pod to control which nodes to
# schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys `key`,
# `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
external_dns_pod_node_affinity = []
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the external-dns Pod to schedule on
# nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration
# rule.
external_dns_pod_tolerations = []
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the polling interval for syncing the
# domains by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart
# (1m).
external_dns_poll_interval = null
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided domain names.
# Empty list (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three
# constraints (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters = []
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided IDs. Empty list
# (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints
# (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters = []
# Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided tags. Each item
# in the list should specify tag key and tag value as a map. Empty list
# (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints
# (var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters,
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and
# var.external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters = []
# Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the amount of time the Hosted Zones are
# cached in external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (0 -
# no caching).
external_dns_route53_zones_cache_duration = null
# K8s resources type to be observed for new DNS entries by ExternalDNS.
external_dns_sources = ["ingress","service"]
# When enabled, triggers external-dns run loop on create/update/delete events
# (optional, in addition of regular interval)
external_dns_trigger_loop_on_event = false
# List of ARNs of Fargate execution IAM Roles that should get permissions to
# ship logs using fluent-bit. This must be provided if
# enable_fargate_fluent_bit is true.
fargate_fluent_bit_execution_iam_role_arns = []
# Additional filters that fluent-bit should apply to log output. This string
# should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_filter).
fargate_fluent_bit_extra_filters = ""
# Additional parsers that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string should
# be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
fargate_fluent_bit_extra_parsers = ""
# A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the Fargate
# Execution IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the
# tag value.
fargate_fluent_bit_iam_policy_tags = {}
# Whether or not Kubernetes metadata is added to the log files
fargate_fluent_bit_include_kubernetes_metadata = true
# Prefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for
# each Fargate pod.
fargate_fluent_bit_log_stream_prefix = "fargate"
# A list of availability zones in the region that we CANNOT use to deploy the
# EKS Fargate workers. You can use this to avoid availability zones that may
# not be able to provision the resources (e.g ran out of capacity). If empty,
# will allow all availability zones.
fargate_worker_disallowed_availability_zones = ["us-east-1d","us-east-1e","ca-central-1d"]
# Can be used to add additional filter configuration blocks. This string
# should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected
# directly into the fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_additional_filters = ""
# Can be used to add more inputs. This string should be formatted according to
# Fluent Bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/classic-mode/configuration-file#config_input).
fluent_bit_additional_inputs = ""
# Can be used to add additional outputs with this value.
fluent_bit_additional_outputs = ""
# Configurations for forwarding logs to AWS managed Elasticsearch. Set to null
# if you do not wish to forward the logs to ES.
fluent_bit_aws_elasticsearch_configuration = null
# Configurations for forwarding logs to CloudWatch Logs using a higher
# performance plugin. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to
# CloudWatch Logs using this plugin. This plugin is enabled by default in
# fluent-bit.
fluent_bit_cloudwatch_logs_configuration = {"autoCreateGroup":null,"autoRetryRequests":null,"enabled":true,"endpoint":null,"externalId":null,"extraOutputs":null,"logFormat":null,"logGroupName":"/aws/eks/fluentbit-cloudwatch/logs","logGroupTemplate":null,"logKey":null,"logRetentionDays":null,"logStreamName":null,"logStreamPrefix":"fluentbit-","logStreamTemplate":null,"match":"*","metricDimensions":null,"metricNamespace":null,"region":"us-east-1","roleArn":null,"stsEndpoint":null}
# Configurations for adjusting the default filter settings. Set to null if you
# do not wish to use the default filter.
fluent_bit_default_filter_configuration = {"bufferSize":"32k","enabled":true,"extraFilters":null,"k8sLoggingExclude":"On","k8sLoggingParser":"On","keepLog":"On","kubeURL":"https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local:443","match":"kube.*","mergeLog":"On","mergeLogKey":"data"}
# Configurations for adjusting the default input settings. Set to null if you
# do not wish to use the default filter.
fluent_bit_default_input_configuration = {"db":"/var/log/flb_kube.db","dockerMode":"On","enabled":true,"memBufLimit":"5MB","parser":"docker","path":"/var/log/containers/*.log","refreshInterval":"10","skipLongLines":"On","tag":"kube.*"}
# Can be used to provide additional kubernetes plugin configuration parameters
# for the default kubernetes filter that is pre-configured in the
# aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart. This string should be formatted according to
# Fluent Bit docs, as it will append to the default kubernetes filter
# configuration.
fluent_bit_extra_filters = ""
# Can be used to append to existing input. This string should be formatted
# according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the
# fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_extra_inputs = ""
# Additional output streams that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string
# should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs
# (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
fluent_bit_extra_outputs = ""
# Can be used to add additional log parsers. This string should be formatted
# according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the
# fluent-bit.conf file.
fluent_bit_extra_parsers = ""
# Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis Firehose. Set to null if you
# do not wish to forward the logs to Firehose.
fluent_bit_firehose_configuration = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the fluentbit
# IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
fluent_bit_iam_policy_tags = {}
# A map of custom tags to apply to the fluentbit IAM Role if enabled. The key
# is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
fluent_bit_iam_role_tags = {}
# Pull policy for the image. When null, uses the default setting
# `IfNotPresent` set in the chart.
fluent_bit_image_pull_policy = null
# The Container repository to use for looking up the aws-for-fluent-bit
# Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default
# repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
fluent_bit_image_repository = null
# Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis stream. Set to null if you do
# not wish to forward the logs to Kinesis.
fluent_bit_kinesis_configuration = null
fluent_bit_kinesis_streams_configuration = null
# If set to true, that means that the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should
# use for streaming logs already exists and does not need to be created.
fluent_bit_log_group_already_exists = false
# The ARN of the KMS key to use to encrypt the logs in the CloudWatch Log
# Group used for storing container logs streamed with FluentBit. Set to null
# to disable encryption.
fluent_bit_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# Name of the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should use to stream logs to.
# When null (default), uses the eks_cluster_name as the Log Group name.
fluent_bit_log_group_name = null
# number of days to retain log events. Possible values are: 1, 3, 5, 7, 14,
# 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 365, 400, 545, 731, 1827, 3653, and 0. Select 0
# to never expire.
fluent_bit_log_group_retention = 0
# ARN of the lambda function to trigger when events arrive at the fluent bit
# log group.
fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_arn = null
# Filter pattern for the CloudWatch subscription. Only used if
# var.fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_arn is set.
fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_filter = ""
# Prefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for
# each pod. When null (default), the prefix is set to 'fluentbit'.
fluent_bit_log_stream_prefix = null
# Node selector constraints for scheduling pods.
fluent_bit_node_selector = null
fluent_bit_opensearch_configuration = null
# Pod annotations to apply to the deployment.
fluent_bit_pod_annotations = null
# Configure affinity rules for the fluent-bit Pods to control which nodes to
# schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys `key`,
# `values`, and `operator`, corresponding to the 3 properties of
# matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on
# the node.
fluent_bit_pod_node_affinity = []
# Specify the resource limits and requests for the fluent-bit pods. Set to
# null (default) to use chart defaults.
fluent_bit_pod_resources = null
# Configure tolerations rules to allow the fluent-bit Pods to schedule on
# nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration
# rule.
fluent_bit_pod_tolerations = []
# Create a restricted pod security policy.
fluent_bit_rbac_psp_enabled = false
fluent_bit_s3_configuration = null
# Merge and mask sensitive values like apikeys or passwords that are part of
# the helm charts `values.yaml`. These sensitive values will show up in the
# final metadata as clear text unless passed in as K:V pairs that are injected
# into the `values.yaml`. Key should be the paramater path and value should be
# the value.
fluent_bit_sensitive_values = {}
# Annotations to apply to the Service Account. If
# `iam_role_for_service_accounts_config` is provided, then this module will
# automatically add the annotation `eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn = <IAM Role
# ARN> to the Service Account to leverage IRSA. Annotations provided by this
# variable will be merged with the module applied Annotations.
fluent_bit_service_account_annotations = {}
# Whether a new service account should be created.
fluent_bit_service_account_create = true
# Name of the service account.
fluent_bit_service_account_name = "aws-for-fluent-bit"
# Optional update strategy for the Kubernetes Deployment.
fluent_bit_update_strategy_type = "RollingUpdate"
