OpenVPN Server
Overview
This service deploys an OpenVPN Server.
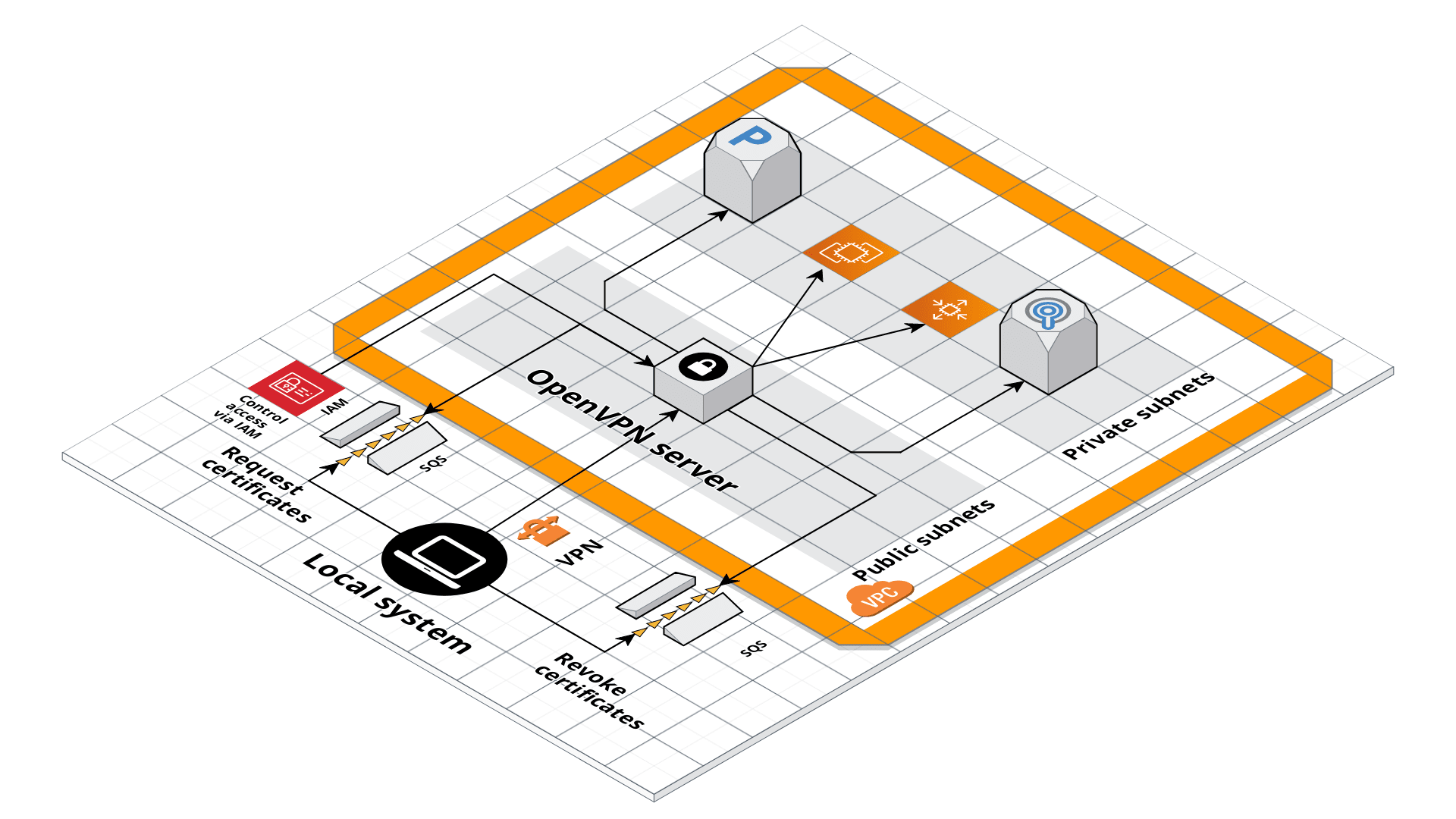 OpenVPN server architecture
OpenVPN server architecture
This server acts as the entrypoint to the VPC in which it is deployed. You must connect to it with an OpenVPN client before you can connect to any of your other servers, which are in private subnets. This way, you minimize the surface area you expose to attackers, and can focus all your efforts on locking down just a single server.
