Amazon Relational Database Service
Overview
This service contains code to deploy an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) cluster that can run MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, or MariaDB. The cluster is managed by AWS and automatically handles standby failover, read replicas, backups, patching, and encryption. For Aurora, use the Aurora service.
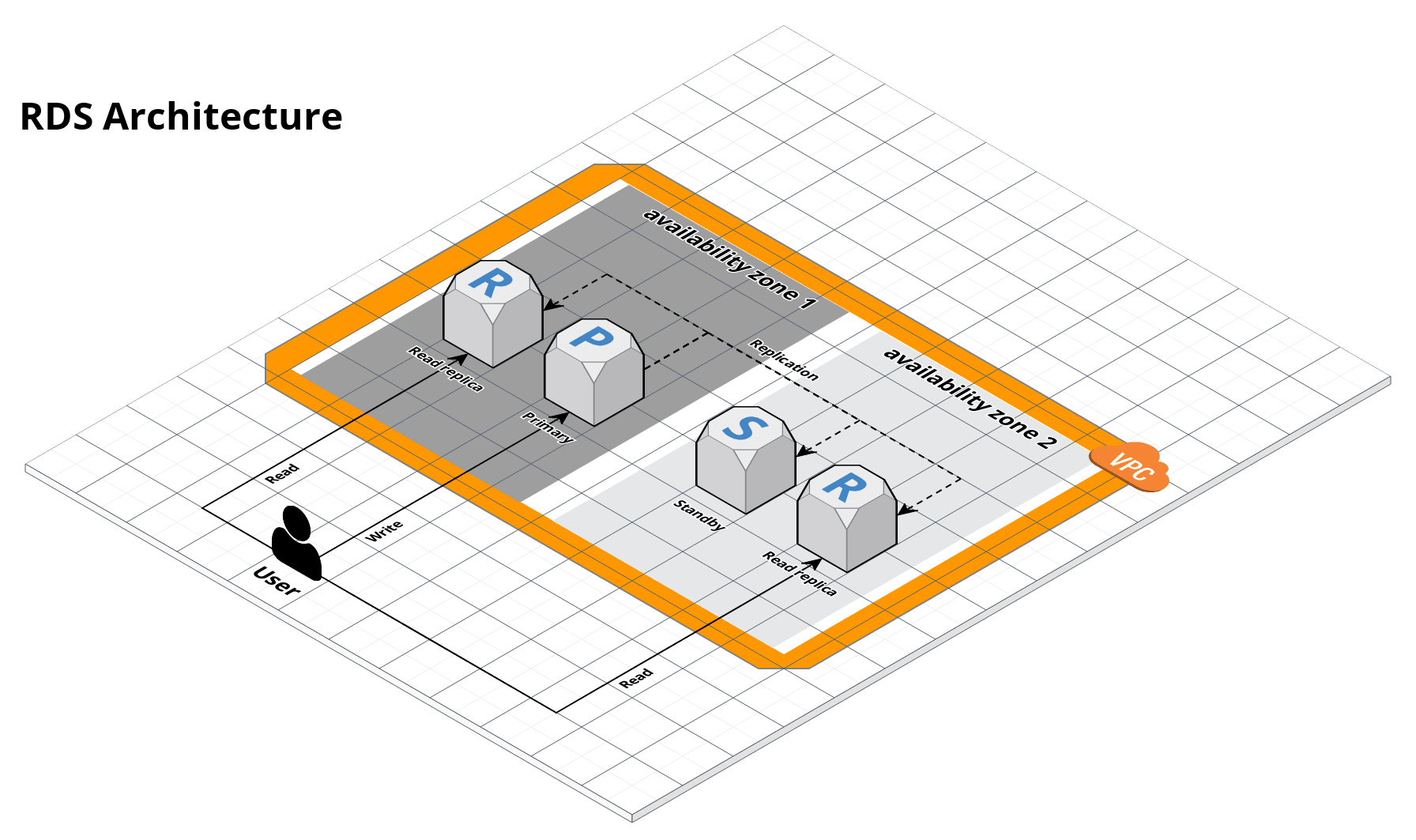 RDS architecture
RDS architecture
Features
- Deploy a fully-managed native relational database
- Supports, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and MariaDB
- Automatic failover to a standby in another availability zone
- Read replicas
- Automatic nightly snapshots
- Automatic cross account snapshots
- Automatic scaling of storage
- CloudWatch Alarms for alerting when CPU, memory, and disk metrics exceed certain thresholds
- CloudWatch dashboard widgets for RDS statistics
- Integrate with Kubernetes Service Discovery
Learn
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
- What is Amazon RDS?
- Common gotchas with RDS
- RDS documentation: Amazon’s docs for RDS that cover core concepts such as the types of databases supported, security, backup & restore, and monitoring.
- Designing Data Intensive Applications: the best book we’ve found for understanding data systems, including relational databases, NoSQL, replication, sharding, consistency, and so on.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
-
examples/for-production folder: The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog.
