ECS Deploy Runner
Overview
This service deploys ECS Deploy Runner, the central component of Gruntwork Pipelines.
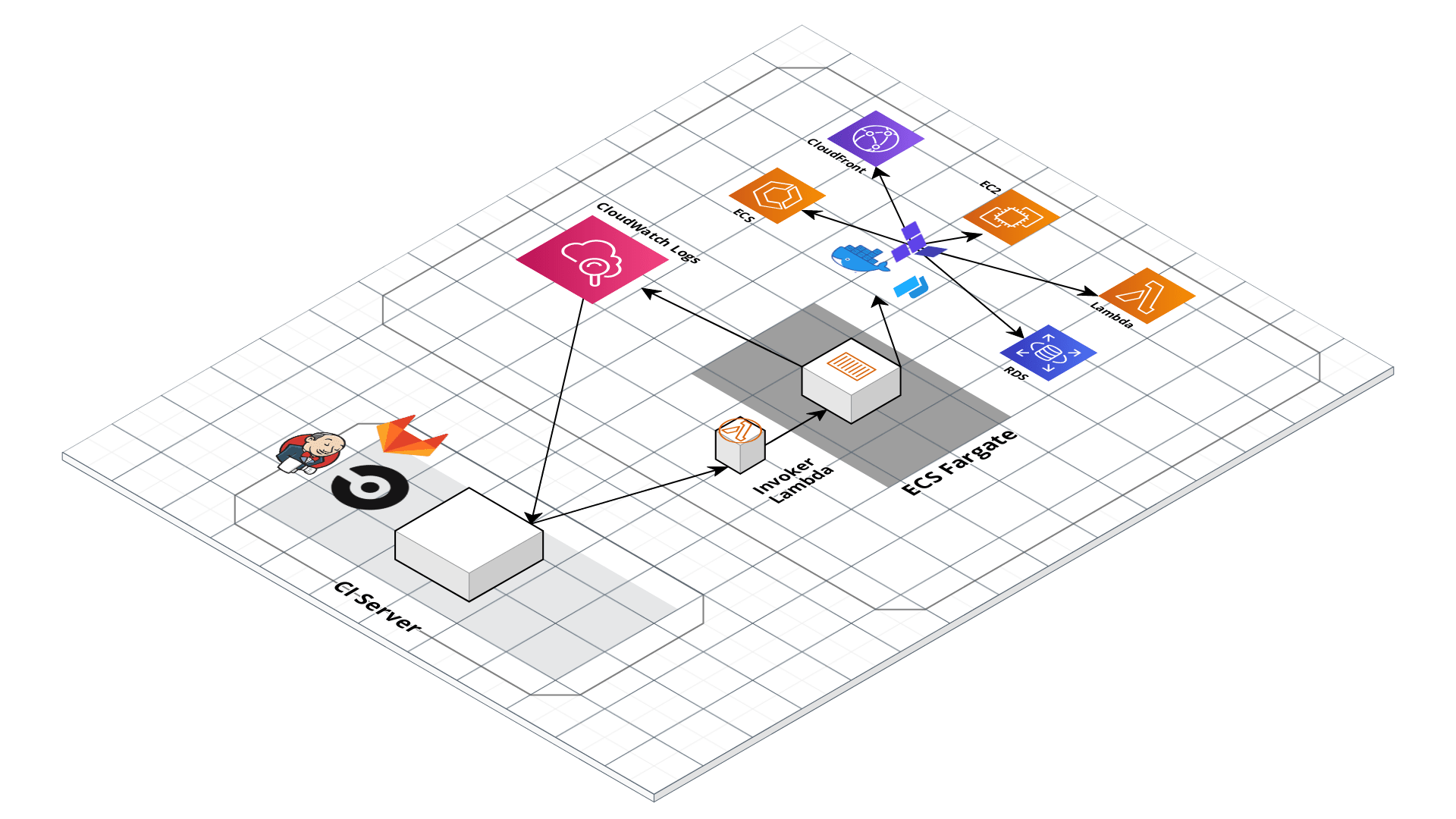 Gruntwork Pipelines architecture
Gruntwork Pipelines architecture
Gruntwork Pipelines is a code framework and approach that enables you to use your preferred CI tool to set up an end-to-end pipeline for infrastructure code (Terraform) and app code packaged in multiple formats, including container images (Docker) and Amazon Machine Images (AMIs built with Packer).
Features
- Set up a Terraform and Terragrunt pipeline based on best practices
- Run deployments using Fargate or EC2 tasks on the ECS cluster
- Configure the pipeline for building Packer and Docker images and for running
planandapplyoperations - Grant fine-grained permissions for running deployments with minimum necessary privileges
- Stream output from the pipeline to CloudWatch Logs
- Protect secrets needed by the pipeline using AWS Secrets Manager
- Use KMS grants to allow the ECS task containers to access shared secrets and encrypted images between accounts
- Easily upgrade Terraform versions with Terraform version management support
Under the hood, this is all implemented using Terraform modules from the Gruntwork terraform-aws-ci repo.
Learn
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
Core concepts
- For a comprehensive guide to Gruntwork Pipelines, refer to How to configure a production-grade CI-CD workflow for infrastructure code.
- For an overview of how the various parts fit together to form the complete pipeline, refer to the ECS Deploy Runner Core Concepts.
- The rest of the docs within the ecs-deploy-runner module in the terraform-aws-ci repository may also help with context.
- The ECS Deploy Runner standard configuration
is a shortcut for setting up the
ecs-deploy-runnermodule in a manner consistent with Gruntwork recommendations.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
- shared account ecs-deploy-runner configuration in the for-production folder:
The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog.