# Optionally use a cri parser instead of the default Docker parser. This
# should be used for EKS v1.24 and later.
fluent_bit_use_cri_parser_conf = true
# Which version of aws-for-fluent-bit to install. When null, uses the default
# version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
fluent_bit_version = null
# A map of PriorityClass configurations, with the key as the PriorityClass
# name.
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
kubernetes_priority_classes = {}
# Policy for how DNS records are sychronized between sources and providers
# (options: sync, upsert-only).
route53_record_update_policy = "sync"
# When true, the ALB ingress controller pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
schedule_alb_ingress_controller_on_fargate = false
# When true, the cluster autoscaler pods will be scheduled on Fargate. It is
# recommended to run the cluster autoscaler on Fargate to avoid the autoscaler
# scaling down a node where it is running (and thus shutting itself down
# during a scale down event). However, since Fargate is only supported on a
# handful of regions, we don't default to true here.
schedule_cluster_autoscaler_on_fargate = false
# When true, the external-dns pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
schedule_external_dns_on_fargate = false
# Configure Kubernetes Services to lookup external DNS records. This can be
# useful to bind friendly internal service names to domains (e.g. the RDS
# database endpoint).
service_dns_mappings = {}
# If this variable is set to true, then use an exec-based plugin to
# authenticate and fetch tokens for EKS. This is useful because EKS clusters
# use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the middle of an
# 'apply' or 'destroy', and since the native Kubernetes provider in Terraform
# doesn't have a way to fetch up-to-date tokens, we recommend using an
# exec-based provider as a workaround. Use the use_kubergrunt_to_fetch_token
# input variable to control whether kubergrunt or aws is used to fetch tokens.
use_exec_plugin_for_auth = true
# EKS clusters use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the
# middle of an 'apply' or 'destroy'. To avoid this issue, we use an exec-based
# plugin to fetch an up-to-date token. If this variable is set to true, we'll
# use kubergrunt to fetch the token (in which case, kubergrunt must be
# installed and on PATH); if this variable is set to false, we'll use the aws
# CLI to fetch the token (in which case, aws must be installed and on PATH).
# Note this functionality is only enabled if use_exec_plugin_for_auth is set
# to true.
use_kubergrunt_to_fetch_token = true
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
}
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
aws_regionstringThe AWS region in which all resources will be created
eks_cluster_namestringThe name of the EKS cluster where the core services will be deployed into.
Configuration for using the IAM role with Service Accounts feature to provide permissions to the applications. This expects a map with two properties: openid_connect_provider_arn and openid_connect_provider_url. The openid_connect_provider_arn is the ARN of the OpenID Connect Provider for EKS to retrieve IAM credentials, while openid_connect_provider_url is the URL. Set to null if you do not wish to use IAM role with Service Accounts.
object({
openid_connect_provider_arn = string
openid_connect_provider_url = string
})
ARN of IAM Role to use as the Pod execution role for Fargate. Required if any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate. Set to null if none of the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
vpc_idstringThe ID of the VPC where the EKS cluster is deployed.
worker_vpc_subnet_idslist(string)The subnet IDs to use for EKS worker nodes. Used when provisioning Pods on to Fargate. Required if any of the services are being scheduled on Fargate. Set to empty list if none of the Pods are being scheduled on Fargate.
Optional
ARN of IAM Role to assume to create and control ALB's. This is useful if your VPC is shared from another account and needs to be created somewhere else.
nullThe version of the aws-load-balancer-controller helmchart to use.
"1.4.1"alb_ingress_controller_default_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this controller
{}The repository of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should be deployed.
"602401143452.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/amazon/aws-load-balancer-controller"The tag of the aws-load-balancer-controller docker image that should be deployed.
"v2.4.1"A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile IAM Execution Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller Fargate Profile if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}alb_ingress_controller_iam_policy_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Policies if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}alb_ingress_controller_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Controller IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}alb_ingress_controller_pod_node_affinitylist(object(…))Configure affinity rules for the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to control which nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys key, values, and operator, corresponding to the 3 properties of matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on the node.
list(object({
key = string
values = list(string)
operator = string
}))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a matchExpression for requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/affinity-and-anti-affinity for the various
configuration option.
Example:
[
{
"key" = "node-label-key"
"values" = ["node-label-value", "another-node-label-value"]
"operator" = "In"
}
]
Translates to:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- node-label-value
- another-node-label-value
alb_ingress_controller_pod_tolerationslist(map(…))Configure tolerations rules to allow the ALB Ingress Controller Pod to schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration rule.
list(map(any))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a particular toleration. See
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/ for the various rules you can specify.
Example:
[
{
key = "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable"
operator = "Exists"
effect = "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds = 6000
}
]
Minimum time to wait after a scale up event before any node is considered for scale down.
"10m"ARN of permissions boundary to apply to the autoscaler IAM role - the IAM role created for the Autoscaler
nullNumber for the log level verbosity. Lower numbers are less verbose, higher numbers are more verbose. (Default: 4)
4Minimum time to wait since the node became unused before the node is considered for scale down by the autoscaler.
"10m"If true cluster autoscaler will never delete nodes with pods with local storage, e.g. EmptyDir or HostPath
trueaws_cloudwatch_agent_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Agent IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}The Container repository to use for looking up the cloudwatch-agent Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
nullaws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_node_affinitylist(object(…))Configure affinity rules for the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pod to control which nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys key, values, and operator, corresponding to the 3 properties of matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on the node.
list(object({
key = string
values = list(string)
operator = string
}))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a matchExpression for requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/affinity-and-anti-affinity for the various
configuration option.
Example:
[
{
"key" = "node-label-key"
"values" = ["node-label-value", "another-node-label-value"]
"operator" = "In"
}
]
Translates to:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- node-label-value
- another-node-label-value
Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/ for more information.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
nullDetails
We use any type here to avoid maintaining the kubernetes defined type spec for the resources here. That way, we can
support wide range of kubernetes versions.
Details
Example value:
{
requests = {
memory = "1024Mi"
cpu = "250m"
}
limits = {
memory = "1024Mi"
cpu = "250m"
}
}
aws_cloudwatch_agent_pod_tolerationslist(map(…))Configure tolerations rules to allow the AWS CloudWatch Agent Pods to schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration rule.
list(map(any))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a particular toleration. See
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/ for the various rules you can specify.
Example:
[
{
key = "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable"
operator = "Exists"
effect = "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds = 6000
}
]
Which version of amazon/cloudwatch-agent to install. When null, uses the default version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
nullThe name of the aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart to fetch from the repository. This should always be aws-for-fluent-bit unless fetching from a different repository.
"aws-for-fluent-bit"The Kubernetes namespace to install the Helm chart to.
"kube-system"The version of the aws-for-fluent-bit helm chart to deploy. Note that this is different from the app/container version (use aws_for_fluent_bit_version to control the app/container version).
"0.1.34"The Helm Release Name to create when installing the chart to the cluster.
"aws-for-fluent-bit"Restrict the cluster autoscaler to a list of absolute ASG ARNs upon initial apply to ensure no new ASGs can be managed by the autoscaler without explicitly running another apply. Setting this to false will ensure that the cluster autoscaler is automatically given access to manage any new ASGs with the k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/CLUSTER_NAME tag applied.
trueThe version of the cluster-autoscaler helm chart to deploy. Note that this is different from the app/container version, which is sepecified with cluster_autoscaler_version.
"9.46.6"cluster_autoscaler_container_extra_argsmap(string)Map of extra arguments to pass to the container.
{}A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}cluster_autoscaler_fargate_profile_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler Fargate Profile if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}cluster_autoscaler_iam_policy_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Policies if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}cluster_autoscaler_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the Autoscaler IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}cluster_autoscaler_pod_annotationsmap(string)Annotations to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
{}cluster_autoscaler_pod_labelsmap(string)Labels to apply to the cluster autoscaler pod(s), as key value pairs.
{}cluster_autoscaler_pod_node_affinitylist(object(…))Configure affinity rules for the cluster-autoscaler Pod to control which nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys key, values, and operator, corresponding to the 3 properties of matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on the node.
list(object({
key = string
values = list(string)
operator = string
}))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a matchExpression for requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/affinity-and-anti-affinity for the various
configuration option.