Sample Usage
- Terraform
- Terragrunt
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S RDS MODULE
#
# NOTE: This module uses some sensitive variables marked inline with "# SENSITIVE".
# When using values other than defaults for these variables, set them through environment variables or
# another secure method.
#
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
module "rds" {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/data-stores/rds?ref=v2.0.0"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB.
allocated_storage = <number>
# The version of var.engine to use (e.g. 8.0.17 for mysql).
engine_version = <string>
# The name used to namespace all the RDS resources created by these templates,
# including the cluster and cluster instances (e.g. mysql-stage). Must be
# unique in this region. Must be a lowercase string.
name = <string>
# The list of IDs of the subnets in which to deploy RDS. The list must only
# contain subnets in var.vpc_id.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The ID of the VPC in which to deploy RDS.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and
# disk space usage) should send notifications. Also used for the alarms if the
# share snapshot backup job fails.
alarms_sns_topic_arns = []
# The list of network CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from. One of
# var.allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or
# var.allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the
# database to be reachable.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks = []
# The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from for
# dual-stack configurations. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the
# private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS read replicas
# from for dual-stack configurations. If not set, read replica instances will
# use the same security group as the master instance.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# The list of IDs or Security Groups to allow network access to RDS from. All
# security groups must either be in the VPC specified by var.vpc_id, or a
# peered VPC with the VPC specified by var.vpc_id. One of
# var.allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or
# var.allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the
# database to be reachable.
allow_connections_from_security_groups = []
# Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be
# permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and
# will never be automatically applied.
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
# If true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be
# used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy
# can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and
# generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
allow_manage_key_permissions_with_iam = false
# Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or
# during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may
# cause degraded performance or downtime.
apply_immediately = false
# Indicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB
# instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set
# var.engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use
# 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details.
auto_minor_version_upgrade = true
# The description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Security group for the var.name DB' if not specified
aws_db_security_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to var.name
# if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_name = null
# How often, in seconds, the backup job is expected to run. This is the same
# as var.schedule_expression, but unfortunately, Terraform offers no way to
# convert rate expressions to seconds. We add a CloudWatch alarm that triggers
# if the metric in var.create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace isn't
# updated within this time period, as that indicates the backup failed to run.
backup_job_alarm_period = 3600
# Sets how the backup job alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA
# state. Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
backup_job_alarm_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must
# be 1 or greater to support read replicas.
backup_retention_period = 30
# The daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g.
# 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup
# runs.
backup_window = "06:00-07:00"
# The Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS
# instance.
ca_cert_identifier = null
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to
# this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this
# list is empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will
# be used.
cmk_administrator_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given
# permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
cmk_external_user_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this CMK
# (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this list is
# empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will be
# used.
cmk_user_iam_arns = []
# Copy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
copy_tags_to_snapshot = false
# If set to true, create a KMS CMK and use it to encrypt data on disk in the
# database. The permissions for this CMK will be assigned by the following
# variables: cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns,
# cmk_external_user_iam_arns, allow_manage_key_permissions.
create_custom_kms_key = false
# Set to true if you want a DNS record automatically created and pointed at
# the RDS endpoints.
create_route53_entry = false
# The namespace to use for the CloudWatch metric we report every time a new
# RDS snapshot is created. We add a CloudWatch alarm on this metric to notify
# us if the backup job fails to run for any reason. Defaults to the cluster
# name.
create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace = null
# Timeout for DB creating
creating_timeout = "40m"
# Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new
# parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be
# launched with the default parameter group.
custom_parameter_group = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group
# created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
custom_tags = {}
# Parameters for the cpu usage widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_cpu_usage_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the database connections widget to output for use in a
# CloudWatch dashboard.
dashboard_db_connections_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the available disk space widget to output for use in a
# CloudWatch dashboard.
dashboard_disk_space_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the available memory widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_memory_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_read_latency_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_write_latency_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# The friendly name or ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager secret that contains
# database configuration information in the format outlined by this document:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/userguide/best-practices.html.
# The engine, username, password, dbname, and port fields must be included in
# the JSON. Note that even with this precaution, this information will be
# stored in plaintext in the Terraform state file! See the following blog post
# for more details:
# https://blog.gruntwork.io/a-comprehensive-guide-to-managing-secrets-in-your-terraform-code-1d586955ace1.
# If you do not wish to use Secrets Manager, leave this as null, and use the
# master_username, master_password, db_name, engine, and port variables.
db_config_secrets_manager_id = null
# The name for your database of up to 8 alpha-numeric characters. If you do
# not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create an empty database on the RDS
# instance. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the
# description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
db_name = null
# Specifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB
# instance is deleted
delete_automated_backups = true
# Timeout for DB deleting
deleting_timeout = "60m"
# Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage,
# memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS
# topics to send notifications to using var.alarms_sns_topic_arn.
enable_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# When true, enable CloudWatch metrics for the manual snapshots created for
# the purpose of sharing with another account.
enable_cloudwatch_metrics = true
# Enable deletion protection on the RDS instance. If this is enabled, the
# database cannot be deleted prior to disabling
enable_deletion_protection = false
# Set to true to enable alarms related to performance, such as read and write
# latency alarms. Set to false to disable those alarms if you aren't sure what
# would be reasonable perf numbers for your RDS set up or if those numbers are
# too unpredictable.
enable_perf_alarms = true
# When true, enable CloudWatch alarms for the manual snapshots created for the
# purpose of sharing with another account. Only used if
# var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
enable_share_snapshot_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no
# logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit,
# error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and
# upgrade (PostgreSQL).
enabled_cloudwatch_logs_exports = []
# The DB engine to use (e.g. mysql). This can also be provided via AWS Secrets
# Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
engine = null
# The number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the
# alarm. Setting this as null (the default) will make it equal to the
# evaluation period
high_cpu_utilization_datapoints_to_alarm = null
# The number of periods over which data is compared to the specified
# threshold.
high_cpu_utilization_evaluation_periods = 3
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization
# percentage.
high_cpu_utilization_period = 60
# The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount,
# Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
high_cpu_utilization_statistic = "Average"
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance has a CPU utilization percentage above
# this threshold.
high_cpu_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_cpu_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the read latency.