Sample Usage
- Terraform
- Terragrunt
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S ECS-DEPLOY-RUNNER MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
module "ecs_deploy_runner" {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/mgmt/ecs-deploy-runner?ref=v1.3.0"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Configuration options for the ami-builder container of the ECS deploy runner
# stack. This container will be used for building AMIs in the CI/CD pipeline
# using packer. Set to `null` to disable this container.
ami_builder_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
allowed_repos = list(string)
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# Configuration options for the docker-image-builder container of the ECS
# deploy runner stack. This container will be used for building docker images
# in the CI/CD pipeline. Set to `null` to disable this container.
docker_image_builder_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
allowed_repos = list(string)
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
git_config = object(
username_secrets_manager_arn = string
password_secrets_manager_arn = string
)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# List of IDs of private subnets that can be used for running the ECS task and
# Lambda function.
private_subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# Configuration options for the terraform-applier container of the ECS deploy
# runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure
# deployment actions (including automated variable updates) in the CI/CD
# pipeline with Terraform / Terragrunt. Set to `null` to disable this
# container.
terraform_applier_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
allowed_update_variable_names = list(string)
allowed_apply_git_refs = list(string)
machine_user_git_info = object(
name = string
email = string
)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# Configuration options for the terraform-planner container of the ECS deploy
# runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure plan
# (including validate) actions in the CI/CD pipeline with Terraform /
# Terragrunt. Set to `null` to disable this container.
terraform_planner_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# ID of the VPC where the ECS task and Lambda function should run.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Container configurations that should be added to the ECS Deploy Runner that
# should be added in addition to the standard containers. This can be used to
# customize your deployment of the ECS Deploy Runner beyond the standard use
# cases.
additional_container_images = {}
# Configuration for storing artifacts from the underlying commands. When set,
# stdout, stderr, and interleaved output will be stored in the configured S3
# bucket. Set to null if you do not wish for artifacts to be stored. Note that
# when null, the args for configuring storage of outputs will not be
# available.
artifact_config = null
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_tags = null
# The default CPU units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The
# invoker allows users to override the CPU at run time, but this value will be
# used if the user provides no value for the CPU. Options here:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
container_cpu = 1024
# The default launch type of the ECS deploy runner workers. This launch type
# will be used if it is not overridden during invocation of the lambda
# function. Must be FARGATE or EC2.
container_default_launch_type = "FARGATE"
# The maximum CPU units that is allowed to be specified by the user when
# invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
container_max_cpu = 8192
# The maximum memory units that is allowed to be specified by the user when
# invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
container_max_memory = 32768
# The default memory units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The
# invoker allows users to override the memory at run time, but this value will
# be used if the user provides no value for memory. Options here:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
container_memory = 2048
# Unlike hardcoded_options, this is used for hardcoded positional args and
# will always be passed in at the end of the args list.
docker_image_builder_hardcoded_args = ["--idempotent"]
# Which options and args to always pass in alongside the ones provided by the
# command. This is a map of option keys to args to pass in. Each arg in the
# list will be passed in as a separate option. This will be passed in first,
# before the args provided by the user in the event data.
docker_image_builder_hardcoded_options = {}
# Worker configuration of a EC2 worker pool for the ECS cluster. An EC2 worker
# pool supports caching of Docker images, so your builds may run faster,
# whereas Fargate is serverless, so you have no persistent EC2 instances to
# manage and pay for. If null, no EC2 worker pool will be allocated and the
# deploy runner will be in Fargate only mode. Note that when this variable is
# set, this example module will automatically lookup and use the base ECS
# optimized AMI that AWS provides.
ec2_worker_pool_configuration = null
# Tags to apply on the ECS Deploy Runner (ECS cluster, tasks, and invoker
# Lambda function), encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values
# are tag values.
ecs_deploy_runner_tags = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# A custom name to set for the CloudWatch Log Group used to stream the
# container logs. When null, the Log Group will default to /ecs/{var.name}.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_name = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# The ARN of the destination to deliver matching log events to. Kinesis stream
# or Lambda function ARN. Only applicable if
# var.ecs_task_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group is true, and
# var.container_images is non-empty.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn = null
# The method used to distribute log data to the destination. Only applicable
# when var.ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a
# kinesis stream. Valid values are `Random` and `ByLogStream`.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_distribution = null
# A valid CloudWatch Logs filter pattern for subscribing to a filtered stream
# of log events.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_filter_pattern = ""
# ARN of an IAM role that grants Amazon CloudWatch Logs permissions to deliver
# ingested log events to the destination. Only applicable when
# var.ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a kinesis
# stream.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_role_arn = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the ECS Task execution. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, AWS ECS will automatically create a basic log group
# to use.
ecs_task_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# List of AWS IAM groups that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_groups = []
# List of AWS IAM roles that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_roles = []
# List of AWS IAM usernames that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_users = []
# Configurations for invoking ECS Deploy Runner on a schedule. Use this to
# configure any periodic background jobs that you would like run through the
# ECS Deploy Runner (e.g., regularly running plan on your infrastructure to
# detect drift). Input is a map of unique schedule name to its settings.
invoke_schedule = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data for the invoker lambda function.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group for the invoker
# lambda function. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group for the invoker lambda function,
# encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the invoker lambda function execution. This is useful if you wish to
# customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention
# periods and KMS encryption. When false, AWS Lambda will automatically create
# a basic log group to use.
invoker_lambda_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# Create multi-region resources in the specified regions. The best practice is
# to enable multi-region services in all enabled regions in your AWS account.
# This variable must NOT be set to null or empty. Otherwise, we won't know
# which regions to use and authenticate to, and may use some not enabled in
# your AWS account (e.g., GovCloud, China, etc). To get the list of regions
# enabled in your AWS account, you can use the AWS CLI: aws ec2
# describe-regions.
kms_grant_opt_in_regions = ["eu-north-1","ap-south-1","eu-west-3","eu-west-2","eu-west-1","ap-northeast-2","ap-northeast-1","sa-east-1","ca-central-1","ap-southeast-1","ap-southeast-2","eu-central-1","us-east-1","us-east-2","us-west-1","us-west-2"]
# Name of this instance of the deploy runner stack. Used to namespace all
# resources.
name = "ecs-deploy-runner"