Example:
[
{
"key" = "node-label-key"
"values" = ["node-label-value", "another-node-label-value"]
"operator" = "In"
}
]
Translates to:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- node-label-value
- another-node-label-value
Pod resource requests and limits to use. Refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/ for more information. This is most useful for configuring CPU+Memory availability for Fargate, which defaults to 0.25 vCPU and 256MB RAM.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
{
limits = {
cpu = "250m",
memory = "1024Mi"
},
requests = {
cpu = "250m",
memory = "1024Mi"
}
}
Details
We use any type here to avoid maintaining the kubernetes defined type spec for the resources here. That way, we can
support wide range of kubernetes versions.
Details
cluster-autoscaler is known to fail on Fargate when the default resource limits are used, so we set a saner default
here.
cluster_autoscaler_pod_tolerationslist(map(…))Configure tolerations rules to allow the cluster-autoscaler Pod to schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration rule.
list(map(any))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a particular toleration. See
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/ for the various rules you can specify.
Example:
[
{
key = "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable"
operator = "Exists"
effect = "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds = 6000
}
]
The name to use for the helm release for cluster-autoscaler. This is useful to force a redeployment of the cluster-autoscaler component.
"cluster-autoscaler"Which docker repository to use to install the cluster autoscaler. Check the following link for valid repositories to use https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/releases
"registry.k8s.io/autoscaling/cluster-autoscaler"ARN of IAM Role to use for the Cluster Autoscaler. Only used when create_cluster_autoscaler_role is false.
nullSpecifies an 'expander' for the cluster autoscaler. This helps determine which ASG to scale when additional resource capacity is needed.
"least-waste"The name of the service account to create for the cluster autoscaler.
"cluster-autoscaler-aws-cluster-autoscaler"Which version of the cluster autoscaler to install. This should match the major/minor version (e.g., v1.20) of your Kubernetes Installation. See https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler#releases for a list of versions.
"v1.33.0"When set to true, create a new dedicated IAM Role for the cluster autoscaler. When set to true, iam_role_for_service_accounts_config is required.
truedefault_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply to all AWS resources managed by this module.
{}Whether or not to enable the AWS LB Ingress controller.
trueWhether to enable the AWS CloudWatch Agent DaemonSet for collecting container and node metrics from worker nodes (self-managed ASG or managed node groups).
trueWhether or not to enable cluster-autoscaler for Autoscaling EKS worker nodes.
trueWhether or not to enable external-dns for DNS entry syncing with Route 53 for Services and Ingresses.
trueWhether or not to enable fluent-bit on EKS Fargate workers for log aggregation.
trueWhether or not to enable fluent-bit for log aggregation.
trueDuration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the interval between making changes to Route 53 by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (1s).
nullThe maximum number of changes that should be applied in a batch by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (1000).
nullexternal_dns_chart_namestringName of the Helm chart for external-dns. This should usually be 'external-dns' but may differ in the case of overriding the repository URL.
"external-dns"Helm chart repository URL to obtain the external-dns chart from. Useful when using Bitnami charts that are older than 6 months due to Bitnami's lifecycle policy which removes older chart from the main index.
"https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami"The version of the helm chart to use. Note that this is different from the app/container version.
"6.12.2"external_dns_fargate_profile_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}external_dns_fargate_profile_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS Fargate Profile if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}external_dns_iam_policy_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Policies if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}external_dns_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the External DNS IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}The registry to use for the external-dns image.
nullThe container image repository to pull the images from. This allows overriding the default image repository for external-dns. For example, bitnamilegacy/external-dns.
"bitnamilegacy/external-dns"external_dns_pod_node_affinitylist(object(…))Configure affinity rules for the external-dns Pod to control which nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys key, values, and operator, corresponding to the 3 properties of matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on the node.
list(object({
key = string
values = list(string)
operator = string
}))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a matchExpression for requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/affinity-and-anti-affinity for the various
configuration option.
Example:
[
{
"key" = "node-label-key"
"values" = ["node-label-value", "another-node-label-value"]
"operator" = "In"
}
]
Translates to:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- node-label-value
- another-node-label-value
external_dns_pod_tolerationslist(map(…))Configure tolerations rules to allow the external-dns Pod to schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration rule.
list(map(any))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a particular toleration. See
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/ for the various rules you can specify.
Example:
[
{
key = "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable"
operator = "Exists"
effect = "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds = 6000
}
]
Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the polling interval for syncing the domains by external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (1m).
nullexternal_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filterslist(string)Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided domain names. Empty list (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints (external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters, external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
[]external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filterslist(string)Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided IDs. Empty list (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints (external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters, external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
[]external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filterslist(object(…))Only create records in hosted zones that match the provided tags. Each item in the list should specify tag key and tag value as a map. Empty list (default) means match all zones. Zones must satisfy all three constraints (external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_tag_filters, external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_id_filters, and external_dns_route53_hosted_zone_domain_filters).
list(object({
key = string
value = string
}))
[]Example
[
{
key = "Name"
value = "current"
}
]
Duration string (e.g. 1m) indicating the amount of time the Hosted Zones are cached in external-dns. When null, use the default defined in the chart (0 - no caching).
nullexternal_dns_sourceslist(string)K8s resources type to be observed for new DNS entries by ExternalDNS.
[
"ingress",
"service"
]
Details
NOTE ON ISTIO: By default, external-dns will listen for "ingress" and "service" events. To use it with Istio, make
sure to include the "istio-gateway" events here. See the docs for more details:
https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/external-dns/blob/master/docs/tutorials/istio.md
When enabled, triggers external-dns run loop on create/update/delete events (optional, in addition of regular interval)
falsefargate_fluent_bit_execution_iam_role_arnslist(string)List of ARNs of Fargate execution IAM Roles that should get permissions to ship logs using fluent-bit. This must be provided if enable_fargate_fluent_bit is true.
[]Additional filters that fluent-bit should apply to log output. This string should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_filter).
""Additional parsers that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
""fargate_fluent_bit_iam_policy_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the Fargate Execution IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}Whether or not Kubernetes metadata is added to the log files
truePrefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for each Fargate pod.
"fargate"fargate_worker_disallowed_availability_zoneslist(string)A list of availability zones in the region that we CANNOT use to deploy the EKS Fargate workers. You can use this to avoid availability zones that may not be able to provision the resources (e.g ran out of capacity). If empty, will allow all availability zones.
[
"us-east-1d",
"us-east-1e",
"ca-central-1d"
]
Can be used to add additional filter configuration blocks. This string should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the fluent-bit.conf file.
""Can be used to add more inputs. This string should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/classic-mode/configuration-file#config_input).
""Can be used to add additional outputs with this value.
""Configurations for forwarding logs to AWS managed Elasticsearch. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to ES.
object({
# Whether this plugin should be enabled or not.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/elasticsearch
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. (Default "*")
match = optional(string)
# The url of the Elastic Search endpoint you want log records sent to.
host = optional(string)
# The region in which your Amazon OpenSearch Service cluster is in. (Default "us-east-1")
awsRegion = optional(string)
# Enable AWS Sigv4 Authentication for Amazon ElasticSearch Service. (Default "On")
awsAuth = optional(string)
# Enable or disable TLS support. (Default "On")
tls = optional(string)
# TCP Port of the target service. (Default "443")
port = optional(string)
# Integer value to set the maximum number of retries allowed. N must be >= 1. (Default "6")
retryLimit = optional(string)
# Enable or disable Replace_Dots. (Default "On")
replaceDots = optional(string)
# OpenSearch 2.0 and above needs to have type option being removed by setting Suppress_Type_Name On
suppressTypeName = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
Whether this plugin should be enabled or not.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/elasticsearch
Details
The log filter. (Default "*")
Details
The url of the Elastic Search endpoint you want log records sent to.