high_read_latency_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance read latency (average amount of time
# taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
high_read_latency_threshold = 5
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_read_latency_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the write latency.
high_write_latency_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance write latency (average amount of time
# taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
high_write_latency_threshold = 5
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_write_latency_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The ID of the Route 53 hosted zone into which the Route 53 DNS record should
# be written
hosted_zone_id = null
# Specifies whether mappings of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
# accounts to database accounts is enabled. Disabled by default.
iam_database_authentication_enabled = false
# The instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro)
instance_type = "db.t3.micro"
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this
# implies a storage_type of 'io1'. Can only be set when storage_type is 'gp3'
# or 'io1'. Set to 0 to disable.
iops = 0
# The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK)
# that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If you leave this blank,
# the default RDS KMS key for the account will be used. If you set
# var.create_custom_kms_key to true, this value will be ignored and a custom
# key will be created and used instead.
kms_key_arn = null
# The license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for
# available license models. Set to an empty string to use the default.
license_model = null
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free disk space.
low_disk_space_available_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the amount of disk space, in Bytes, on the DB instance
# drops below this threshold.
low_disk_space_available_threshold = 1000000000
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
low_disk_space_available_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free memory.
low_memory_available_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the amount of free memory, in Bytes, on the DB instance
# drops below this threshold.
low_memory_available_threshold = 100000000
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
low_memory_available_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur
# (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or
# there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
maintenance_window = "sun:07:00-sun:08:00"
# Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets
# Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
manage_master_user_password = null
# The value to use for the master password of the database. This can also be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
master_password = null # SENSITIVE
# The value to use for the master username of the database. This can also be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
master_username = null
# When configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale
# the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore
# differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to
# allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
max_allocated_storage = 0
# The interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics
# are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring
# metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced
# Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes
# or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
monitoring_interval = 0
# The ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring
# metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but
# monitoring_role_arn is left as an empty string, a default IAM role that
# allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
monitoring_role_arn = null
# Optionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will
# default to just /.
monitoring_role_arn_path = "/"
# The name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to
# var.name-monitoring-role if not specified.
monitoring_role_name = null
# Specifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability
# zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
multi_az = false
# The number of read replicas to deploy
num_read_replicas = 0
# Name of a DB option group to associate.
option_group_name = null
# Specifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can
# be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See
# https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details.
performance_insights_enabled = false
# Amount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Valid values are
# 7, 731 (2 years) or a multiple of 31.
performance_insights_retention_period = 7
# The port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306). Alternatively, this can be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