# When non-null, set the security group name of the ECS Deploy Runner ECS Task
# to this string. When null, a unique name will be generated by Terraform to
# avoid conflicts when deploying multiple instances of the ECS Deploy Runner.
outbound_security_group_name = null
# If true, this module will create grants for a given shared secrets KMS key.
# You must pass a value for shared_secrets_kms_cmk_arn if this is set to true.
# Defaults to false.
shared_secrets_enabled = false
# The ARN of the KMS CMK used for sharing AWS Secrets Manager secrets between
# accounts.
shared_secrets_kms_cmk_arn = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a
# basic log group to use.
should_create_cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2 = true
# Map of names to ARNs of KMS CMKs that are used to encrypt snapshots
# (including AMIs). This module will create the necessary KMS key grants to
# allow the respective deploy containers access to utilize the keys for
# managing the encrypted snapshots. The keys are arbitrary names that are used
# to identify the key.
snapshot_encryption_kms_cmk_arns = {}
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S ECS-DEPLOY-RUNNER MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
terraform {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/mgmt/ecs-deploy-runner?ref=v1.3.0"
}
inputs = {
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Configuration options for the ami-builder container of the ECS deploy runner
# stack. This container will be used for building AMIs in the CI/CD pipeline
# using packer. Set to `null` to disable this container.
ami_builder_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
allowed_repos = list(string)
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# Configuration options for the docker-image-builder container of the ECS
# deploy runner stack. This container will be used for building docker images
# in the CI/CD pipeline. Set to `null` to disable this container.
docker_image_builder_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
allowed_repos = list(string)
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
git_config = object(
username_secrets_manager_arn = string
password_secrets_manager_arn = string
)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# List of IDs of private subnets that can be used for running the ECS task and
# Lambda function.
private_subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# Configuration options for the terraform-applier container of the ECS deploy
# runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure
# deployment actions (including automated variable updates) in the CI/CD
# pipeline with Terraform / Terragrunt. Set to `null` to disable this
# container.
terraform_applier_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
allowed_update_variable_names = list(string)
allowed_apply_git_refs = list(string)
machine_user_git_info = object(
name = string
email = string
)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# Configuration options for the terraform-planner container of the ECS deploy
# runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure plan
# (including validate) actions in the CI/CD pipeline with Terraform /
# Terragrunt. Set to `null` to disable this container.
terraform_planner_config = <object(
container_image = object(
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
)
iam_policy = map(object(
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
))
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
environment_vars = map(string)
)>
# ID of the VPC where the ECS task and Lambda function should run.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Container configurations that should be added to the ECS Deploy Runner that
# should be added in addition to the standard containers. This can be used to
# customize your deployment of the ECS Deploy Runner beyond the standard use
# cases.
additional_container_images = {}
# Configuration for storing artifacts from the underlying commands. When set,
# stdout, stderr, and interleaved output will be stored in the configured S3
# bucket. Set to null if you do not wish for artifacts to be stored. Note that
# when null, the args for configuring storage of outputs will not be
# available.
artifact_config = null
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_tags = null
# The default CPU units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The
# invoker allows users to override the CPU at run time, but this value will be
# used if the user provides no value for the CPU. Options here:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
container_cpu = 1024
# The default launch type of the ECS deploy runner workers. This launch type
# will be used if it is not overridden during invocation of the lambda
# function. Must be FARGATE or EC2.
container_default_launch_type = "FARGATE"
# The maximum CPU units that is allowed to be specified by the user when
# invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
container_max_cpu = 8192
# The maximum memory units that is allowed to be specified by the user when
# invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
container_max_memory = 32768
# The default memory units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The
# invoker allows users to override the memory at run time, but this value will
# be used if the user provides no value for memory. Options here:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
container_memory = 2048
# Unlike hardcoded_options, this is used for hardcoded positional args and
# will always be passed in at the end of the args list.
docker_image_builder_hardcoded_args = ["--idempotent"]
# Which options and args to always pass in alongside the ones provided by the
# command. This is a map of option keys to args to pass in. Each arg in the
# list will be passed in as a separate option. This will be passed in first,
# before the args provided by the user in the event data.
docker_image_builder_hardcoded_options = {}
# Worker configuration of a EC2 worker pool for the ECS cluster. An EC2 worker
# pool supports caching of Docker images, so your builds may run faster,
# whereas Fargate is serverless, so you have no persistent EC2 instances to
# manage and pay for. If null, no EC2 worker pool will be allocated and the
# deploy runner will be in Fargate only mode. Note that when this variable is
# set, this example module will automatically lookup and use the base ECS
# optimized AMI that AWS provides.
ec2_worker_pool_configuration = null
# Tags to apply on the ECS Deploy Runner (ECS cluster, tasks, and invoker
# Lambda function), encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values
# are tag values.
ecs_deploy_runner_tags = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# A custom name to set for the CloudWatch Log Group used to stream the
# container logs. When null, the Log Group will default to /ecs/{var.name}.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_name = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# The ARN of the destination to deliver matching log events to. Kinesis stream
# or Lambda function ARN. Only applicable if
# var.ecs_task_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group is true, and
# var.container_images is non-empty.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn = null
# The method used to distribute log data to the destination. Only applicable
# when var.ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a
# kinesis stream. Valid values are `Random` and `ByLogStream`.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_distribution = null
# A valid CloudWatch Logs filter pattern for subscribing to a filtered stream
# of log events.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_filter_pattern = ""
# ARN of an IAM role that grants Amazon CloudWatch Logs permissions to deliver
# ingested log events to the destination. Only applicable when
# var.ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a kinesis
# stream.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_role_arn = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the ECS Task execution. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, AWS ECS will automatically create a basic log group
# to use.
ecs_task_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# List of AWS IAM groups that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_groups = []
# List of AWS IAM roles that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_roles = []
# List of AWS IAM usernames that should be given access to invoke the deploy
# runner.
iam_users = []
# Configurations for invoking ECS Deploy Runner on a schedule. Use this to
# configure any periodic background jobs that you would like run through the
# ECS Deploy Runner (e.g., regularly running plan on your infrastructure to
# detect drift). Input is a map of unique schedule name to its settings.
invoke_schedule = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data for the invoker lambda function.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group for the invoker
# lambda function. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group for the invoker lambda function,
# encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
invoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the invoker lambda function execution. This is useful if you wish to
# customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention
# periods and KMS encryption. When false, AWS Lambda will automatically create
# a basic log group to use.
invoker_lambda_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# Create multi-region resources in the specified regions. The best practice is