Features
- An AMI to run on the OpenVPN Server
- An Auto Scaling Group of size 1 (for fault tolerance)
- An Elastic IP Address (EIP)
- IAM Role and IAM instance profile
- Security group.
- A DNS record
- Harden the OS by installing
fail2ban,ntp,auto-update,ip-lockdown, and more - Send all logs and metrics to CloudWatch
- Configure alerts in CloudWatch for CPU, memory, and disk space usage
- Manage SSH access with IAM groups using
ssh-grunt
Under the hood, this is all implemented using Terraform modules from the Gruntwork terraform-aws-openvpn repo.
Learn
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
Core concepts
To understand core concepts like why you should use an OpenVPN server, how to connect to the vpn, how to use the VPN server to connect to other systems on the AWS VPC, see the openvpn-server documentation documentation in the package-openvpn repo.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-production folder: The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, configure CI / CD for your apps and infrastructure.
Sample Usage
- Terraform
- Terragrunt
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S OPENVPN-SERVER MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
module "openvpn_server" {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/mgmt/openvpn-server?ref=v2.0.0"
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# A list of IP address ranges in CIDR format from which VPN access will be
# permitted. Attempts to access the OpenVPN Server from all other IP addresses
# will be blocked.
allow_vpn_from_cidr_list = <list(string)>
# The AMI to run on the OpenVPN Server. This should be built from the Packer
# template under openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. One of var.ami or
# var.ami_filters is required. Set to null if looking up the ami with filters.
ami = <string>
# Properties on the AMI that can be used to lookup a prebuilt AMI for use with
# the OpenVPN server. You can build the AMI using the Packer template
# openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. Only used if var.ami is null. One of var.ami
# or var.ami_filters is required. Set to null if passing the ami ID directly.
ami_filters = <object(
owners = list(string)
filters = list(object(
name = string
values = list(string)
))
)>
# The name of the S3 bucket that will be used to backup PKI secrets. This is a
# required variable because bucket names must be globally unique across all
# AWS customers.
backup_bucket_name = <string>
# An object with fields for the country, state, locality, organization,
# organizational unit, and email address to use with the OpenVPN CA
# certificate.
ca_cert_fields = <object(
ca_country = string
ca_state = string
ca_locality = string
ca_org = string
ca_org_unit = string
ca_email = string
)>
# The ids of the subnets where this server should be deployed.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The ID of the VPC in which to deploy the OpenVPN server.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and
# disk space usage) should send notifications.
alarms_sns_topic_arn = []
# If true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be
# used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy
# can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and
# generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
allow_manage_key_permissions_with_iam = false
# The IP address ranges in CIDR format from which to allow incoming SSH
# requests to the OpenVPN server.
allow_ssh_from_cidr_list = []
# The IDs of security groups from which to allow incoming SSH requests to the
# OpenVPN server.
allow_ssh_from_security_group_ids = []
# The base domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Used to lookup the
# Hosted Zone ID to use for creating the Route 53 domain entry. Only used if
# var.create_route53_entry is true.
base_domain_name = null
# Tags to use to filter the Route 53 Hosted Zones that might match
# var.domain_name.
base_domain_name_tags = {}
# Cloud init scripts to run on the OpenVPN server while it boots. See the part
# blocks in
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/template/d/cloudinit_config.html for
# syntax.
cloud_init_parts = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to
# this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this
# list is empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will
# be used.
cmk_administrator_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given
# permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
cmk_external_user_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this KMS
# Master Key (e.g. arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/foo).
cmk_user_iam_arns = []
# Set to true to add var.domain_name as a Route 53 DNS A record for the
# OpenVPN server
create_route53_entry = false
# The default OS user for the OpenVPN AMI. For AWS Ubuntu AMIs, which is what
# the Packer template in openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl uses, the default OS
# user is 'ubuntu'.
default_user = "ubuntu"