port = null
# The domain name to create a route 53 record for the primary endpoint of the
# RDS database.
primary_domain_name = null
# If you wish to make your database accessible from the public Internet, set
# this flag to true (WARNING: NOT RECOMMENDED FOR REGULAR USAGE!!). The
# default is false, which means the database is only accessible from within
# the VPC, which is much more secure. This flag MUST be false for serverless
# mode.
publicly_accessible = false
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the
# read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means
# disable automated backups.
replica_backup_retention_period = 0
# The domain name to create a route 53 record for the read replicas of the RDS
# database.
replica_domain_name = null
# The maximum number of snapshots to keep around for the purpose of cross
# account sharing. Once this number is exceeded, a lambda function will delete
# the oldest snapshots. Only used if var.share_snapshot_with_another_account
# is true.
share_snapshot_max_snapshots = 30
# An expression that defines how often to run the lambda function to take
# snapshots for the purpose of cross account sharing. For example, cron(0 20 *
# * ? *) or rate(5 minutes). Required if
# var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true
share_snapshot_schedule_expression = null
# The ID of the AWS Account that the snapshot should be shared with. Required
# if var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
share_snapshot_with_account_id = null
# If set to true, take periodic snapshots of the RDS DB that should be shared
# with another account.
share_snapshot_with_another_account = false
# Determines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is
# deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete
# this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data! You almost
# never want to set this to true, unless you are doing automated or manual
# testing.
skip_final_snapshot = false
# If non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID.
# This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g:
# rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
snapshot_identifier = null
# Specifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
storage_encrypted = true
# The storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when
# var.storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage
# value is below a per-engine threshold.
storage_throughput = null
# The type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of
# 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose
# SSD that needs iops independently), or 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD).
storage_type = "gp2"
# Time zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by
# Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL
# User Guide
# (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone)
# for more information.
timezone = null
# The number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the
# alarm. Setting this as empty string (the default) will make it equal to the
# evaluation period
too_many_db_connections_datapoints_to_alarm = null
# The number of periods over which data is compared to the specified
# threshold.
too_many_db_connections_evaluation_periods = 3
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the number of DB connections
too_many_db_connections_period = 60
# The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount,
# Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
too_many_db_connections_statistic = "Maximum"
# Trigger an alarm if the number of connections to the DB instance goes above
# this threshold.
too_many_db_connections_threshold = null
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
too_many_db_connections_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# Timeout for DB updating
updating_timeout = "80m"
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S RDS MODULE
#
# NOTE: This module uses some sensitive variables marked inline with "# SENSITIVE".
# When using values other than defaults for these variables, set them through environment variables or
# another secure method.
#
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
terraform {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/data-stores/rds?ref=v2.0.0"
}
inputs = {
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB.
allocated_storage = <number>
# The version of var.engine to use (e.g. 8.0.17 for mysql).
engine_version = <string>
# The name used to namespace all the RDS resources created by these templates,
# including the cluster and cluster instances (e.g. mysql-stage). Must be
# unique in this region. Must be a lowercase string.
name = <string>
# The list of IDs of the subnets in which to deploy RDS. The list must only
# contain subnets in var.vpc_id.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The ID of the VPC in which to deploy RDS.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and
# disk space usage) should send notifications. Also used for the alarms if the
# share snapshot backup job fails.
alarms_sns_topic_arns = []
# The list of network CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from. One of
# var.allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or
# var.allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the
# database to be reachable.
allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks = []
# The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from for
# dual-stack configurations. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the
# private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
# The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS read replicas
# from for dual-stack configurations. If not set, read replica instances will
# use the same security group as the master instance.
allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blocks_to_read_replicas = []
# The list of IDs or Security Groups to allow network access to RDS from. All
# security groups must either be in the VPC specified by var.vpc_id, or a
# peered VPC with the VPC specified by var.vpc_id. One of
# var.allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or
# var.allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the
# database to be reachable.
allow_connections_from_security_groups = []
# Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be
# permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and
# will never be automatically applied.
allow_major_version_upgrade = true
# If true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be
# used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy
# can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and
# generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
allow_manage_key_permissions_with_iam = false
# Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or
# during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may
# cause degraded performance or downtime.
apply_immediately = false
# Indicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB
# instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set
# var.engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use
# 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance.html#engine_version
# for more details.
auto_minor_version_upgrade = true
# The description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to
# 'Security group for the var.name DB' if not specified
aws_db_security_group_description = null
# The name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to var.name
# if not specified.
aws_db_security_group_name = null
# How often, in seconds, the backup job is expected to run. This is the same
# as var.schedule_expression, but unfortunately, Terraform offers no way to
# convert rate expressions to seconds. We add a CloudWatch alarm that triggers
# if the metric in var.create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace isn't
# updated within this time period, as that indicates the backup failed to run.
backup_job_alarm_period = 3600
# Sets how the backup job alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA
# state. Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
backup_job_alarm_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must
# be 1 or greater to support read replicas.
backup_retention_period = 30
# The daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g.
# 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup
# runs.
backup_window = "06:00-07:00"
# The Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS
# instance.
ca_cert_identifier = null
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to
# this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this
# list is empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will
# be used.
cmk_administrator_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given
# permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
cmk_external_user_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this CMK
# (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this list is
# empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will be
# used.
cmk_user_iam_arns = []
# Copy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
copy_tags_to_snapshot = false
# If set to true, create a KMS CMK and use it to encrypt data on disk in the
# database. The permissions for this CMK will be assigned by the following
# variables: cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns,
# cmk_external_user_iam_arns, allow_manage_key_permissions.
create_custom_kms_key = false
# Set to true if you want a DNS record automatically created and pointed at
# the RDS endpoints.
create_route53_entry = false
# The namespace to use for the CloudWatch metric we report every time a new
# RDS snapshot is created. We add a CloudWatch alarm on this metric to notify
# us if the backup job fails to run for any reason. Defaults to the cluster
# name.
create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace = null
# Timeout for DB creating
creating_timeout = "40m"
# Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new
# parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be
# launched with the default parameter group.
custom_parameter_group = null
# A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group
# created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
custom_tags = {}
# Parameters for the cpu usage widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_cpu_usage_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the database connections widget to output for use in a
# CloudWatch dashboard.
dashboard_db_connections_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the available disk space widget to output for use in a
# CloudWatch dashboard.
dashboard_disk_space_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the available memory widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_memory_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_read_latency_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch
# dashboard.
dashboard_write_latency_widget_parameters = {"height":6,"period":60,"width":8}
# The friendly name or ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager secret that contains
# database configuration information in the format outlined by this document:
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/userguide/best-practices.html.