# to enable multi-region services in all enabled regions in your AWS account.
# This variable must NOT be set to null or empty. Otherwise, we won't know
# which regions to use and authenticate to, and may use some not enabled in
# your AWS account (e.g., GovCloud, China, etc). To get the list of regions
# enabled in your AWS account, you can use the AWS CLI: aws ec2
# describe-regions.
kms_grant_opt_in_regions = ["eu-north-1","ap-south-1","eu-west-3","eu-west-2","eu-west-1","ap-northeast-2","ap-northeast-1","sa-east-1","ca-central-1","ap-southeast-1","ap-southeast-2","eu-central-1","us-east-1","us-east-2","us-west-1","us-west-2"]
# Name of this instance of the deploy runner stack. Used to namespace all
# resources.
name = "ecs-deploy-runner"
# When non-null, set the security group name of the ECS Deploy Runner ECS Task
# to this string. When null, a unique name will be generated by Terraform to
# avoid conflicts when deploying multiple instances of the ECS Deploy Runner.
outbound_security_group_name = null
# If true, this module will create grants for a given shared secrets KMS key.
# You must pass a value for shared_secrets_kms_cmk_arn if this is set to true.
# Defaults to false.
shared_secrets_enabled = false
# The ARN of the KMS CMK used for sharing AWS Secrets Manager secrets between
# accounts.
shared_secrets_kms_cmk_arn = null
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a
# basic log group to use.
should_create_cloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2 = true
# Map of names to ARNs of KMS CMKs that are used to encrypt snapshots
# (including AMIs). This module will create the necessary KMS key grants to
# allow the respective deploy containers access to utilize the keys for
# managing the encrypted snapshots. The keys are arbitrary names that are used
# to identify the key.
snapshot_encryption_kms_cmk_arns = {}
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
}
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
ami_builder_configobject(…)Configuration options for the ami-builder container of the ECS deploy runner stack. This container will be used for building AMIs in the CI/CD pipeline using packer. Set to null to disable this container.
object({
# Docker repo and image tag to use as the container image for the ami builder. This should be based on the
# Dockerfile in terraform-aws-ci/modules/ecs-deploy-runner/docker/deploy-runner.
container_image = object({
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
})
# An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
# ami builder. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
# fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
# Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
# variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
# iam_policy = {
# S3Access = {
# actions = ["s3:*"]
# resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
# effect = "Allow"
# },
# EC2Access = {
# actions = ["ec2:*"],
# resources = ["*"]
# effect = "Allow"
# }
# }
iam_policy = map(object({
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
}))
# List of repositories that are allowed to build docker images. These should be the SSH git URL of the repository
# (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
allowed_repos = list(string)
# List of repositories (matching the regex) that are allowed to build AMIs. These should be the SSH git URL of the repository
# (e.g., "(git@github.com:gruntwork-io/)+" ).
# Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
# The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing remote
# git repositories containing packer templates.
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
# Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
# The following keys are supported:
#
# - github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
# - bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
# passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
# ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the packer process as environment
# variables. For example,
# secrets_manager_env_vars = {
# GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
# }
# Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
# in the container that can then be passed through to the AMI via the `env` directive in the packer template.
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
# Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
# Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
environment_vars = map(string)
})
Details
An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
ami builder. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
iam_policy = {
S3Access = {
actions = ["s3:*"]
resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
effect = "Allow"
},
EC2Access = {
actions = ["ec2:*"],
resources = ["*"]
effect = "Allow"
}
}
Details
List of repositories that are allowed to build docker images. These should be the SSH git URL of the repository
(e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
Details
List of repositories (matching the regex) that are allowed to build AMIs. These should be the SSH git URL of the repository
(e.g., "(git@github.com:gruntwork-io/)+" ).
Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
Details
The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing remote
git repositories containing packer templates.
Details
Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
The following keys are supported:
- github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
- bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
Details
ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the packer process as environment
variables. For example,
secrets_manager_env_vars = {
GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
}
Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
in the container that can then be passed through to the AMI via the `env` directive in the packer template.
Details
Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
docker_image_builder_configobject(…)Configuration options for the docker-image-builder container of the ECS deploy runner stack. This container will be used for building docker images in the CI/CD pipeline. Set to null to disable this container.
object({
# Docker repo and image tag to use as the container image for the docker image builder. This should be based on the
# Dockerfile in terraform-aws-ci/modules/ecs-deploy-runner/docker/kaniko.
container_image = object({
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
})
# An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the docker
# image builder. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
# fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
# Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
# variables (git_config and secrets_manager_env_vars).
# iam_policy = {
# S3Access = {
# actions = ["s3:*"]
# resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
# effect = "Allow"
# },
# EC2Access = {
# actions = ["ec2:*"],
# resources = ["*"]
# effect = "Allow"
# }
# }
iam_policy = map(object({
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
}))
# List of repositories that are allowed to build docker images. These should be the https git URL of the repository
# (e.g., https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
allowed_repos = list(string)
# List of repositories (matching the regex) that are allowed to build AMIs. These should be the https git URL of the repository
# (e.g., "https://github.com/gruntwork-io/.+" ).
# Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
allowed_repos_regex = list(string)
# ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that can be used for authenticating to HTTPS based git repos that contain the
# Dockerfile for building the images. The associated user is recommended to be limited to read access only.
#
# Settings for each git service provider:
#
# Github:
# - `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid Personal Access Token for the corresponding machine user.
# - `password_secrets_manager_arn` should be set to null.
#
# BitBucket:
# - `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain the bitbucket username for the corresponding machine user.
# - `password_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid App password for the corresponding machine user.
#
# GitLab:
# - `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain the hardcoded string "oauth2" (without the quotes).
# - `password_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid Personal Access Token for the corresponding machine user.
git_config = object({
username_secrets_manager_arn = string
password_secrets_manager_arn = string
})
# ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the docker build process as environment
# variables that can be passed in as build args. For example,
# secrets_manager_env_vars = {
# GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
# }
# Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
# in the container that can then be passed through to the docker build if you pass in
# `--build-arg GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`.
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
# Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
# Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
environment_vars = map(string)
})
Details
An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the docker
image builder. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
variables (git_config and secrets_manager_env_vars).
iam_policy = {
S3Access = {
actions = ["s3:*"]
resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
effect = "Allow"
},
EC2Access = {
actions = ["ec2:*"],
resources = ["*"]
effect = "Allow"
}
}
Details
List of repositories that are allowed to build docker images. These should be the https git URL of the repository
(e.g., https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
Details
List of repositories (matching the regex) that are allowed to build AMIs. These should be the https git URL of the repository
(e.g., "https://github.com/gruntwork-io/.+" ).
Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
Details
ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that can be used for authenticating to HTTPS based git repos that contain the
Dockerfile for building the images. The associated user is recommended to be limited to read access only.
Settings for each git service provider:
Github:
- `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid Personal Access Token for the corresponding machine user.
- `password_secrets_manager_arn` should be set to null.
BitBucket:
- `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain the bitbucket username for the corresponding machine user.
- `password_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid App password for the corresponding machine user.
GitLab:
- `username_secrets_manager_arn` should contain the hardcoded string "oauth2" (without the quotes).
- `password_secrets_manager_arn` should contain a valid Personal Access Token for the corresponding machine user.
Details
ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the docker build process as environment
variables that can be passed in as build args. For example,
secrets_manager_env_vars = {
GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
}
Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
in the container that can then be passed through to the docker build if you pass in
`--build-arg GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`.
Details
Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
private_subnet_idslist(string)List of IDs of private subnets that can be used for running the ECS task and Lambda function.
terraform_applier_configobject(…)Configuration options for the terraform-applier container of the ECS deploy runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure deployment actions (including automated variable updates) in the CI/CD pipeline with Terraform / Terragrunt. Set to null to disable this container.
object({
# Docker repo and image tag to use as the container image for the ami builder. This should be based on the
# Dockerfile in terraform-aws-ci/modules/ecs-deploy-runner/docker/deploy-runner.
container_image = object({
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
})
# An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
# terraform applier. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
# fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
# Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
# variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
# iam_policy = {
# S3Access = {
# actions = ["s3:*"]
# resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
# effect = "Allow"
# },
# EC2Access = {
# actions = ["ec2:*"],
# resources = ["*"]
# effect = "Allow"
# }
# }
iam_policy = map(object({
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
}))
# List of Git repository containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
# configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
# URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
# NOTE: when only a single repository is provided, this will automatically be included as a hardcoded option.
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
# List of Git repositories (matching the regex) containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
# configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
# URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
# Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
# List of variable names that are allowed to be automatically updated by the CI/CD pipeline. Recommended to set to:
# ["tag", "docker_tag", "ami_version_tag", "ami"]
allowed_update_variable_names = list(string)
# A list of Git Refs (branch or tag) that are approved for running apply on. Any git ref that does not match this
# list will not be allowed to run `apply` or `apply-all`. This is useful for protecting against internal threats
# where users have access to the CI script and bypass the approval flow by commiting a new CI flow on their branch.
# Set to null to allow all refs to apply.
allowed_apply_git_refs = list(string)
# User information to use when commiting updates to the infrastructure live configuration.
machine_user_git_info = object({
name = string
email = string
})
# The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing remote
# repository containing the live infrastructure configuration. This SSH key should be for a machine user that has write
# access to the code when using with terraform-update-variable.
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
# Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
# The following keys are supported:
#
# - github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
# - bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
# passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
# List of additional allowed options to pass to terraform plan. This is useful for passing in additional options
# that are not supported by the pipeline by default. For example, if you want to pass in the -var option,
# you would set this to ["-var"].
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
# ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the terraform/terragrunt process as
# environment variables. For example,
# secrets_manager_env_vars = {
# GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
# }
# Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
# in the container that can then be accessed through terraform/terragrunt.
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
# Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
# Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
environment_vars = map(string)
})
Details
An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
terraform applier. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
iam_policy = {
S3Access = {
actions = ["s3:*"]
resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
effect = "Allow"
},
EC2Access = {
actions = ["ec2:*"],
resources = ["*"]
effect = "Allow"
}
}
Details
List of Git repository containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
NOTE: when only a single repository is provided, this will automatically be included as a hardcoded option.
Details
List of Git repositories (matching the regex) containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
Details
List of variable names that are allowed to be automatically updated by the CI/CD pipeline. Recommended to set to:
["tag", "docker_tag", "ami_version_tag", "ami"]
Details
A list of Git Refs (branch or tag) that are approved for running apply on. Any git ref that does not match this
list will not be allowed to run `apply` or `apply-all`. This is useful for protecting against internal threats
where users have access to the CI script and bypass the approval flow by commiting a new CI flow on their branch.
Set to null to allow all refs to apply.
Details
User information to use when commiting updates to the infrastructure live configuration.
Details
The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing remote
repository containing the live infrastructure configuration. This SSH key should be for a machine user that has write
access to the code when using with terraform-update-variable.
Details
Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
The following keys are supported:
- github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
- bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
Details
List of additional allowed options to pass to terraform plan. This is useful for passing in additional options
that are not supported by the pipeline by default. For example, if you want to pass in the -var option,
you would set this to ["-var"].
Details
ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the terraform/terragrunt process as
environment variables. For example,
secrets_manager_env_vars = {
GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
}
Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
in the container that can then be accessed through terraform/terragrunt.
Details
Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
terraform_planner_configobject(…)Configuration options for the terraform-planner container of the ECS deploy runner stack. This container will be used for running infrastructure plan (including validate) actions in the CI/CD pipeline with Terraform / Terragrunt. Set to null to disable this container.
object({
# Docker repo and image tag to use as the container image for the ami builder. This should be based on the
# Dockerfile in terraform-aws-ci/modules/ecs-deploy-runner/docker/deploy-runner.
container_image = object({
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
})
# An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
# terraform planner. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
# fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
# Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
# variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
# iam_policy = {
# S3Access = {
# actions = ["s3:*"]
# resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
# effect = "Allow"
# },
# EC2Access = {
# actions = ["ec2:*"],
# resources = ["*"]
# effect = "Allow"
# }
# }
iam_policy = map(object({
resources = list(string)
actions = list(string)
effect = string
}))
# List of git repositories containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
# configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to run plan on. These should be the SSH
# git URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
# NOTE: when only a single repository is provided, this will automatically be included as a hardcoded option.
infrastructure_live_repositories = list(string)
# List of Git repositories (matching the regex) containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
# configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
# URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
# Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
infrastructure_live_repositories_regex = list(string)
# The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing the
# infrastructure live repository.
repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn = string
# Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
# The following keys are supported:
#
# - github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# - bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
# Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
# bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
# - bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
# passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
repo_access_https_tokens = map(string)
# List of additional allowed options to pass to terraform plan. This is useful for passing in additional options
# that are not supported by the pipeline by default. For example, if you want to pass in the -var option,
# you would set this to ["-var"].
additional_allowed_options = list(string)
# ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the terraform/terragrunt process as
# environment variables. For example,
# secrets_manager_env_vars = {
# GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
# }
# Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
# in the container that can then be accessed through terraform/terragrunt.
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
# Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
# Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
environment_vars = map(string)
})
Details
An object defining the IAM policy statements to attach to the IAM role associated with the ECS task for the
terraform planner. Accepts a map of objects, where the map keys are sids for IAM policy statements, and the object
fields are the resources, actions, and the effect (\"Allow\" or \"Deny\") of the statement.