# The domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Only used if
# var.create_route53_entry is true. If null, set to <NAME>.<BASE_DOMAIN_NAME>.
domain_name = null
# If true, the launched EC2 instance will be EBS-optimized. Note that for most
# instance types, EBS optimization does not incur additional cost, and that
# many newer EC2 instance types have EBS optimization enabled by default.
# However, if you are running previous generation instances, there may be an
# additional cost per hour to run your instances with EBS optimization
# enabled. Please see:
# https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/#EBS-Optimized_Instances
ebs_optimized = true
# Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage,
# memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS
# topics to send notifications to using var.alarms_sns_topic_arn.
enable_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# Set to true to send logs to CloudWatch. This is useful in combination with
# https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/logs/cloudwatch-log-aggregation-scripts
# to do log aggregation in CloudWatch.
enable_cloudwatch_log_aggregation = true
# Set to true to add IAM permissions to send custom metrics to CloudWatch.
# This is useful in combination with
# https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/agents/cloudwatch-agent
# to get memory and disk metrics in CloudWatch for your OpenVPN server.
enable_cloudwatch_metrics = true
# Enable fail2ban to block brute force log in attempts. Defaults to true.
enable_fail2ban = true
# Enable ip-lockdown to block access to the instance metadata. Defaults to
# true.
enable_ip_lockdown = true
# Set to true to add IAM permissions for ssh-grunt
# (https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-security/tree/master/modules/ssh-grunt),
# which will allow you to manage SSH access via IAM groups.
enable_ssh_grunt = true
# The ARNs of external AWS accounts where your IAM users are defined. This
# module will create IAM roles that users in those accounts will be able to
# assume to get access to the request/revocation SQS queues.
external_account_arns = []
# Since our IAM users are defined in a separate AWS account, this variable is
# used to specify the ARN of an IAM role that allows ssh-grunt to retrieve IAM
# group and public SSH key info from that account.
external_account_ssh_grunt_role_arn = ""
# When a terraform destroy is run, should the backup s3 bucket be destroyed
# even if it contains files. Should only be set to true for
# testing/development
force_destroy = false
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization percentage
# for the ASG.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster CPU utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the root disk utilization
# percentage for the ASG.
high_asg_disk_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster root disk utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_disk_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_disk_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the Memory utilization
# percentage for the ASG.
high_asg_memory_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster Memory utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_memory_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_memory_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The ID of the Route 53 Hosted Zone in which the domain should be created.
# Only used if var.create_route53_entry is true. If null, lookup the hosted
# zone ID using the var.base_domain_name.
hosted_zone_id = null
# The type of instance to run for the OpenVPN Server
instance_type = "t3.micro"
# The name of a Key Pair that can be used to SSH to this instance. Leave blank
# if you don't want to enable Key Pair auth.
keypair_name = null
# The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK)
# that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If null, a key will be
# created with permissions assigned by the following variables:
# cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns, cmk_external_user_iam_arns,
# allow_manage_key_permissions.
kms_key_arn = null
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification list
# requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed with
# 'openvpn-lists-'.
list_queue_name = "queue"
# The name of the OpenVPN Server and the other resources created by these
# templates
name = "vpn"
# Tags to apply to every resource created by the openvpn-server module.
openvpn_server_tags = {}
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive new certificate
# requests.
request_queue_name = "queue"
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification
# revocation requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed
# with 'openvpn-requests-'.
revocation_queue_name = "queue"
# The size of the OpenVPN EC2 instance root volume, in GB.
root_volume_size = 8
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a
# basic log group to use.
should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# If you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which
# users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server. This value is only used
# if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
ssh_grunt_iam_group = "ssh-grunt-users"
# If you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which
# users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server with sudo permissions.
# This value is only used if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
ssh_grunt_iam_group_sudo = "ssh-grunt-sudo-users"
# The tenancy of this server. Must be one of: default, dedicated, or host.
tenancy = "default"