# The engine, username, password, dbname, and port fields must be included in
# the JSON. Note that even with this precaution, this information will be
# stored in plaintext in the Terraform state file! See the following blog post
# for more details:
# https://blog.gruntwork.io/a-comprehensive-guide-to-managing-secrets-in-your-terraform-code-1d586955ace1.
# If you do not wish to use Secrets Manager, leave this as null, and use the
# master_username, master_password, db_name, engine, and port variables.
db_config_secrets_manager_id = null
# The name for your database of up to 8 alpha-numeric characters. If you do
# not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create an empty database on the RDS
# instance. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the
# description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
db_name = null
# Specifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB
# instance is deleted
delete_automated_backups = true
# Timeout for DB deleting
deleting_timeout = "60m"
# Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage,
# memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS
# topics to send notifications to using var.alarms_sns_topic_arn.
enable_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# When true, enable CloudWatch metrics for the manual snapshots created for
# the purpose of sharing with another account.
enable_cloudwatch_metrics = true
# Enable deletion protection on the RDS instance. If this is enabled, the
# database cannot be deleted prior to disabling
enable_deletion_protection = false
# Set to true to enable alarms related to performance, such as read and write
# latency alarms. Set to false to disable those alarms if you aren't sure what
# would be reasonable perf numbers for your RDS set up or if those numbers are
# too unpredictable.
enable_perf_alarms = true
# When true, enable CloudWatch alarms for the manual snapshots created for the
# purpose of sharing with another account. Only used if
# var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
enable_share_snapshot_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no
# logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit,
# error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and
# upgrade (PostgreSQL).
enabled_cloudwatch_logs_exports = []
# The DB engine to use (e.g. mysql). This can also be provided via AWS Secrets
# Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
engine = null
# The number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the
# alarm. Setting this as null (the default) will make it equal to the
# evaluation period
high_cpu_utilization_datapoints_to_alarm = null
# The number of periods over which data is compared to the specified
# threshold.
high_cpu_utilization_evaluation_periods = 3
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization
# percentage.
high_cpu_utilization_period = 60
# The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount,
# Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
high_cpu_utilization_statistic = "Average"
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance has a CPU utilization percentage above
# this threshold.
high_cpu_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_cpu_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the read latency.
high_read_latency_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance read latency (average amount of time
# taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
high_read_latency_threshold = 5
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_read_latency_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the write latency.
high_write_latency_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the DB instance write latency (average amount of time
# taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
high_write_latency_threshold = 5
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_write_latency_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The ID of the Route 53 hosted zone into which the Route 53 DNS record should
# be written
hosted_zone_id = null
# Specifies whether mappings of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
# accounts to database accounts is enabled. Disabled by default.
iam_database_authentication_enabled = false
# The instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro)
instance_type = "db.t3.micro"
# The amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this
# implies a storage_type of 'io1'. Can only be set when storage_type is 'gp3'
# or 'io1'. Set to 0 to disable.
iops = 0
# The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK)
# that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If you leave this blank,
# the default RDS KMS key for the account will be used. If you set
# var.create_custom_kms_key to true, this value will be ignored and a custom
# key will be created and used instead.
kms_key_arn = null
# The license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for
# available license models. Set to an empty string to use the default.
license_model = null
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free disk space.
low_disk_space_available_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the amount of disk space, in Bytes, on the DB instance
# drops below this threshold.
low_disk_space_available_threshold = 1000000000
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
low_disk_space_available_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free memory.
low_memory_available_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the amount of free memory, in Bytes, on the DB instance
# drops below this threshold.
low_memory_available_threshold = 100000000
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
low_memory_available_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur
# (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or
# there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
maintenance_window = "sun:07:00-sun:08:00"
# Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets
# Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
manage_master_user_password = null
# The value to use for the master password of the database. This can also be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
master_password = null # SENSITIVE
# The value to use for the master username of the database. This can also be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
master_username = null
# When configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale
# the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore
# differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to
# allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
max_allocated_storage = 0
# The interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics
# are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring
# metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced
# Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes
# or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
monitoring_interval = 0
# The ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring
# metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but
# monitoring_role_arn is left as an empty string, a default IAM role that
# allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
monitoring_role_arn = null
# Optionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will
# default to just /.
monitoring_role_arn_path = "/"