Details
The region in which your Amazon OpenSearch Service cluster is in. (Default "us-east-1")
Details
Enable AWS Sigv4 Authentication for Amazon ElasticSearch Service. (Default "On")
Details
Enable or disable TLS support. (Default "On")
Details
TCP Port of the target service. (Default "443")
Details
Integer value to set the maximum number of retries allowed. N must be >= 1. (Default "6")
Details
Enable or disable Replace_Dots. (Default "On")
Details
OpenSearch 2.0 and above needs to have type option being removed by setting Suppress_Type_Name On
Details
Append extra outputs with value
Configurations for forwarding logs to CloudWatch Logs using a higher performance plugin. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to CloudWatch Logs using this plugin. This plugin is enabled by default in fluent-bit.
object({
# Setting this to true retains existing behaviour that users might be relying on.
# Enable this to activate the new higher performance plugin
# See for details: https://github.com/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-logs-for-fluent-bit
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. default (`*`)
match = optional(string)
# The AWS region that holds the CloudWatch Log Group where the logs will be streamed to. default (`us-east-1`)
region = optional(string)
# The name of the AWS CloudWatch Log Group to use for all the logs shipped by the cluster. Set to null to use chart.
# default (`/aws/eks/fluentbit-cloudwatch/logs`).
logGroupName = optional(string)
# Uses a record_accessor to dynamically generate a log group name based on the contents
# of the log record. See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatch#log-stream-and-group-name-templating-using-record_accessor-syntax.
# This is optional.
logGroupTemplate = optional(string)
# The name of the CloudWatch Log Stream that you want log records sent to.
logStreamName = optional(string)
# Prefix to append to all CloudWatch Log Streams in the group shipped by fluentbit. Use "" if you do not with to
# attach a prefix, or null to use chart default (`fluentbit-`).
logStreamPrefix = optional(string)
# Uses a record_accessor to dynamically generate a log stream name based on the contents
# of the log record. See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatch#log-stream-and-group-name-templating-using-record_accessor-syntax.
# This is optional.
logStreamTemplate = optional(string)
# By default, the whole log record will be sent to CloudWatch. If you specify a key name with this option,
# then only the value of that key will be sent to CloudWatch. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker
# log driver, you can specify logKey log and only the log message will be sent to CloudWatch.
logKey = optional(string)
# An optional parameter that can be used to tell CloudWatch the format of the data. A value of json/emf enables
# CloudWatch to extract custom metrics embedded in a JSON payload. See the Embedded Metric Format.
logFormat = optional(string)
# ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
roleArn = optional(string)
# Automatically create the log group. default (`true`)
autoCreateGroup = optional(string)
# If set to a number greater than zero, and newly create log group's retention policy is set to this many days.
logRetentionDays = optional(string)
# Specify a custom endpoint for the CloudWatch Logs API.
endpoint = optional(string)
# An optional string used to configure the Cloudwatch Namespace for metrics.
# See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatch#metrics-tutorial
metricNamespace = optional(string)
# An optional string used to configure the Cloudwatch dimensions used for metrics.
# See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatch#metrics-tutorial
metricDimensions = optional(string)
# Specify a custom STS endpoint for the AWS STS API.
stsEndpoint = optional(string)
# Enable automatic retries for transient network errors when pushing logs to
# Cloudwatch, and reduce the number of "connection timeout after xx seconds"
# or "broken connection to xx" errors. This will force an immediate retry when
# a network error has been detected.
autoRetryRequests = optional(string)
# Specify an external ID for STS when a role, provided by the roleArn, required an external ID.
externalId = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value.
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
{
autoCreateGroup = null,
autoRetryRequests = null,
enabled = true,
endpoint = null,
externalId = null,
extraOutputs = null,
logFormat = null,
logGroupName = "/aws/eks/fluentbit-cloudwatch/logs",
logGroupTemplate = null,
logKey = null,
logRetentionDays = null,
logStreamName = null,
logStreamPrefix = "fluentbit-",
logStreamTemplate = null,
match = "*",
metricDimensions = null,
metricNamespace = null,
region = "us-east-1",
roleArn = null,
stsEndpoint = null
}
Details
The log filter. default (`*`)
Details
The AWS region that holds the CloudWatch Log Group where the logs will be streamed to. default (`us-east-1`)
Details
The name of the AWS CloudWatch Log Group to use for all the logs shipped by the cluster. Set to null to use chart.
default (`/aws/eks/fluentbit-cloudwatch/logs`).
Details
Uses a record_accessor to dynamically generate a log group name based on the contents
of the log record. See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatchlog-stream-and-group-name-templating-using-record_accessor-syntax.
This is optional.
Details
The name of the CloudWatch Log Stream that you want log records sent to.
Details
Prefix to append to all CloudWatch Log Streams in the group shipped by fluentbit. Use "" if you do not with to
attach a prefix, or null to use chart default (`fluentbit-`).
Details
Uses a record_accessor to dynamically generate a log stream name based on the contents
of the log record. See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatchlog-stream-and-group-name-templating-using-record_accessor-syntax.
This is optional.
Details
By default, the whole log record will be sent to CloudWatch. If you specify a key name with this option,
then only the value of that key will be sent to CloudWatch. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker
log driver, you can specify logKey log and only the log message will be sent to CloudWatch.
Details
An optional parameter that can be used to tell CloudWatch the format of the data. A value of json/emf enables
CloudWatch to extract custom metrics embedded in a JSON payload. See the Embedded Metric Format.
Details
ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
Details
Automatically create the log group. default (`true`)
Details
If set to a number greater than zero, and newly create log group's retention policy is set to this many days.
Details
Specify a custom endpoint for the CloudWatch Logs API.
Details
An optional string used to configure the Cloudwatch Namespace for metrics.
See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatchmetrics-tutorial
Details
An optional string used to configure the Cloudwatch dimensions used for metrics.
See https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/cloudwatchmetrics-tutorial
Details
Specify a custom STS endpoint for the AWS STS API.
Details
Enable automatic retries for transient network errors when pushing logs to
Cloudwatch, and reduce the number of "connection timeout after xx seconds"
or "broken connection to xx" errors. This will force an immediate retry when
a network error has been detected.
Details
Specify an external ID for STS when a role, provided by the roleArn, required an external ID.
Details
Append extra outputs with value.
Configurations for adjusting the default filter settings. Set to null if you do not wish to use the default filter.
object({
# This assumes the filter is being created (ie, not null), and provides a
# means to disable it.
enabled = optional(bool)
# This option allows a different pattern to be configured for matching in
# logs, defaults to "kube.*"
match = optional(string)
# The internal cluster URL used, used to connect to the Kubernetes API
# service. defaults to "https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local:443"
kubeURL = optional(string)
# Enables or disables the means to map fields as part of the log structure,
# efaults to "On"
mergeLog = optional(string)
# Configures the key used when mapping fields into the log structure,
# defaults to "data"
mergeLogKey = optional(string)
# Allow Fluent-bit to retain a log message once its been merged, can
# be useful for additional processing. Defaults to "On"
keepLog = optional(string)
# Allows Kubernetes Pods to provide pre-defined parsers, defaults to "On".
k8sLoggingParser = optional(string)
# Allows Kubernetes Pods logs to be excluded from the processor(s).
k8sLoggingExclude = optional(string)
# Allow larger buffer sizes for the HTTP client when reading responses from
# the Kubernetes API service. Defaults to "32k".
bufferSize = optional(string)
# Append to existing filter with value
extraFilters = optional(string)
})
{
bufferSize = "32k",
enabled = true,
extraFilters = null,
k8sLoggingExclude = "On",
k8sLoggingParser = "On",
keepLog = "On",
kubeURL = "https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local:443",
match = "kube.*",
mergeLog = "On",
mergeLogKey = "data"
}
Details
This option allows a different pattern to be configured for matching in
logs, defaults to "kube.*"
Details
The internal cluster URL used, used to connect to the Kubernetes API
service. defaults to "https://kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local:443"
Details
Enables or disables the means to map fields as part of the log structure,
efaults to "On"
Details
Configures the key used when mapping fields into the log structure,
defaults to "data"
Details
Allow Fluent-bit to retain a log message once its been merged, can
be useful for additional processing. Defaults to "On"
Details
Allows Kubernetes Pods to provide pre-defined parsers, defaults to "On".
Details
Allows Kubernetes Pods logs to be excluded from the processor(s).
Details
Allow larger buffer sizes for the HTTP client when reading responses from
the Kubernetes API service. Defaults to "32k".