# Set this variable to true to enable the use of Instance Metadata Service
# Version 1 in this module's aws_launch_template. Note that while IMDsv2 is
# preferred due to its special security hardening, we allow this in order to
# support the use case of AMIs built outside of these modules that depend on
# IMDSv1.
use_imdsv1 = true
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
# When true, generate Diffie-Hellman parameters using strong primes. Note that
# while stronger primes make the keys more cryptographically secure, the
# effective security gains are known to be insignificant in practice.
use_strong_prime = false
# A list of CIDR ranges to be routed over the VPN.
vpn_route_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of domains to push down to the client to resolve over VPN. This will
# configure the OpenVPN server to pass through domains that should be resolved
# over the VPN connection (as opposed to the locally configured resolver) to
# the client. Note that for each domain, all subdomains will be resolved as
# well. E.g., if you pass in 'mydomain.local', subdomains such as
# 'hello.world.mydomain.local' and 'example.mydomain.local' will also be
# forwarded to through the VPN server.
vpn_search_domains = []
# The subnet IP and mask vpn clients will be assigned addresses from. For
# example, 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0. This is a non-routed network that only
# exists between the VPN server and the client. Therefore, it should NOT
# overlap with VPC addressing, or the client won't be able to access any of
# the VPC IPs. In general, we recommend using internal, non-RFC 1918 IP
# addresses, such as 172.16.xx.yy.
vpn_subnet = "172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0"
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DEPLOY GRUNTWORK'S OPENVPN-SERVER MODULE
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
terraform {
source = "git::git@github.com:gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-service-catalog.git//modules/mgmt/openvpn-server?ref=v2.0.0"
}
inputs = {
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUIRED VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# A list of IP address ranges in CIDR format from which VPN access will be
# permitted. Attempts to access the OpenVPN Server from all other IP addresses
# will be blocked.
allow_vpn_from_cidr_list = <list(string)>
# The AMI to run on the OpenVPN Server. This should be built from the Packer
# template under openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. One of var.ami or
# var.ami_filters is required. Set to null if looking up the ami with filters.
ami = <string>
# Properties on the AMI that can be used to lookup a prebuilt AMI for use with
# the OpenVPN server. You can build the AMI using the Packer template
# openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. Only used if var.ami is null. One of var.ami
# or var.ami_filters is required. Set to null if passing the ami ID directly.
ami_filters = <object(
owners = list(string)
filters = list(object(
name = string
values = list(string)
))
)>
# The name of the S3 bucket that will be used to backup PKI secrets. This is a
# required variable because bucket names must be globally unique across all
# AWS customers.
backup_bucket_name = <string>
# An object with fields for the country, state, locality, organization,
# organizational unit, and email address to use with the OpenVPN CA
# certificate.
ca_cert_fields = <object(
ca_country = string
ca_state = string
ca_locality = string
ca_org = string
ca_org_unit = string
ca_email = string
)>
# The ids of the subnets where this server should be deployed.
subnet_ids = <list(string)>
# The ID of the VPC in which to deploy the OpenVPN server.
vpc_id = <string>
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# OPTIONAL VARIABLES
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and
# disk space usage) should send notifications.
alarms_sns_topic_arn = []
# If true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be
# used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy
# can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and
# generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
allow_manage_key_permissions_with_iam = false
# The IP address ranges in CIDR format from which to allow incoming SSH
# requests to the OpenVPN server.
allow_ssh_from_cidr_list = []
# The IDs of security groups from which to allow incoming SSH requests to the
# OpenVPN server.
allow_ssh_from_security_group_ids = []
# The base domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Used to lookup the
# Hosted Zone ID to use for creating the Route 53 domain entry. Only used if
# var.create_route53_entry is true.
base_domain_name = null
# Tags to use to filter the Route 53 Hosted Zones that might match
# var.domain_name.
base_domain_name_tags = {}
# Cloud init scripts to run on the OpenVPN server while it boots. See the part
# blocks in
# https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/template/d/cloudinit_config.html for
# syntax.
cloud_init_parts = {}
# The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for
# encrypting log data.
cloudwatch_log_group_kms_key_id = null
# The number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to
# https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days
# for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
cloudwatch_log_group_retention_in_days = null
# Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys
# are tag keys and values are tag values.
cloudwatch_log_group_tags = null
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to
# this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this
# list is empty, and var.kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will
# be used.
cmk_administrator_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given
# permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
cmk_external_user_iam_arns = []
# A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this KMS
# Master Key (e.g. arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/foo).
cmk_user_iam_arns = []
# Set to true to add var.domain_name as a Route 53 DNS A record for the
# OpenVPN server
create_route53_entry = false
# The default OS user for the OpenVPN AMI. For AWS Ubuntu AMIs, which is what
# the Packer template in openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl uses, the default OS
# user is 'ubuntu'.
default_user = "ubuntu"