# The name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to
# var.name-monitoring-role if not specified.
monitoring_role_name = null
# Specifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability
# zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
multi_az = false
# The number of read replicas to deploy
num_read_replicas = 0
# Name of a DB option group to associate.
option_group_name = null
# Specifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can
# be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See
# https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details.
performance_insights_enabled = false
# Amount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Valid values are
# 7, 731 (2 years) or a multiple of 31.
performance_insights_retention_period = 7
# The port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306). Alternatively, this can be
# provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of
# db_config_secrets_manager_id.
port = null
# The domain name to create a route 53 record for the primary endpoint of the
# RDS database.
primary_domain_name = null
# If you wish to make your database accessible from the public Internet, set
# this flag to true (WARNING: NOT RECOMMENDED FOR REGULAR USAGE!!). The
# default is false, which means the database is only accessible from within
# the VPC, which is much more secure. This flag MUST be false for serverless
# mode.
publicly_accessible = false
# How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the
# read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means
# disable automated backups.
replica_backup_retention_period = 0
# The domain name to create a route 53 record for the read replicas of the RDS
# database.
replica_domain_name = null
# The maximum number of snapshots to keep around for the purpose of cross
# account sharing. Once this number is exceeded, a lambda function will delete
# the oldest snapshots. Only used if var.share_snapshot_with_another_account
# is true.
share_snapshot_max_snapshots = 30
# An expression that defines how often to run the lambda function to take
# snapshots for the purpose of cross account sharing. For example, cron(0 20 *
# * ? *) or rate(5 minutes). Required if
# var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true
share_snapshot_schedule_expression = null
# The ID of the AWS Account that the snapshot should be shared with. Required
# if var.share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
share_snapshot_with_account_id = null
# If set to true, take periodic snapshots of the RDS DB that should be shared
# with another account.
share_snapshot_with_another_account = false
# Determines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is
# deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete
# this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data! You almost
# never want to set this to true, unless you are doing automated or manual
# testing.
skip_final_snapshot = false
# If non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID.
# This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g:
# rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
snapshot_identifier = null
# Specifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
storage_encrypted = true
# The storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when
# var.storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage
# value is below a per-engine threshold.
storage_throughput = null
# The type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of
# 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose
# SSD that needs iops independently), or 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD).
storage_type = "gp2"
# Time zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by
# Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL
# User Guide
# (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone)
# for more information.
timezone = null
# The number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the
# alarm. Setting this as empty string (the default) will make it equal to the
# evaluation period
too_many_db_connections_datapoints_to_alarm = null
# The number of periods over which data is compared to the specified
# threshold.
too_many_db_connections_evaluation_periods = 3
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the number of DB connections
too_many_db_connections_period = 60
# The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount,
# Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
too_many_db_connections_statistic = "Maximum"
# Trigger an alarm if the number of connections to the DB instance goes above
# this threshold.
too_many_db_connections_threshold = null
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
too_many_db_connections_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# Timeout for DB updating
updating_timeout = "80m"
}
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
allocated_storagenumberThe amount of storage space the DB should use, in GB.
engine_versionstringThe version of engine to use (e.g. 8.0.17 for mysql).
namestringThe name used to namespace all the RDS resources created by these templates, including the cluster and cluster instances (e.g. mysql-stage). Must be unique in this region. Must be a lowercase string.
subnet_idslist(string)The list of IDs of the subnets in which to deploy RDS. The list must only contain subnets in vpc_id.
vpc_idstringThe ID of the VPC in which to deploy RDS.
Optional
alarms_sns_topic_arnslist(string)The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and disk space usage) should send notifications. Also used for the alarms if the share snapshot backup job fails.
[]allow_connections_from_cidr_blockslist(string)The list of network CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from. One of allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the database to be reachable.
[]allow_connections_from_ipv6_cidr_blockslist(string)The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS from for dual-stack configurations. Should typically be the IPv6 CIDR blocks of the private app subnet in this VPC plus the private subnet in the mgmt VPC.
[]The list of IPv6 CIDR blocks to allow network access to RDS read replicas from for dual-stack configurations. If not set, read replica instances will use the same security group as the master instance.
[]allow_connections_from_security_groupslist(string)The list of IDs or Security Groups to allow network access to RDS from. All security groups must either be in the VPC specified by vpc_id, or a peered VPC with the VPC specified by vpc_id. One of allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the database to be reachable.
[]Indicates whether major version upgrades (e.g. 9.4.x to 9.5.x) will ever be permitted. Note that these updates must always be manually performed and will never be automatically applied.
trueIf true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
falseSpecifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may cause degraded performance or downtime.
falseIndicates that minor engine upgrades will be applied automatically to the DB instance during the maintenance window. If set to true, you should set engine_version to MAJOR.MINOR and omit the .PATCH at the end (e.g., use 5.7 and not 5.7.11); otherwise, you'll get Terraform state drift. See https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/db_instance.html#engine_version for more details.
trueThe description of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to 'Security group for the name DB' if not specified
nullThe name of the aws_db_security_group that is created. Defaults to name if not specified.
nullbackup_job_alarm_periodnumberHow often, in seconds, the backup job is expected to run. This is the same as schedule_expression, but unfortunately, Terraform offers no way to convert rate expressions to seconds. We add a CloudWatch alarm that triggers if the metric in create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace isn't updated within this time period, as that indicates the backup failed to run.
3600Details
Default to hourly
Sets how the backup job alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"backup_retention_periodnumberHow many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas.
30backup_windowstringThe daily time range during which automated backups are created (e.g. 04:00-09:00). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded while a backup runs.
"06:00-07:00"ca_cert_identifierstringThe Certificate Authority (CA) certificates bundle to use on the RDS instance.
nullcmk_administrator_iam_arnslist(string)A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this list is empty, and kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will be used.