Note that you do not need to explicitly grant read access to the secrets manager entries set on the other
variables (repo_access_ssh_key_secrets_manager_arn and secrets_manager_env_vars).
iam_policy = {
S3Access = {
actions = ["s3:*"]
resources = ["arn:aws:s3:::mybucket"]
effect = "Allow"
},
EC2Access = {
actions = ["ec2:*"],
resources = ["*"]
effect = "Allow"
}
}
Details
List of git repositories containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to run plan on. These should be the SSH
git URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
NOTE: when only a single repository is provided, this will automatically be included as a hardcoded option.
Details
List of Git repositories (matching the regex) containing infrastructure live configuration (top level terraform or terragrunt
configuration to deploy infrastructure) that the deploy runner is allowed to deploy. These should be the SSH git
URL of the repository (e.g., git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-ci.git).
Note that this is a list of individual regex because HCL doesn't allow bitwise operator: https://github.com/hashicorp/terraform/issues/25326
Details
The ARN of a secrets manager entry containing the raw contents of a SSH private key to use when accessing the
infrastructure live repository.
Details
Configurations for setting up private git repo access to https based git URLs for each supported VCS platform.
The following keys are supported:
- github_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitHub
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- gitlab_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a GitLab
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
- bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn : The ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager entry containing contents of a BitBucket
Personal Access Token for accessing git repos over HTTPS.
bitbucket_username is required if this is set.
- bitbucket_username : The username of the BitBucket user associated with the bitbucket token
passed in with bitbucket_token_secrets_manager_arn.
Details
List of additional allowed options to pass to terraform plan. This is useful for passing in additional options
that are not supported by the pipeline by default. For example, if you want to pass in the -var option,
you would set this to ["-var"].
Details
ARNs of AWS Secrets Manager entries that you would like to expose to the terraform/terragrunt process as
environment variables. For example,
secrets_manager_env_vars = {
GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN = "ARN_OF_PAT"
}
Will inject the secret value stored in the secrets manager entry ARN_OF_PAT as the env var `GITHUB_OAUTH_TOKEN`
in the container that can then be accessed through terraform/terragrunt.
Details
Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
vpc_idstringID of the VPC where the ECS task and Lambda function should run.
Optional
additional_container_imagesmap(object(…))Container configurations that should be added to the ECS Deploy Runner that should be added in addition to the standard containers. This can be used to customize your deployment of the ECS Deploy Runner beyond the standard use cases.
map(object({
# Docker container identifiers
docker_image = string
docker_tag = string
# Map of environment variable names to secret manager arns of secrets to share with the container during runtime.
# Note that the container processes will not be able to directly read these secrets directly using the Secrets
# Manager API (they are only available implicitly through the env vars).
secrets_manager_env_vars = map(string)
# Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
# Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
environment_vars = map(string)
# List of additional secrets manager entries that the container should have access to, but not directly injected as
# environment variables. These secrets can be read by the container processes using the Secrets Manager API, unlike
# those shared as environment variables with `secrets_manager_env_vars`.
additional_secrets_manager_arns = list(string)
# Security configuration for each script for each container. Each entry in the map corresponds to a script in the
# triggers directory. If a script is not included in the map, then the default is to allow no additional args to be
# passed in when invoked.
script_config = map(object({
# Which options and args to always pass in alongside the ones provided by the command.
# This is a map of option keys to args to pass in. Each arg in the list will be passed in as a separate option.
# E.g., if you had {'foo': ['bar', 'baz', 'car']}, then this will be: `--foo bar --foo baz --foo car`
# This will be passed in first, before the args provided by the user in the event data.
hardcoded_options = map(list(string))
# Unlike hardcoded_options, this is used for hardcoded positional args and will always be passed in at the end of
# the args list.
hardcoded_args = list(string)
# Whether or not positional args are allowed to be passed in.
allow_positional_args = bool
# This is a list of option keys that are explicitly allowed. When set, any option key that is not present in this
# list will cause an exception. Note that `null` means allow any option, as opposed to `[]` which means allow no
# option. Only one of `allowed_options` or `restricted_options` should be used.
allowed_options = list(string)
# List of options without arguments
allowed_options_without_args = list(string)
# This is a list of option keys that are not allowed. When set, any option key passed in that is in this list will
# cause an exception. Empty list means allow any option (unless restricted by allowed_options).
restricted_options = list(string)
# This is a map of option keys to a regex for specifying what args are allowed to be passed in for that option key.
# There is no restriction to the option if there is no entry in this map.
restricted_options_regex = map(string)
}))
# Whether or not the particular container is the default container for the pipeline. This container is used when no
# name is provided to the infrastructure deployer. Exactly one must be marked as the default. An arbitrary container
# will be picked amongst the list of defaults when multiple are marked as default.
# If no containers are marked as default, then the invoker lambda function always requires a container name to be
# provided.
default = bool
}))
{}Details
Map of environment variable names to secret manager arns of secrets to share with the container during runtime.
Note that the container processes will not be able to directly read these secrets directly using the Secrets
Manager API (they are only available implicitly through the env vars).
Details
Map of environment variable names to values share with the container during runtime.
Do NOT use this for sensitive variables! Use secrets_manager_env_vars for secrets.
Details
List of additional secrets manager entries that the container should have access to, but not directly injected as
environment variables. These secrets can be read by the container processes using the Secrets Manager API, unlike
those shared as environment variables with `secrets_manager_env_vars`.