# The domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Only used if
# var.create_route53_entry is true. If null, set to <NAME>.<BASE_DOMAIN_NAME>.
domain_name = null
# If true, the launched EC2 instance will be EBS-optimized. Note that for most
# instance types, EBS optimization does not incur additional cost, and that
# many newer EC2 instance types have EBS optimization enabled by default.
# However, if you are running previous generation instances, there may be an
# additional cost per hour to run your instances with EBS optimization
# enabled. Please see:
# https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/#EBS-Optimized_Instances
ebs_optimized = true
# Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage,
# memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS
# topics to send notifications to using var.alarms_sns_topic_arn.
enable_cloudwatch_alarms = true
# Set to true to send logs to CloudWatch. This is useful in combination with
# https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/logs/cloudwatch-log-aggregation-scripts
# to do log aggregation in CloudWatch.
enable_cloudwatch_log_aggregation = true
# Set to true to add IAM permissions to send custom metrics to CloudWatch.
# This is useful in combination with
# https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/agents/cloudwatch-agent
# to get memory and disk metrics in CloudWatch for your OpenVPN server.
enable_cloudwatch_metrics = true
# Enable fail2ban to block brute force log in attempts. Defaults to true.
enable_fail2ban = true
# Enable ip-lockdown to block access to the instance metadata. Defaults to
# true.
enable_ip_lockdown = true
# Set to true to add IAM permissions for ssh-grunt
# (https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-security/tree/master/modules/ssh-grunt),
# which will allow you to manage SSH access via IAM groups.
enable_ssh_grunt = true
# The ARNs of external AWS accounts where your IAM users are defined. This
# module will create IAM roles that users in those accounts will be able to
# assume to get access to the request/revocation SQS queues.
external_account_arns = []
# Since our IAM users are defined in a separate AWS account, this variable is
# used to specify the ARN of an IAM role that allows ssh-grunt to retrieve IAM
# group and public SSH key info from that account.
external_account_ssh_grunt_role_arn = ""
# When a terraform destroy is run, should the backup s3 bucket be destroyed
# even if it contains files. Should only be set to true for
# testing/development
force_destroy = false
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization percentage
# for the ASG.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster CPU utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_cpu_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the root disk utilization
# percentage for the ASG.
high_asg_disk_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster root disk utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_disk_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_disk_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The period, in seconds, over which to measure the Memory utilization
# percentage for the ASG.
high_asg_memory_utilization_period = 60
# Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster Memory utilization
# percentage above this threshold.
high_asg_memory_utilization_threshold = 90
# Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state.
# Based on
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data.
# Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
high_asg_memory_utilization_treat_missing_data = "missing"
# The ID of the Route 53 Hosted Zone in which the domain should be created.
# Only used if var.create_route53_entry is true. If null, lookup the hosted
# zone ID using the var.base_domain_name.
hosted_zone_id = null
# The type of instance to run for the OpenVPN Server
instance_type = "t3.micro"
# The name of a Key Pair that can be used to SSH to this instance. Leave blank
# if you don't want to enable Key Pair auth.
keypair_name = null
# The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK)
# that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If null, a key will be
# created with permissions assigned by the following variables:
# cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns, cmk_external_user_iam_arns,
# allow_manage_key_permissions.
kms_key_arn = null
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification list
# requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed with
# 'openvpn-lists-'.
list_queue_name = "queue"
# The name of the OpenVPN Server and the other resources created by these
# templates
name = "vpn"
# Tags to apply to every resource created by the openvpn-server module.
openvpn_server_tags = {}
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive new certificate
# requests.
request_queue_name = "queue"
# The name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification
# revocation requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed
# with 'openvpn-requests-'.
revocation_queue_name = "queue"
# The size of the OpenVPN EC2 instance root volume, in GB.
root_volume_size = 8
# When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation
# from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the
# CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS
# encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a
# basic log group to use.
should_create_cloudwatch_log_group = true
# If you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which
# users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server. This value is only used
# if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
ssh_grunt_iam_group = "ssh-grunt-users"