[]cmk_external_user_iam_arnslist(string)A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
[]cmk_user_iam_arnslist(object(…))A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this list is empty, and kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will be used.
list(object({
name = list(string)
conditions = list(object({
test = string
variable = string
values = list(string)
}))
}))
[]Example
[
{
name = "arn:aws:iam::0000000000:user/dev"
conditions = [{
test = "StringLike"
variable = "kms:ViaService"
values = ["s3.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com"]
}]
},
]
Copy all the RDS instance tags to snapshots. Default is false.
falseIf set to true, create a KMS CMK and use it to encrypt data on disk in the database. The permissions for this CMK will be assigned by the following variables: cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns, cmk_external_user_iam_arns, allow_manage_key_permissions.
falseSet to true if you want a DNS record automatically created and pointed at the RDS endpoints.
falseThe namespace to use for the CloudWatch metric we report every time a new RDS snapshot is created. We add a CloudWatch alarm on this metric to notify us if the backup job fails to run for any reason. Defaults to the cluster name.
nullcreating_timeoutstringTimeout for DB creating
"40m"custom_parameter_groupobject(…)Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB. This will create a new parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be launched with the default parameter group.
object({
# Name of the parameter group to create
name = string
# Description of the parameter group to create
description = string
# The family of the DB parameter group.
family = string
# The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
parameters = list(object({
# Parameter name to configure.
name = string
# Vaue to set the parameter.
value = string
# When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
apply_method = string
}))
})
nullDetails
Description of the parameter group to create
Details
The family of the DB parameter group.
Details
The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
Details
Vaue to set the parameter.
Details
When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
custom_tagsmap(string)A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS Instance and the Security Group created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
{}Parameters for the cpu usage widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
Parameters for the database connections widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
Parameters for the available disk space widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
dashboard_memory_widget_parametersobject(…)Parameters for the available memory widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
Details
The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
space.
The friendly name or ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager secret that contains database configuration information in the format outlined by this document: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/userguide/best-practices.html. The engine, username, password, dbname, and port fields must be included in the JSON. Note that even with this precaution, this information will be stored in plaintext in the Terraform state file! See the following blog post for more details: https://blog.gruntwork.io/a-comprehensive-guide-to-managing-secrets-in-your-terraform-code-1d586955ace1. If you do not wish to use Secrets Manager, leave this as null, and use the master_username, master_password, db_name, engine, and port variables.
nulldb_namestringThe name for your database of up to 8 alpha-numeric characters. If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create an empty database on the RDS instance. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullSpecifies whether to remove automated backups immediately after the DB instance is deleted
truedeleting_timeoutstringTimeout for DB deleting
"60m"Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage, memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS topics to send notifications to using alarms_sns_topic_arn.
trueWhen true, enable CloudWatch metrics for the manual snapshots created for the purpose of sharing with another account.
trueEnable deletion protection on the RDS instance. If this is enabled, the database cannot be deleted prior to disabling
falseSet to true to enable alarms related to performance, such as read and write latency alarms. Set to false to disable those alarms if you aren't sure what would be reasonable perf numbers for your RDS set up or if those numbers are too unpredictable.
trueWhen true, enable CloudWatch alarms for the manual snapshots created for the purpose of sharing with another account. Only used if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
trueenabled_cloudwatch_logs_exportslist(string)List of log types to enable for exporting to CloudWatch logs. If omitted, no logs will be exported. Valid values (depending on engine): alert, audit, error, general, listener, slowquery, trace, postgresql (PostgreSQL) and upgrade (PostgreSQL).
[]enginestringThe DB engine to use (e.g. mysql). This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullThe number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the alarm. Setting this as null (the default) will make it equal to the evaluation period
nullThe number of periods over which data is compared to the specified threshold.
3The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization percentage.
60The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount, Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
"Average"Trigger an alarm if the DB instance has a CPU utilization percentage above this threshold.
90Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"high_read_latency_periodnumberThe period, in seconds, over which to measure the read latency.
60Trigger an alarm if the DB instance read latency (average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
5Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"The period, in seconds, over which to measure the write latency.
60Trigger an alarm if the DB instance write latency (average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
5Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"hosted_zone_idstringThe ID of the Route 53 hosted zone into which the Route 53 DNS record should be written
nullSpecifies whether mappings of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) accounts to database accounts is enabled. Disabled by default.
falseinstance_typestringThe instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.t3.micro)
"db.t3.micro"iopsnumberThe amount of provisioned IOPS for the primary instance. Setting this implies a storage_type of 'io1'. Can only be set when storage_type is 'gp3' or 'io1'. Set to 0 to disable.
0kms_key_arnstringThe Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK) that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If you leave this blank, the default RDS KMS key for the account will be used. If you set create_custom_kms_key to true, this value will be ignored and a custom key will be created and used instead.
nulllicense_modelstringThe license model to use for this DB. Check the docs for your RDS DB for available license models. Set to an empty string to use the default.
nullThe period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free disk space.
60Trigger an alarm if the amount of disk space, in Bytes, on the DB instance drops below this threshold.
1000000000Details
Default is 1GB (1 billion bytes)
Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free memory.
60Trigger an alarm if the amount of free memory, in Bytes, on the DB instance drops below this threshold.
100000000Details
Default is 100MB (100 million bytes)
Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"maintenance_windowstringThe weekly day and time range during which system maintenance can occur (e.g. wed:04:00-wed:04:30). Time zone is UTC. Performance may be degraded or there may even be a downtime during maintenance windows.
"sun:07:00-sun:08:00"Set to true to allow RDS to manage the master user password in Secrets Manager. Cannot be set if password is provided.
nullmaster_passwordstringThe value to use for the master password of the database. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullmaster_usernamestringThe value to use for the master username of the database. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullmax_allocated_storagenumberWhen configured, the upper limit to which Amazon RDS can automatically scale the storage of the DB instance. Configuring this will automatically ignore differences to allocated_storage. Must be greater than or equal to allocated_storage or 0 to disable Storage Autoscaling.