Details
Security configuration for each script for each container. Each entry in the map corresponds to a script in the
triggers directory. If a script is not included in the map, then the default is to allow no additional args to be
passed in when invoked.
Details
Unlike hardcoded_options, this is used for hardcoded positional args and will always be passed in at the end of
the args list.
Details
Whether or not positional args are allowed to be passed in.
Details
This is a list of option keys that are explicitly allowed. When set, any option key that is not present in this
list will cause an exception. Note that `null` means allow any option, as opposed to `[]` which means allow no
option. Only one of `allowed_options` or `restricted_options` should be used.
Details
List of options without arguments
Details
This is a list of option keys that are not allowed. When set, any option key passed in that is in this list will
cause an exception. Empty list means allow any option (unless restricted by allowed_options).
Details
This is a map of option keys to a regex for specifying what args are allowed to be passed in for that option key.
There is no restriction to the option if there is no entry in this map.
Details
Whether or not the particular container is the default container for the pipeline. This container is used when no
name is provided to the infrastructure deployer. Exactly one must be marked as the default. An arbitrary container
will be picked amongst the list of defaults when multiple are marked as default.
If no containers are marked as default, then the invoker lambda function always requires a container name to be
provided.
artifact_configobject(…)Configuration for storing artifacts from the underlying commands. When set, stdout, stderr, and interleaved output will be stored in the configured S3 bucket. Set to null if you do not wish for artifacts to be stored. Note that when null, the args for configuring storage of outputs will not be available.
object({
# Whether to allow user to selectively decide when artifacts should be stored in S3. When true,
# users must provide `--store-outputs true` to the script args in the infrastructure-deployer call to store the
# outputs. When false, every run will be hardcoded to `--store-outputs true`.
allow_runtime_selection = bool
# S3 bucket and region (us-east-1) where the outputs will be stored.
bucket_name = string
region = string
# Key prefix to use if lambda event does not specify. Outputs will be stored at PREFIX/stdout, PREFIX/stderr, and
# PREFIX/interleaved. Note that this will overwrite the output even if the key already exists.
default_key_prefix = string
})
nullDetails
S3 bucket and region (us-east-1) where the outputs will be stored.
Details
Key prefix to use if lambda event does not specify. Outputs will be stored at PREFIX/stdout, PREFIX/stderr, and
PREFIX/interleaved. Note that this will overwrite the output even if the key already exists.
The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for encrypting log data.
nullThe number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
nullcloudwatch_log_group_for_ec2_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
nullcontainer_cpunumberThe default CPU units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The invoker allows users to override the CPU at run time, but this value will be used if the user provides no value for the CPU. Options here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
1024The default launch type of the ECS deploy runner workers. This launch type will be used if it is not overridden during invocation of the lambda function. Must be FARGATE or EC2.
"FARGATE"container_max_cpunumberThe maximum CPU units that is allowed to be specified by the user when invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
8192container_max_memorynumberThe maximum memory units that is allowed to be specified by the user when invoking the deploy runner with the Lambda function.
32768container_memorynumberThe default memory units for the instances that Fargate will spin up. The invoker allows users to override the memory at run time, but this value will be used if the user provides no value for memory. Options here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html#fargate-tasks-size.
2048docker_image_builder_hardcoded_argslist(string)Unlike hardcoded_options, this is used for hardcoded positional args and will always be passed in at the end of the args list.
[
"--idempotent"
]docker_image_builder_hardcoded_optionsmap(list(…))Which options and args to always pass in alongside the ones provided by the command. This is a map of option keys to args to pass in. Each arg in the list will be passed in as a separate option. This will be passed in first, before the args provided by the user in the event data.
map(list(string))
{}Worker configuration of a EC2 worker pool for the ECS cluster. An EC2 worker pool supports caching of Docker images, so your builds may run faster, whereas Fargate is serverless, so you have no persistent EC2 instances to manage and pay for. If null, no EC2 worker pool will be allocated and the deploy runner will be in Fargate only mode. Note that when this variable is set, this example module will automatically lookup and use the base ECS optimized AMI that AWS provides.
Any types represent complex values of variable type. For details, please consult `variables.tf` in the source repo.
nullExample
ec2_worker_pool_configuration = {
ami_filters = {
owners = ["self"]
filters = [{
name = "tag:version_tag"
values = ["v0.20.4"]
}]
}
}
Details
We expect the following attributes on this object:
- ami [string] (REQUIRED) : The ID of an AMI to use when deploying the instance. Either ami or ami_filters must be
provided.
- ami_filters [AMIFilter] (REQUIRED) : Properties on the AMI that can be used to lookup a prevuild AMI for use with
the EC2 worker pool.
- min_size [number] (default: 1) : The minimum number of EC2 Instances launchable for this ECS Cluster. Useful for
auto-scaling limits.
- max_size [number] (default: 2) : The maximum number of EC2 Instances that must be running for this ECS Cluster. We
recommend making this twice min_size, even if you don't plan on scaling the
cluster up and down, as the extra capacity will be used to deploy updates to the
cluster.
- instance_type [string] (default: m5.large) : Instance type (e.g. t2.micro) to use for the EC2 instances. We
recommend using at least large class instances.
- cloud_init_parts [map(CloudInitPart)] (default: {}) : Cloud init scripts to run on the host while it
boots. See the part blocks in
https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/template/d/cloudinit_config.html
for syntax.
- enable_cloudwatch_log_aggregation [bool] (default: true) : Whether or not to send server logs to the CloudWatch
Logs service.
- enable_cloudwatch_metrics [bool] (default: true) : Whether or not to send metrics to the CloudWatch service.
- enable_asg_cloudwatch_alarms [bool] (default: true) : Whether or not to configure cloudwatch alarms for the ASG.
- enable_fail2ban [bool] (default: true) : Whether or not to enable the fail2ban service on the server.
- enable_ip_lockdown [bool] (default: true) : Whether or not to enable the ip-lockdown service on the server.
- alarms_sns_topic_arn [string] (default: null) : The ARN of an SNS topic for cloudwatch to send alerts to.