Details
Append to existing filter with value
Configurations for adjusting the default input settings. Set to null if you do not wish to use the default filter.
object({
# This assumes the filter is being created (ie, not null), and provides a
# means to disable it.
enabled = bool
# This option allows a tag name associated to all records coming from this plugin.
# logs, defaults to "kube.*"
tag = string
# This option allows to change the default path where the plugin will look for
# Docker containers logs, defaults to "/var/log/containers/*.log"
path = string
# This option allows to change the default database file where the plugin will
# store the state of the logs, defaults to "/var/log/flb_kube.db"
db = string
# This option allows to change the default parser used to read the Docker
# containers logs, defaults to "docker"
parser = string
# This option enabled or disables the Docker Mode, defaults to "On"
dockerMode = string
# This option allows to change the default memory limit used, defaults to "5MB"
memBufLimit = string
# This option allows to change the default number of lines to skip if a line
# is bigger than the buffer size, defaults to "On"
skipLongLines = string
# This option allows to change the default refresh interval to check the
# status of the monitored files, defaults to "10"
refreshInterval = string
})
{
db = "/var/log/flb_kube.db",
dockerMode = "On",
enabled = true,
memBufLimit = "5MB",
parser = "docker",
path = "/var/log/containers/*.log",
refreshInterval = "10",
skipLongLines = "On",
tag = "kube.*"
}
Details
This option allows a tag name associated to all records coming from this plugin.
logs, defaults to "kube.*"
Details
This option allows to change the default path where the plugin will look for
Docker containers logs, defaults to "/var/log/containers/*.log"
Details
This option allows to change the default database file where the plugin will
store the state of the logs, defaults to "/var/log/flb_kube.db"
Details
This option allows to change the default parser used to read the Docker
containers logs, defaults to "docker"
Details
This option enabled or disables the Docker Mode, defaults to "On"
Details
This option allows to change the default memory limit used, defaults to "5MB"
Details
This option allows to change the default number of lines to skip if a line
is bigger than the buffer size, defaults to "On"
Details
This option allows to change the default refresh interval to check the
status of the monitored files, defaults to "10"
Details
Default settings for input
fluent_bit_extra_filtersstringCan be used to provide additional kubernetes plugin configuration parameters for the default kubernetes filter that is pre-configured in the aws-for-fluent-bit Helm chart. This string should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will append to the default kubernetes filter configuration.
""fluent_bit_extra_inputsstringCan be used to append to existing input. This string should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the fluent-bit.conf file.
""fluent_bit_extra_outputsstringAdditional output streams that fluent-bit should export logs to. This string should be formatted according to the Fluent-bit docs (https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/configuration-file#config_output).
""fluent_bit_extra_parsersstringCan be used to add additional log parsers. This string should be formatted according to Fluent Bit docs, as it will be injected directly into the fluent-bit.conf file.
""fluent_bit_firehose_configurationobject(…)Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis Firehose. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to Firehose.
object({
# Whether this plugin should be enabled or not
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter
match = optional(string)
# The region which your Firehose delivery stream(s) is/are in.
region = optional(string)
# The name of the delivery stream you want log records sent to. This must already exist.
deliveryStream = optional(string)
# By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify a key name(s) with this
# option, then only those keys and values will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using
# the Fluentd Docker log driver, you can specify data_keys log and only the log message will be sent
# to Kinesis. If you specify multiple keys, they should be comma delimited.
dataKeys = optional(string)
# ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
roleArn = optional(string)
# Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Firehose API.
endpoint = optional(string)
# Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will
# not be added to records sent to Kinesis.
timeKey = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
Whether this plugin should be enabled or not
Details
The log filter
Details
The region which your Firehose delivery stream(s) is/are in.
Details
The name of the delivery stream you want log records sent to. This must already exist.
Details
By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify a key name(s) with this
option, then only those keys and values will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using
the Fluentd Docker log driver, you can specify data_keys log and only the log message will be sent
to Kinesis. If you specify multiple keys, they should be comma delimited.
Details
ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
Details
Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Firehose API.
Details
Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will
not be added to records sent to Kinesis.
Details
Append extra outputs with value
fluent_bit_iam_policy_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the IAM Policies created for the fluentbit IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}fluent_bit_iam_role_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the fluentbit IAM Role if enabled. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}Pull policy for the image. When null, uses the default setting IfNotPresent set in the chart.
nullThe Container repository to use for looking up the aws-for-fluent-bit Container image when deploying the pods. When null, uses the default repository set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
nullfluent_bit_kinesis_configurationobject(…)Configurations for forwarding logs to Kinesis stream. Set to null if you do not wish to forward the logs to Kinesis.
object({
# Whether this plugin should be enabled or not
# https://github.com/aws/amazon-kinesis-streams-for-fluent-bit
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. (Default "*")
match = optional(string)
# The region which your Kinesis Data Stream is in.
region = optional(string)
# The name of the stream you want log records sent to. This must already exist.
# Maps to kinesis.stream Helm chart value
stream = optional(string)
# A partition key is used to group data by shard within a stream. A Kinesis Data Stream uses the partition key
# that is associated with each data record to determine which shard a given data record belongs to. For example,
# if your logs come from Docker containers, you can use container_id as the partition key, and the logs will be
# grouped and stored on different shards depending upon the id of the container they were generated from. As
# the data within a shard are coarsely ordered, you will get all your logs from one container in one shard roughly
# in order. If you don't set a partition key or put an invalid one, a random key will be generated, and the logs
# will be directed to random shards. If the partition key is invalid, the plugin will print an warning message.
partitionKey = optional(string)
# If you set append_newline as true, a newline will be addded after each log record
appendNewline = optional(string)
# Replace dot characters in key names with the value of this option.
replaceDots = optional(string)
# By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify key name(s) with this option, then
# only those keys and values will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker log
# driver, you can specify data_keys log and only the log message will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify multiple
# keys, they should be comma delimited.
dataKeys = optional(string)
# ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
roleArn = optional(string)
# Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Streams API.
endpoint = optional(string)
# Specify a custom endpoint for the STS API; used to assume your custom role provided with kinesis.roleArn.
stsEndpoint = optional(string)
# Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will not be added
# to records sent to Kinesis.
timeKey = optional(string)
# strftime compliant format string for the timestamp; for example, %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z. This option is used with time_key.
timeKeyFormat = optional(string)
# Setting compression to zlib will enable zlib compression of each record. By default this feature is disabled
# and records are not compressed.
compression = optional(string)
# Setting aggregation to true will enable KPL aggregation of records sent to Kinesis. This feature isn't compatible
# with the partitionKey feature.
# See more about KPL aggregation: https://github.com/aws/amazon-kinesis-streams-for-fluent-bit#kpl-aggregation
aggregation = optional(string)
# Experimental feature flags
experimental_concurrency = optional(string)
experimental_concurrencyRetries = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
The log filter. (Default "*")
Details
The region which your Kinesis Data Stream is in.
Details
The name of the stream you want log records sent to. This must already exist.
Maps to kinesis.stream Helm chart value
Details
A partition key is used to group data by shard within a stream. A Kinesis Data Stream uses the partition key
that is associated with each data record to determine which shard a given data record belongs to. For example,
if your logs come from Docker containers, you can use container_id as the partition key, and the logs will be
grouped and stored on different shards depending upon the id of the container they were generated from. As
the data within a shard are coarsely ordered, you will get all your logs from one container in one shard roughly
in order. If you don't set a partition key or put an invalid one, a random key will be generated, and the logs
will be directed to random shards. If the partition key is invalid, the plugin will print an warning message.
Details
If you set append_newline as true, a newline will be addded after each log record
Details
Replace dot characters in key names with the value of this option.
Details
By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify key name(s) with this option, then
only those keys and values will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker log
driver, you can specify data_keys log and only the log message will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify multiple
keys, they should be comma delimited.
Details
ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
Details
Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Streams API.
Details
Specify a custom endpoint for the STS API; used to assume your custom role provided with kinesis.roleArn.
Details
Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will not be added
to records sent to Kinesis.
Details
strftime compliant format string for the timestamp; for example, %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z. This option is used with time_key.
Details
Setting compression to zlib will enable zlib compression of each record. By default this feature is disabled
and records are not compressed.
Details
Setting aggregation to true will enable KPL aggregation of records sent to Kinesis. This feature isn't compatible
with the partitionKey feature.