# If you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which
# users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server with sudo permissions.
# This value is only used if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
ssh_grunt_iam_group_sudo = "ssh-grunt-sudo-users"
# The tenancy of this server. Must be one of: default, dedicated, or host.
tenancy = "default"
# Set this variable to true to enable the use of Instance Metadata Service
# Version 1 in this module's aws_launch_template. Note that while IMDsv2 is
# preferred due to its special security hardening, we allow this in order to
# support the use case of AMIs built outside of these modules that depend on
# IMDSv1.
use_imdsv1 = true
# When true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather
# than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies
# are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single
# resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies
# when targeting compliance with various security standards.
use_managed_iam_policies = true
# When true, generate Diffie-Hellman parameters using strong primes. Note that
# while stronger primes make the keys more cryptographically secure, the
# effective security gains are known to be insignificant in practice.
use_strong_prime = false
# A list of CIDR ranges to be routed over the VPN.
vpn_route_cidr_blocks = []
# A list of domains to push down to the client to resolve over VPN. This will
# configure the OpenVPN server to pass through domains that should be resolved
# over the VPN connection (as opposed to the locally configured resolver) to
# the client. Note that for each domain, all subdomains will be resolved as
# well. E.g., if you pass in 'mydomain.local', subdomains such as
# 'hello.world.mydomain.local' and 'example.mydomain.local' will also be
# forwarded to through the VPN server.
vpn_search_domains = []
# The subnet IP and mask vpn clients will be assigned addresses from. For
# example, 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0. This is a non-routed network that only
# exists between the VPN server and the client. Therefore, it should NOT
# overlap with VPC addressing, or the client won't be able to access any of
# the VPC IPs. In general, we recommend using internal, non-RFC 1918 IP
# addresses, such as 172.16.xx.yy.
vpn_subnet = "172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0"
}
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
allow_vpn_from_cidr_listlist(string)A list of IP address ranges in CIDR format from which VPN access will be permitted. Attempts to access the OpenVPN Server from all other IP addresses will be blocked.
amistringThe AMI to run on the OpenVPN Server. This should be built from the Packer template under openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. One of ami or ami_filters is required. Set to null if looking up the ami with filters.
ami_filtersobject(…)Properties on the AMI that can be used to lookup a prebuilt AMI for use with the OpenVPN server. You can build the AMI using the Packer template openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl. Only used if ami is null. One of ami or ami_filters is required. Set to null if passing the ami ID directly.
object({
# List of owners to limit the search. Set to null if you do not wish to limit the search by AMI owners.
owners = list(string)
# Name/Value pairs to filter the AMI off of. There are several valid keys, for a full reference, check out the
# documentation for describe-images in the AWS CLI reference
# (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/ec2/describe-images.html).
filters = list(object({
name = string
values = list(string)
}))
})
Details
Name/Value pairs to filter the AMI off of. There are several valid keys, for a full reference, check out the
documentation for describe-images in the AWS CLI reference
(https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/ec2/describe-images.html).
backup_bucket_namestringThe name of the S3 bucket that will be used to backup PKI secrets. This is a required variable because bucket names must be globally unique across all AWS customers.
ca_cert_fieldsobject(…)An object with fields for the country, state, locality, organization, organizational unit, and email address to use with the OpenVPN CA certificate.
object({
ca_country = string
ca_state = string
ca_locality = string
ca_org = string
ca_org_unit = string
ca_email = string
})
subnet_idslist(string)The ids of the subnets where this server should be deployed.
vpc_idstringThe ID of the VPC in which to deploy the OpenVPN server.
Optional
alarms_sns_topic_arnlist(string)The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and disk space usage) should send notifications.
[]If true, both the CMK's Key Policy and IAM Policies (permissions) can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. If false, only the CMK's Key Policy can be used to grant permissions on the CMK. False is more secure (and generally preferred), but true is more flexible and convenient.
falseallow_ssh_from_cidr_listlist(string)The IP address ranges in CIDR format from which to allow incoming SSH requests to the OpenVPN server.
[]allow_ssh_from_security_group_idslist(string)The IDs of security groups from which to allow incoming SSH requests to the OpenVPN server.
[]base_domain_namestringThe base domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Used to lookup the Hosted Zone ID to use for creating the Route 53 domain entry. Only used if create_route53_entry is true.
nullbase_domain_name_tagsmap(string)Tags to use to filter the Route 53 Hosted Zones that might match domain_name.