0monitoring_intervalnumberThe interval, in seconds, between points when Enhanced Monitoring metrics are collected for the DB instance. To disable collecting Enhanced Monitoring metrics, specify 0. Valid Values: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60. Enhanced Monitoring metrics are useful when you want to see how different processes or threads on a DB instance use the CPU.
0monitoring_role_arnstringThe ARN for the IAM role that permits RDS to send enhanced monitoring metrics to CloudWatch Logs. If monitoring_interval is greater than 0, but monitoring_role_arn is left as an empty string, a default IAM role that allows enhanced monitoring will be created.
nullmonitoring_role_arn_pathstringOptionally add a path to the IAM monitoring role. If left blank, it will default to just /.
"/"monitoring_role_namestringThe name of the enhanced_monitoring_role that is created. Defaults to name-monitoring-role if not specified.
nullmulti_azboolSpecifies if a standby instance should be deployed in another availability zone. If the primary fails, this instance will automatically take over.
falsenum_read_replicasnumberThe number of read replicas to deploy
0option_group_namestringName of a DB option group to associate.
nullSpecifies whether Performance Insights are enabled. Performance Insights can be enabled for specific versions of database engines. See https://aws.amazon.com/rds/performance-insights/ for more details.
falseAmount of time in days to retain Performance Insights data. Valid values are 7, 731 (2 years) or a multiple of 31.
7portnumberThe port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306). Alternatively, this can be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullprimary_domain_namestringThe domain name to create a route 53 record for the primary endpoint of the RDS database.
nullIf you wish to make your database accessible from the public Internet, set this flag to true (WARNING: NOT RECOMMENDED FOR REGULAR USAGE!!). The default is false, which means the database is only accessible from within the VPC, which is much more secure. This flag MUST be false for serverless mode.
falseHow many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up on the read replicas. Must be 1 or greater to support read replicas. 0 means disable automated backups.
0replica_domain_namestringThe domain name to create a route 53 record for the read replicas of the RDS database.
nullThe maximum number of snapshots to keep around for the purpose of cross account sharing. Once this number is exceeded, a lambda function will delete the oldest snapshots. Only used if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
30An expression that defines how often to run the lambda function to take snapshots for the purpose of cross account sharing. For example, cron(0 20 * * ? *) or rate(5 minutes). Required if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true
nullThe ID of the AWS Account that the snapshot should be shared with. Required if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
nullIf set to true, take periodic snapshots of the RDS DB that should be shared with another account.
falseDetermines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data! You almost never want to set this to true, unless you are doing automated or manual testing.
falsesnapshot_identifierstringIf non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID. This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g: rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
nullSpecifies whether the DB instance is encrypted.
truestorage_throughputnumberThe storage throughput value for the DB instance. Can only be set when storage_type is 'gp3'. Cannot be specified if the allocated_storage value is below a per-engine threshold.
nullstorage_typestringThe type of storage to use for the primary instance. Must be one of 'standard' (magnetic), 'gp2' (general purpose SSD), 'gp3' (general purpose SSD that needs iops independently), or 'io1' (provisioned IOPS SSD).
"gp2"timezonestringTime zone of the DB instance. timezone is currently only supported by Microsoft SQL Server. The timezone can only be set on creation. See MSSQL User Guide (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/CHAP_SQLServer.html#SQLServer.Concepts.General.TimeZone) for more information.
nullThe number of datapoints in CloudWatch Metric statistic, which triggers the alarm. Setting this as empty string (the default) will make it equal to the evaluation period
nullThe number of periods over which data is compared to the specified threshold.
3The period, in seconds, over which to measure the number of DB connections
60The statistic to apply to the alarm's associated metric. [SampleCount, Average, Sum, Minimum, Maximum]
"Maximum"Trigger an alarm if the number of connections to the DB instance goes above this threshold.
nullDetails
The max number of connections allowed by RDS depends a) the type of DB, b) the DB instance type, and c) the
use case, and it can vary from ~30 all the way up to 5,000, so we cannot pick a reasonable default here.
Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"updating_timeoutstringTimeout for DB updating
"80m"A list of all the CloudWatch Dashboard metric widgets available in this module.
The name of the empty database created on this RDS DB instance.
The ARN of master user secret. Only available when manage_master_user_password is set to true
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs CPU usage (percentage) on the RDS DB instance.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the number of active database connections on the RDS DB Instance.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs available disk space (in bytes) on the RDS DB instance.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs available memory (in bytes) on the RDS DB instance.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation on reads.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation on writes.
The name of the RDS DB instance.
The number of read replicas for the RDS DB instance.
The port of the RDS DB instance.
The ARN of the RDS DB instance.
The endpoint of the RDS DB instance that you can make requests to.
The host portion of the RDS DB instance endpoint. primary_endpoint is in the form '<host>:<port>', and this output returns just the host part.
The ID of the RDS DB instance.
A list of ARNs of the RDS DB instance's read replicas.
A list of endpoints of the RDS DB instance's read replicas.
A list of IDs of the RDS DB instance's read replicas.
The ID of the Security Group that controls access to the RDS DB instance.