See more about KPL aggregation: https://github.com/aws/amazon-kinesis-streams-for-fluent-bitkpl-aggregation
Details
Experimental feature flags
Details
Append extra outputs with value
object({
# It has all the core features of the Golang Fluent Bit plugin released in 2019. The Golang plugin was
# named kinesis; this new high performance and highly efficient kinesis plugin is called kinesis_streams
# to prevent conflicts/confusion.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/kinesis
# https://github.com/aws/amazon-kinesis-streams-for-fluent-bit
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. (Default "*")
match = optional(string)
# The AWS region.
region = optional(string)
# The name of the Kinesis Streams Delivery Stream that you want log records send to.
stream = optional(string)
# ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
role_arn = optional(string)
# Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Streams API.
endpoint = optional(string)
# Custom endpoint for the STS API.
sts_endpoint = optional(string)
# Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will not be
# added to records sent to Kinesis.
time_key = optional(string)
# strftime compliant format string for the timestamp; for example, the default is %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S. Supports
# millisecond precision with %3N and supports nanosecond precision with %9N and %L; for example, adding %3N to
# support millisecond %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%3N. This option is used with time_key.
time_key_format = optional(string)
# Specify an external ID for the STS API, can be used with the role_arn parameter if your role requries an external ID.
external_id = optional(string)
# Immediately retry failed requests to AWS services once. This option does not affect the normal Fluent Bit
# retry mechanism with backoff. Instead, it enables an immediate retry with no delay for networking errors,
# which may help improve throughput when there are transient/random networking issues. This option defaults to true.
auto_retry_requests = optional(string)
# By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify a key name with this option, then
# only the value of that key will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker log
# driver, you can specify log_key log and only the log message will be sent to Kinesis.
log_key = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
The log filter. (Default "*")
Details
The AWS region.
Details
The name of the Kinesis Streams Delivery Stream that you want log records send to.
Details
ARN of an IAM role to assume (for cross account access).
Details
Specify a custom endpoint for the Kinesis Streams API.
Details
Custom endpoint for the STS API.
Details
Add the timestamp to the record under this key. By default the timestamp from Fluent Bit will not be
added to records sent to Kinesis.
Details
strftime compliant format string for the timestamp; for example, the default is %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S. Supports
millisecond precision with %3N and supports nanosecond precision with %9N and %L; for example, adding %3N to
support millisecond %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%3N. This option is used with time_key.
Details
Specify an external ID for the STS API, can be used with the role_arn parameter if your role requries an external ID.
Details
Immediately retry failed requests to AWS services once. This option does not affect the normal Fluent Bit
retry mechanism with backoff. Instead, it enables an immediate retry with no delay for networking errors,
which may help improve throughput when there are transient/random networking issues. This option defaults to true.
Details
By default, the whole log record will be sent to Kinesis. If you specify a key name with this option, then
only the value of that key will be sent to Kinesis. For example, if you are using the Fluentd Docker log
driver, you can specify log_key log and only the log message will be sent to Kinesis.
If set to true, that means that the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should use for streaming logs already exists and does not need to be created.
falseThe ARN of the KMS key to use to encrypt the logs in the CloudWatch Log Group used for storing container logs streamed with FluentBit. Set to null to disable encryption.
nullName of the CloudWatch Log Group fluent-bit should use to stream logs to. When null (default), uses the eks_cluster_name as the Log Group name.
nullnumber of days to retain log events. Possible values are: 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 365, 400, 545, 731, 1827, 3653, and 0. Select 0 to never expire.
0ARN of the lambda function to trigger when events arrive at the fluent bit log group.
nullFilter pattern for the CloudWatch subscription. Only used if fluent_bit_log_group_subscription_arn is set.
""Prefix string to use for the CloudWatch Log Stream that gets created for each pod. When null (default), the prefix is set to 'fluentbit'.
nullNode selector constraints for scheduling pods.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
nullfluent_bit_opensearch_configurationobject(…)object({
# Whether this plugin should be enabled or not.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/opensearch
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. (Default "*")
match = optional(string)
# The url of the Opensearch Search endpoint you want log records sent to.
host = optional(string)
# TCP Port of the target service.
port = optional(string)
# Enable or disable TLS support.
tls = optional(string)
# OpenSearch accepts new data on HTTP query path "/_bulk". But it is also possible to serve OpenSearch behind a reverse proxy on a subpath.
# This option defines such path on the fluent-bit side. It simply adds a path prefix in the indexing HTTP POST URI.
path = optional(string)
# Specify the buffer size used to read the response from the OpenSearch HTTP service.
bufferSize = optional(string)
# OpenSearch allows to setup filters called pipelines. This option allows to define which pipeline the database should use. For performance
# reasons is strongly suggested to do parsing and filtering on Fluent Bit side, avoid pipelines.
pipeline = optional(string)
# The region in which your Opensearch search is/are in.
awsRegion = optional(string)
# Enable AWS Sigv4 Authentication for Amazon Opensearch Service.
awsAuth = optional(string)
# Specify the custom sts endpoint to be used with STS API for Amazon OpenSearch Service.
awsStsEndpoint = optional(string)
# AWS IAM Role to assume to put records to your Amazon cluster.
awsRoleArn = optional(string)
# External ID for the AWS IAM Role specified with aws_role_arn.
awsExternalId = optional(string)
# Service name to be used in AWS Sigv4 signature. For integration with Amazon OpenSearch Serverless, set toaoss. See the FAQ section on
# Amazon OpenSearch Serverless for more information. To use this option: make sure you setimage.tagtov2.30.0or higher.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/opensearch#faq
awsServiceName = optional(string)
# Optional username credential for access.
httpUser = optional(string)
# Password for user defined in HTTP_User.
httpPasswd = optional(string)
# Index name, supports Record Accessor syntax.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/classic-mode/record-accessor
index = optional(string)
# Type name
type = optional(string)
# Enable Logstash format compatibility. This option takes a boolean value: True/False, On/Off
logstashFormat = optional(string)
# When Logstash_Format is enabled, the Index name is composed using a prefix and the date, e.g: If Logstash_Prefix is equals to 'mydata' your
# index will become 'mydata-YYYY.MM.DD'. The last string appended belongs to the date when the data is being generated.
logstashPrefix = optional(string)
# Time format (based on strftime) to generate the second part of the Index name.
logstashDateFormat = optional(string)
# When Logstash_Format is enabled, each record will get a new timestamp field. The Time_Key property defines the name of that field.
timeKey = optional(string)
# When Logstash_Format is enabled, this property defines the format of the timestamp.
timeKeyFormat = optional(string)
# When Logstash_Format is enabled, enabling this property sends nanosecond precision timestamps.
timeKeyNanos = optional(string)
# When enabled, it append the Tag name to the record.
includeTagKey = optional(string)
# When Include_Tag_Key is enabled, this property defines the key name for the tag.
tagKey = optional(string)
# When enabled, generate _id for outgoing records. This prevents duplicate records when retrying.
generateId = optional(string)
# If set, _id will be the value of the key from incoming record and Generate_ID option is ignored.
idKey = optional(string)
# Operation to use to write in bulk requests.
writeOperation = optional(string)
# When enabled, replace field name dots with underscore.
replaceDots = optional(string)
# When enabled print the OpenSearch API calls to stdout (for diag only)
traceOutput = optional(string)
# When enabled print the OpenSearch API calls to stdout when OpenSearch returns an error (for diag only).
traceError = optional(string)
# Use current time for index generation instead of message record
currentTimeIndex = optional(string)
# When included: the value in the record that belongs to the key will be looked up and over-write the Logstash_Prefix
# for index generation. If the key/value is not found in the record then the Logstash_Prefix option will act as a fallback.
# Nested keys are not supported (if desired, you can use the nest filter plugin to remove nesting)
logstashPrefixKey = optional(string)
# When enabled, mapping types is removed and Type option is ignored.
suppressTypeName = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value. This section helps you extend current chart implementation with ability to add extra parameters.
# For example, you can add network config like opensearch.extraOutputs.net.dns.mode=TCP.
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
The log filter. (Default "*")
Details
The url of the Opensearch Search endpoint you want log records sent to.
Details
TCP Port of the target service.
Details
Enable or disable TLS support.
Details
OpenSearch accepts new data on HTTP query path "/_bulk". But it is also possible to serve OpenSearch behind a reverse proxy on a subpath.
This option defines such path on the fluent-bit side. It simply adds a path prefix in the indexing HTTP POST URI.