{}cloud_init_partsmap(object(…))Cloud init scripts to run on the OpenVPN server while it boots. See the part blocks in https://www.terraform.io/docs/providers/template/d/cloudinit_config.html for syntax.
map(object({
filename = string
content_type = string
content = string
}))
{}The ID (ARN, alias ARN, AWS ID) of a customer managed KMS Key to use for encrypting log data.
nullThe number of days to retain log events in the log group. Refer to https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs/resources/cloudwatch_log_group#retention_in_days for all the valid values. When null, the log events are retained forever.
nullcloudwatch_log_group_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply on the CloudWatch Log Group, encoded as a map where the keys are tag keys and values are tag values.
nullcmk_administrator_iam_arnslist(string)A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given administrator access to this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:user/<iam-user-arn>). If this list is empty, and kms_key_arn is null, the ARN of the current user will be used.
[]cmk_external_user_iam_arnslist(string)A list of IAM ARNs for users from external AWS accounts who should be given permissions to use this CMK (e.g. arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:root).
[]cmk_user_iam_arnslist(object(…))A list of IAM ARNs for users who should be given permissions to use this KMS Master Key (e.g. arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/foo).
list(object({
name = list(string)
conditions = list(object({
test = string
variable = string
values = list(string)
}))
}))
[]Set to true to add domain_name as a Route 53 DNS A record for the OpenVPN server
falsedefault_userstringThe default OS user for the OpenVPN AMI. For AWS Ubuntu AMIs, which is what the Packer template in openvpn-server-ubuntu.pkr.hcl uses, the default OS user is 'ubuntu'.
"ubuntu"domain_namestringThe domain name to use for the OpenVPN server. Only used if create_route53_entry is true. If null, set to <NAME>.<BASE_DOMAIN_NAME>.
nullebs_optimizedboolIf true, the launched EC2 instance will be EBS-optimized. Note that for most instance types, EBS optimization does not incur additional cost, and that many newer EC2 instance types have EBS optimization enabled by default. However, if you are running previous generation instances, there may be an additional cost per hour to run your instances with EBS optimization enabled. Please see: https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/#EBS-Optimized_Instances
trueSet to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage, memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS topics to send notifications to using alarms_sns_topic_arn.
trueSet to true to send logs to CloudWatch. This is useful in combination with https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/logs/cloudwatch-log-aggregation-scripts to do log aggregation in CloudWatch.
trueSet to true to add IAM permissions to send custom metrics to CloudWatch. This is useful in combination with https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-monitoring/tree/master/modules/agents/cloudwatch-agent to get memory and disk metrics in CloudWatch for your OpenVPN server.
trueenable_fail2banboolEnable fail2ban to block brute force log in attempts. Defaults to true.
trueEnable ip-lockdown to block access to the instance metadata. Defaults to true.
trueenable_ssh_gruntboolSet to true to add IAM permissions for ssh-grunt (https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terraform-aws-security/tree/master/modules/ssh-grunt), which will allow you to manage SSH access via IAM groups.
trueexternal_account_arnslist(string)The ARNs of external AWS accounts where your IAM users are defined. This module will create IAM roles that users in those accounts will be able to assume to get access to the request/revocation SQS queues.
[]Since our IAM users are defined in a separate AWS account, this variable is used to specify the ARN of an IAM role that allows ssh-grunt to retrieve IAM group and public SSH key info from that account.
""force_destroyboolWhen a terraform destroy is run, should the backup s3 bucket be destroyed even if it contains files. Should only be set to true for testing/development
falseThe period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization percentage for the ASG.
60Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster CPU utilization percentage above this threshold.
90Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"The period, in seconds, over which to measure the root disk utilization percentage for the ASG.
60Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster root disk utilization percentage above this threshold.
90Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"The period, in seconds, over which to measure the Memory utilization percentage for the ASG.
60Trigger an alarm if the ASG has an average cluster Memory utilization percentage above this threshold.
90Sets how this alarm should handle entering the INSUFFICIENT_DATA state. Based on https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/AlarmThatSendsEmail.html#alarms-and-missing-data. Must be one of: 'missing', 'ignore', 'breaching' or 'notBreaching'.