- default_user [string] (default: ec2-user) : The default OS user that is created on the server.
ecs_deploy_runner_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply on the ECS Deploy Runner (ECS cluster, tasks, and invoker Lambda function), encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
{}The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for encrypting log data.
nullA custom name to set for the CloudWatch Log Group used to stream the container logs. When null, the Log Group will default to /ecs/{name}.
nullThe number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
nullThe ARN of the destination to deliver matching log events to. Kinesis stream or Lambda function ARN. Only applicable if ecs_task_should_create_cloudwatch_log_group is true, and container_images is non-empty.
nullThe method used to distribute log data to the destination. Only applicable when ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a kinesis stream. Valid values are Random and ByLogStream.
nullA valid CloudWatch Logs filter pattern for subscribing to a filtered stream of log events.
""ARN of an IAM role that grants Amazon CloudWatch Logs permissions to deliver ingested log events to the destination. Only applicable when ecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_subscription_destination_arn is a kinesis stream.
nullecs_task_cloudwatch_log_group_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
nullWhen true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation from the ECS Task execution. This is useful if you wish to customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS encryption. When false, AWS ECS will automatically create a basic log group to use.
trueiam_groupslist(string)List of AWS IAM groups that should be given access to invoke the deploy runner.
[]iam_roleslist(string)List of AWS IAM roles that should be given access to invoke the deploy runner.
[]iam_userslist(string)List of AWS IAM usernames that should be given access to invoke the deploy runner.
[]invoke_schedulemap(object(…))Configurations for invoking ECS Deploy Runner on a schedule. Use this to configure any periodic background jobs that you would like run through the ECS Deploy Runner (e.g., regularly running plan on your infrastructure to detect drift). Input is a map of unique schedule name to its settings.
map(object({
# Name of the container in ECS Deploy Runner that should be invoked (e.g., terraform-planner).
container_name = string
# The script within the container that should be invoked (e.g., infrastructure-deploy-script).
script = string
# The args that should be passed to the script.
args = string
# An expression that defines the schedule. For example, cron(0 20 * * ? *) or rate(5 minutes).
schedule_expression = string
}))
{}Details
The script within the container that should be invoked (e.g., infrastructure-deploy-script).
Details
The args that should be passed to the script.
Details
An expression that defines the schedule. For example, cron(0 20 * * ? *) or rate(5 minutes).
The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for encrypting log data for the invoker lambda function.
nullThe number of days to retain log events in the log group for the invoker lambda function. Refer to https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
nullinvoker_lambda_cloudwatch_log_group_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group for the invoker lambda function, encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
nullWhen true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation from the invoker lambda function execution. This is useful if you wish to customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS encryption. When false, AWS Lambda will automatically create a basic log group to use.
truekms_grant_opt_in_regionslist(string)Create multi-region resources in the specified regions. The best practice is to enable multi-region services in all enabled regions in your AWS account. This variable must NOT be set to null or empty. Otherwise, we won't know which regions to use and authenticate to, and may use some not enabled in your AWS account (e.g., GovCloud, China, etc). To get the list of regions enabled in your AWS account, you can use the AWS CLI: aws ec2 describe-regions.
[
"eu-north-1",
"ap-south-1",
"eu-west-3",
"eu-west-2",
"eu-west-1",
"ap-northeast-2",
"ap-northeast-1",
"sa-east-1",
"ca-central-1",
"ap-southeast-1",
"ap-southeast-2",
"eu-central-1",
"us-east-1",
"us-east-2",
"us-west-1",
"us-west-2"
]
Details
By default, skip regions that are not enabled in most AWS accounts:
"af-south-1", Cape Town
"ap-east-1", Hong Kong
"eu-south-1", Milan
"me-central-1", UAE
"me-south-1", Bahrain
"us-gov-east-1", GovCloud
"us-gov-west-1", GovCloud
"cn-north-1", China
"cn-northwest-1", China
"eu-central-2", Zurich
This region is enabled by default but is brand-new and some services like AWS Config don't work.
"ap-northeast-3", Asia Pacific (Osaka)
namestringName of this instance of the deploy runner stack. Used to namespace all resources.
"ecs-deploy-runner"When non-null, set the security group name of the ECS Deploy Runner ECS Task to this string. When null, a unique name will be generated by Terraform to avoid conflicts when deploying multiple instances of the ECS Deploy Runner.
nullIf true, this module will create grants for a given shared secrets KMS key. You must pass a value for shared_secrets_kms_cmk_arn if this is set to true. Defaults to false.
falseThe ARN of the KMS CMK used for sharing AWS Secrets Manager secrets between accounts.
nullWhen true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a basic log group to use.
truesnapshot_encryption_kms_cmk_arnsmap(string)Map of names to ARNs of KMS CMKs that are used to encrypt snapshots (including AMIs). This module will create the necessary KMS key grants to allow the respective deploy containers access to utilize the keys for managing the encrypted snapshots. The keys are arbitrary names that are used to identify the key.
{}When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies when targeting compliance with various security standards.
trueName of the CloudWatch Log Group used to store the log output from the Deploy Runner ECS task.
AWS ARN of the default ECS Task Definition. Can be used to trigger the ECS Task directly.
AWS ARN of the ECS Cluster that can be used to run the deploy runner task.
Map of AWS ARNs of the ECS Task Definition. There are four entries, one for each container in the standard config (docker-image-builder ; ami-builder ; terraform-planner ; terraform-applier).
ECS Task execution role ARN
Map of the families of the ECS Task Definition that is currently live. There are four entries, one for each container in the standard config (docker-image-builder ; ami-builder ; terraform-planner ; terraform-applier).
Map of AWS ARNs and names of the IAM role that will be attached to the ECS task to grant it access to AWS resources. Each container will have its own IAM role. There are four entries, one for each container in the standard config (docker-image-builder ; ami-builder ; terraform-planner ; terraform-applier).
Map of the current revision of the ECS Task Definition that is currently live. There are four entries, one for each container in the standard config (docker-image-builder ; ami-builder ; terraform-planner ; terraform-applier).
The ARN of the IAM policy that allows access to the invoke the deploy runner.
AWS ARN of the invoker lambda function that can be used to invoke a deployment.
Name of the invoker lambda function that can be used to invoke a deployment.
Security Group ID of the ECS task