Details
Specify the buffer size used to read the response from the OpenSearch HTTP service.
Details
OpenSearch allows to setup filters called pipelines. This option allows to define which pipeline the database should use. For performance
reasons is strongly suggested to do parsing and filtering on Fluent Bit side, avoid pipelines.
Details
The region in which your Opensearch search is/are in.
Details
Enable AWS Sigv4 Authentication for Amazon Opensearch Service.
Details
Specify the custom sts endpoint to be used with STS API for Amazon OpenSearch Service.
Details
AWS IAM Role to assume to put records to your Amazon cluster.
Details
External ID for the AWS IAM Role specified with aws_role_arn.
Details
Service name to be used in AWS Sigv4 signature. For integration with Amazon OpenSearch Serverless, set toaoss. See the FAQ section on
Amazon OpenSearch Serverless for more information. To use this option: make sure you setimage.tagtov2.30.0or higher.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/opensearchfaq
Details
Optional username credential for access.
Details
Password for user defined in HTTP_User.
Details
Index name, supports Record Accessor syntax.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/configuring-fluent-bit/classic-mode/record-accessor
Details
Type name
Details
Enable Logstash format compatibility. This option takes a boolean value: True/False, On/Off
Details
When Logstash_Format is enabled, the Index name is composed using a prefix and the date, e.g: If Logstash_Prefix is equals to 'mydata' your
index will become 'mydata-YYYY.MM.DD'. The last string appended belongs to the date when the data is being generated.
Details
Time format (based on strftime) to generate the second part of the Index name.
Details
When Logstash_Format is enabled, each record will get a new timestamp field. The Time_Key property defines the name of that field.
Details
When Logstash_Format is enabled, this property defines the format of the timestamp.
Details
When Logstash_Format is enabled, enabling this property sends nanosecond precision timestamps.
Details
When enabled, it append the Tag name to the record.
Details
When Include_Tag_Key is enabled, this property defines the key name for the tag.
Details
When enabled, generate _id for outgoing records. This prevents duplicate records when retrying.
Details
If set, _id will be the value of the key from incoming record and Generate_ID option is ignored.
Details
Operation to use to write in bulk requests.
Details
When enabled, replace field name dots with underscore.
Details
When enabled print the OpenSearch API calls to stdout (for diag only)
Details
When enabled print the OpenSearch API calls to stdout when OpenSearch returns an error (for diag only).
Details
Use current time for index generation instead of message record
Details
When included: the value in the record that belongs to the key will be looked up and over-write the Logstash_Prefix
for index generation. If the key/value is not found in the record then the Logstash_Prefix option will act as a fallback.
Nested keys are not supported (if desired, you can use the nest filter plugin to remove nesting)
Details
When enabled, mapping types is removed and Type option is ignored.
Details
Append extra outputs with value. This section helps you extend current chart implementation with ability to add extra parameters.
For example, you can add network config like opensearch.extraOutputs.net.dns.mode=TCP.
Pod annotations to apply to the deployment.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
nullfluent_bit_pod_node_affinitylist(object(…))Configure affinity rules for the fluent-bit Pods to control which nodes to schedule on. Each item in the list should be a map with the keys key, values, and operator, corresponding to the 3 properties of matchExpressions. Note that all expressions must be satisfied to schedule on the node.
list(object({
key = string
values = list(string)
operator = string
}))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a matchExpression for requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/affinity-and-anti-affinity for the various
configuration option.
Example:
[
{
"key" = "node-label-key"
"values" = ["node-label-value", "another-node-label-value"]
"operator" = "In"
}
]
Translates to:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-label-key
operator: In
values:
- node-label-value
- another-node-label-value
Specify the resource limits and requests for the fluent-bit pods. Set to null (default) to use chart defaults.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
nullDetails
This object is passed through to the resources section of a pod spec as described in
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
Example:
{
requests = {
cpu = "250m"
memory = "128Mi"
}
limits = {
cpu = "500m"
memory = "256Mi"
}
}
fluent_bit_pod_tolerationslist(map(…))Configure tolerations rules to allow the fluent-bit Pods to schedule on nodes that have been tainted. Each item in the list specifies a toleration rule.
list(map(any))
[]Details
Each item in the list represents a particular toleration. See
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/ for the various rules you can specify.
Example:
[
{
key = "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable"
operator = "Exists"
effect = "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds = 6000
}
]
Create a restricted pod security policy.
falsefluent_bit_s3_configurationobject(…)object({
# Whether this plugin should be enabled or not.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3
enabled = optional(bool)
# The log filter. (Default "*")
match = optional(string)
# S3 Bucket name.
bucket = optional(string)
# The AWS region of your S3 bucket.
region = optional(string)
# Specify the name of the time key in the output record. To disable the time key just set the value to false.
jsonDateKey = optional(string)
# Specify the format of the date. Supported formats are double, epoch, iso8601 (eg: 2018-05-30T09:39:52.000681Z)
# and java_sql_timestamp (eg: 2018-05-30 09:39:52.000681).
jsonDateFormat = optional(string)
# Specifies the size of files in S3. Maximum size is 50G, minimim is 1M.
totalFileSize = optional(string)
# The size of each 'part' for multipart uploads. Max: 50M
uploadChunkSize = optional(string)
# Whenever this amount of time has elapsed, Fluent Bit will complete an upload and create a new file in S3. For
# example, set this value to 60m and you will get a new file every hour.
uploadTimeout = optional(string)
# Directory to locally buffer data before sending. When multipart uploads are used, data will only be buffered until
# the upload_chunk_size is reached. S3 will also store metadata about in progress multipart uploads in this directory;
# this allows pending uploads to be completed even if Fluent Bit stops and restarts. It will also store the
# current $INDEX value if enabled in the S3 key format so that the $INDEX can keep incrementing from its previous
# value after Fluent Bit restarts.
storeDir = optional(string)
# The size of the limitation for disk usage in S3. Limit the amount of s3 buffers in the store_dir to limit
# disk usage. Note: Use store_dir_limit_size instead of storage.total_limit_size which can be used to other plugins,
# because S3 has its own buffering system.
storeDirLimitSize = optional(string)
# Format string for keys in S3. This option supports UUID ($UUID), strftime time formatters, $INDEX, a syntax for selecting
# parts of the Fluent log tag using $TAG/$TAG[n] inspired by the rewrite_tag filter. Check documentation for more details.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3#s3-key-format-and-tag-delimiters
s3KeyFormat = optional(string)
# A series of characters which will be used to split the tag into 'parts' for use with the s3_key_format option.
# See the in depth examples and tutorial in the documentation.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3/
s3KeyFormatTagDelimiters = optional(string)
# Disables behavior where UUID string is automatically appended to end of S3 key name when $UUID is not provided in s3_key_format.
# $UUID, time formatters, $TAG, and other dynamic key formatters all work as expected while this feature is set to true.
staticFilePath = optional(string)
# Use the S3 PutObject API, instead of the multipart upload API. Check documentation for more details.
# https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3
usePutObject = optional(string)
# ARN of an IAM role to assume (ex. for cross account access).
roleArn = optional(string)
# Custom endpoint for the S3 API. An endpoint can contain scheme and port.
endpoint = optional(string)
# Custom endpoint for the STS API.
stsEndpoint = optional(string)
# Predefined Canned ACL policy for S3 objects.
cannedAcl = optional(string)
# Compression type for S3 objects. AWS distro aws-for-fluent-bit supports gzip & arrow.
compression = optional(string)
# A standard MIME type for the S3 object; this will be set as the Content-Type HTTP header.
contentType = optional(string)
# Send the Content-MD5 header with PutObject and UploadPart requests, as is required when Object Lock is enabled.
sendContentMd5 = optional(string)
# Immediately retry failed requests to AWS services once. This option does not affect the normal Fluent Bit retry mechanism
# with backoff. Instead, it enables an immediate retry with no delay for networking errors, which may help improve throughput
# when there are transient/random networking issues. This option defaults to true.
# https://github.com/aws/aws-for-fluent-bit/blob/mainline/troubleshooting/debugging.md#network-connection-issues
autoRetryRequests = optional(string)
# By default, the whole log record will be sent to S3. If you specify a key name with this option, then only the value of that
# key will be sent to S3. For example, if you are using Docker, you can specify log_key log and only the log message will be sent to S3.
logKey = optional(string)
# Normally, when an upload request fails, there is a high chance for the last received chunk to be swapped with a later chunk, resulting
# in data shuffling. This feature prevents this shuffling by using a queue logic for uploads.
preserveDataOrdering = optional(string)
# Specify the storage class for S3 objects. If this option is not specified, objects will be stored with the default 'STANDARD' storage class.
storageClass = optional(string)
# Integer value to set the maximum number of retries allowed. Note: this configuration is released since version 1.9.10 and 2.0.1.