"missing"hosted_zone_idstringThe ID of the Route 53 Hosted Zone in which the domain should be created. Only used if create_route53_entry is true. If null, lookup the hosted zone ID using the base_domain_name.
nullinstance_typestringThe type of instance to run for the OpenVPN Server
"t3.micro"keypair_namestringThe name of a Key Pair that can be used to SSH to this instance. Leave blank if you don't want to enable Key Pair auth.
nullkms_key_arnstringThe Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an existing KMS customer master key (CMK) that will be used to encrypt/decrypt backup files. If null, a key will be created with permissions assigned by the following variables: cmk_administrator_iam_arns, cmk_user_iam_arns, cmk_external_user_iam_arns, allow_manage_key_permissions.
nulllist_queue_namestringThe name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification list requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed with 'openvpn-lists-'.
"queue"namestringThe name of the OpenVPN Server and the other resources created by these templates
"vpn"openvpn_server_tagsmap(string)Tags to apply to every resource created by the openvpn-server module.
{}request_queue_namestringThe name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive new certificate requests.
"queue"revocation_queue_namestringThe name of the sqs queue that will be used to receive certification revocation requests. Note that the queue name will be automatically prefixed with 'openvpn-requests-'.
"queue"root_volume_sizenumberThe size of the OpenVPN EC2 instance root volume, in GB.
8When true, precreate the CloudWatch Log Group to use for log aggregation from the EC2 instances. This is useful if you wish to customize the CloudWatch Log Group with various settings such as retention periods and KMS encryption. When false, the CloudWatch agent will automatically create a basic log group to use.
truessh_grunt_iam_groupstringIf you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server. This value is only used if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
"ssh-grunt-users"ssh_grunt_iam_group_sudostringIf you are using ssh-grunt, this is the name of the IAM group from which users will be allowed to SSH to this OpenVPN server with sudo permissions. This value is only used if enable_ssh_grunt=true.
"ssh-grunt-sudo-users"tenancystringThe tenancy of this server. Must be one of: default, dedicated, or host.
"default"use_imdsv1boolSet this variable to true to enable the use of Instance Metadata Service Version 1 in this module's aws_launch_template. Note that while IMDsv2 is preferred due to its special security hardening, we allow this in order to support the use case of AMIs built outside of these modules that depend on IMDSv1.
trueWhen true, all IAM policies will be managed as dedicated policies rather than inline policies attached to the IAM roles. Dedicated managed policies are friendlier to automated policy checkers, which may scan a single resource for findings. As such, it is important to avoid inline policies when targeting compliance with various security standards.
trueuse_strong_primeboolWhen true, generate Diffie-Hellman parameters using strong primes. Note that while stronger primes make the keys more cryptographically secure, the effective security gains are known to be insignificant in practice.
falsevpn_route_cidr_blockslist(string)A list of CIDR ranges to be routed over the VPN.
[]vpn_search_domainslist(string)A list of domains to push down to the client to resolve over VPN. This will configure the OpenVPN server to pass through domains that should be resolved over the VPN connection (as opposed to the locally configured resolver) to the client. Note that for each domain, all subdomains will be resolved as well. E.g., if you pass in 'mydomain.local', subdomains such as 'hello.world.mydomain.local' and 'example.mydomain.local' will also be forwarded to through the VPN server.
[]vpn_subnetstringThe subnet IP and mask vpn clients will be assigned addresses from. For example, 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0. This is a non-routed network that only exists between the VPN server and the client. Therefore, it should NOT overlap with VPC addressing, or the client won't be able to access any of the VPC IPs. In general, we recommend using internal, non-RFC 1918 IP addresses, such as 172.16.xx.yy.
"172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0"The ARN of the IAM role that can be assumed from external accounts to request certificates.
The name of the IAM role that can be assumed from external accounts to request certificates.
The ARN of the IAM role that can be assumed from external accounts to revoke certificates.
The name of the IAM role that can be assumed from external accounts to revoke certificates.
The AutoScaling Group ID of the OpenVPN server.
The S3 bucket used for backing up the OpenVPN PKI.
The SQS queue used by the openvpn-admin tool for certificate requests.
The SQS queue used by the openvpn-admin tool for certificate revocations.
The elastic IP address of the OpenVPN server.
The ID of the IAM role used by the OpenVPN server.
The name of the OpenVPN admins IAM group (to request and revoke certificates).
The name of the OpenVPN users IAM group (to request certificates).
The private IP address of the OpenVPN server.
The public IP address of the OpenVPN server.
The security group ID of the OpenVPN server.