# For previous version, the number of retries is 5 and is not configurable.
retryLimit = optional(string)
# Specify an external ID for the STS API, can be used with the role_arn parameter if your role requires an external ID.
externalId = optional(string)
# Append extra outputs with value. This section helps you extend current chart implementation with ability to add extra parameters.
# For example, you can add config like s3.extraOutputs.net.dns.mode=TCP.
extraOutputs = optional(string)
})
nullDetails
The log filter. (Default "*")
Details
S3 Bucket name.
Details
The AWS region of your S3 bucket.
Details
Specify the name of the time key in the output record. To disable the time key just set the value to false.
Details
Specify the format of the date. Supported formats are double, epoch, iso8601 (eg: 2018-05-30T09:39:52.000681Z)
and java_sql_timestamp (eg: 2018-05-30 09:39:52.000681).
Details
Specifies the size of files in S3. Maximum size is 50G, minimim is 1M.
Details
The size of each 'part' for multipart uploads. Max: 50M
Details
Whenever this amount of time has elapsed, Fluent Bit will complete an upload and create a new file in S3. For
example, set this value to 60m and you will get a new file every hour.
Details
Directory to locally buffer data before sending. When multipart uploads are used, data will only be buffered until
the upload_chunk_size is reached. S3 will also store metadata about in progress multipart uploads in this directory;
this allows pending uploads to be completed even if Fluent Bit stops and restarts. It will also store the
current $INDEX value if enabled in the S3 key format so that the $INDEX can keep incrementing from its previous
value after Fluent Bit restarts.
Details
The size of the limitation for disk usage in S3. Limit the amount of s3 buffers in the store_dir to limit
disk usage. Note: Use store_dir_limit_size instead of storage.total_limit_size which can be used to other plugins,
because S3 has its own buffering system.
Details
Format string for keys in S3. This option supports UUID ($UUID), strftime time formatters, $INDEX, a syntax for selecting
parts of the Fluent log tag using $TAG/$TAG[n] inspired by the rewrite_tag filter. Check documentation for more details.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3s3-key-format-and-tag-delimiters
Details
A series of characters which will be used to split the tag into 'parts' for use with the s3_key_format option.
See the in depth examples and tutorial in the documentation.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3/
Details
Disables behavior where UUID string is automatically appended to end of S3 key name when $UUID is not provided in s3_key_format.
$UUID, time formatters, $TAG, and other dynamic key formatters all work as expected while this feature is set to true.
Details
Use the S3 PutObject API, instead of the multipart upload API. Check documentation for more details.
https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/pipeline/outputs/s3
Details
ARN of an IAM role to assume (ex. for cross account access).
Details
Custom endpoint for the S3 API. An endpoint can contain scheme and port.
Details
Custom endpoint for the STS API.
Details
Predefined Canned ACL policy for S3 objects.
Details
Compression type for S3 objects. AWS distro aws-for-fluent-bit supports gzip & arrow.
Details
A standard MIME type for the S3 object; this will be set as the Content-Type HTTP header.
Details
Send the Content-MD5 header with PutObject and UploadPart requests, as is required when Object Lock is enabled.
Details
Immediately retry failed requests to AWS services once. This option does not affect the normal Fluent Bit retry mechanism
with backoff. Instead, it enables an immediate retry with no delay for networking errors, which may help improve throughput
when there are transient/random networking issues. This option defaults to true.
https://github.com/aws/aws-for-fluent-bit/blob/mainline/troubleshooting/debugging.mdnetwork-connection-issues
Details
By default, the whole log record will be sent to S3. If you specify a key name with this option, then only the value of that
key will be sent to S3. For example, if you are using Docker, you can specify log_key log and only the log message will be sent to S3.
Details
Normally, when an upload request fails, there is a high chance for the last received chunk to be swapped with a later chunk, resulting
in data shuffling. This feature prevents this shuffling by using a queue logic for uploads.
Details
Specify the storage class for S3 objects. If this option is not specified, objects will be stored with the default 'STANDARD' storage class.
Details
Integer value to set the maximum number of retries allowed. Note: this configuration is released since version 1.9.10 and 2.0.1.
For previous version, the number of retries is 5 and is not configurable.
Details
Specify an external ID for the STS API, can be used with the role_arn parameter if your role requires an external ID.
Details
Append extra outputs with value. This section helps you extend current chart implementation with ability to add extra parameters.
For example, you can add config like s3.extraOutputs.net.dns.mode=TCP.
fluent_bit_sensitive_valuesmap(string)Merge and mask sensitive values like apikeys or passwords that are part of the helm charts values.yaml. These sensitive values will show up in the final metadata as clear text unless passed in as K:V pairs that are injected into the values.yaml. Key should be the paramater path and value should be the value.
{}Details
EXAMPLE
{
"additionalOutputs" = var.extraOutputs
}
fluent_bit_service_account_annotationsmap(string)Annotations to apply to the Service Account. If iam_role_for_service_accounts_config is provided, then this module will automatically add the annotation `eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn = <IAM Role ARN> to the Service Account to leverage IRSA. Annotations provided by this variable will be merged with the module applied Annotations.
{}Whether a new service account should be created.
trueName of the service account.
"aws-for-fluent-bit"Optional update strategy for the Kubernetes Deployment.
"RollingUpdate"Optionally use a cri parser instead of the default Docker parser. This should be used for EKS v1.24 and later.
truefluent_bit_versionstringWhich version of aws-for-fluent-bit to install. When null, uses the default version set in the chart. Only applies to non-fargate workers.
nullkubernetes_priority_classesmap(object(…))A map of PriorityClass configurations, with the key as the PriorityClass name. https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
map(object({
description = string
global_default = bool
value = number
}))
{}Policy for how DNS records are sychronized between sources and providers (options: sync, upsert-only).
"sync"When true, the ALB ingress controller pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
falseWhen true, the cluster autoscaler pods will be scheduled on Fargate. It is recommended to run the cluster autoscaler on Fargate to avoid the autoscaler scaling down a node where it is running (and thus shutting itself down during a scale down event). However, since Fargate is only supported on a handful of regions, we don't default to true here.
falseWhen true, the external-dns pods will be scheduled on Fargate.
falseservice_dns_mappingsmap(object(…))Configure Kubernetes Services to lookup external DNS records. This can be useful to bind friendly internal service names to domains (e.g. the RDS database endpoint).
map(object({
# DNS record to route requests to the Kubernetes Service to.
target_dns = string
# Port to route requests
target_port = number
# Namespace to create the underlying Kubernetes Service in.
namespace = string
}))
{}Details
Port to route requests
Details
Namespace to create the underlying Kubernetes Service in.
If this variable is set to true, then use an exec-based plugin to authenticate and fetch tokens for EKS. This is useful because EKS clusters use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the middle of an 'apply' or 'destroy', and since the native Kubernetes provider in Terraform doesn't have a way to fetch up-to-date tokens, we recommend using an exec-based provider as a workaround. Use the use_kubergrunt_to_fetch_token input variable to control whether kubergrunt or aws is used to fetch tokens.
trueEKS clusters use short-lived authentication tokens that can expire in the middle of an 'apply' or 'destroy'. To avoid this issue, we use an exec-based plugin to fetch an up-to-date token. If this variable is set to true, we'll use kubergrunt to fetch the token (in which case, kubergrunt must be installed and on PATH); if this variable is set to false, we'll use the aws CLI to fetch the token (in which case, aws must be installed and on PATH). Note this functionality is only enabled if use_exec_plugin_for_auth is set to true.
trueWhen true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies when targeting compliance with various security standards.
trueName of the CloudWatch Log Group used to store the container logs.
A list of names of Kubernetes PriorityClass objects created by this module.